Guidelines applicable in the Pharmaceutical Plants:
Worldwide many regulatory authority provides their guidelines for pharmaceutical plants. Majorly we cover the Guidelines applicable to pharmaceutical plants which cover, QMS /Utility Systems/Equipment/ Process/ Computer system validation/ Data Integrity/Quality Control lab procedures/ Production procedures/ VMP plans, etc.
Regulations for Quality Management Systems (QMS):
Deviation:
- Deviation handling and quality risk management WHO.
- ICH Q10 Guidelines (international conference of harmonization) PQS-10).
- 21 CFR 211.100 of USFDA (detailed Deviation description).
- PICS- 2013 – Guide to the good manufacturing practice for medical products.
Guidelines for Risk management ICH-Q9:
- ICH Q9 i.e. (Quality Risk Management – Step 4) was released on November 9, 2005.
- WHO TRS no. 961- 2013 – WHO guideline for the quality risk management.
- PICS PE-009 -15 MAY-2021 for risk management.
Change control
- For change control the Central drugs standard control organization CDSCO / PAC1108.
- ICH-Q10 for the pharmaceutical quality system.
- WHO TRS NO-992, in 2015 annex-3- for the guideline on good manufacturing practice.
- Guideline for the industries – QS guide (for change control and CAPA).
- 21 CFR 211.100 for the (Deviation).
OOS (out of specification) Guidelines:
- USFDA 2022 -Investigating Out-of-Specification (OOS)Test Results for Pharmaceutical and Production Guidance for Industry-May 2022.
Guidelines for CAPA (corrective and preventive action):
- FDA- investigation to determine root causes relating to products, processes, and the quality system.
- ICH Q10 for (international conference of harmonization) PQS-10).
- FDA- Sept 2006 report on pharmaceutical CGMP regulations on change control, CAPA, and risk assessments.
Handling of Market Complains Guidelines:
- Complaints in schedule-M, Drug & Cosmetic Act -1940 & 1945, India.
- 21CFR i.e. code of federal regulation, part-211 of USFDA.
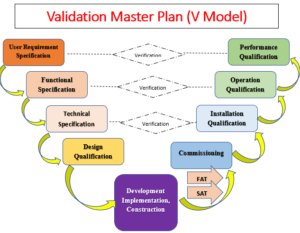
Area Qualification:
- Air velocity-WHO GMP for HVAC-2016/WHO Feb-2018.
- WHO GMP, Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Products.
- ACPH- schedule-M grade B, C, D ACPH should not be less than 20 ACP/min.
- Integrity (PAO)- ISO-14644-3-2005.
- NVPC- Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Products.
- Airflow direction test and visualization- ISO 14644-3 -2019.
- Recovery test- ISO 14644-3 -2019.
- Containment leak test- ISO 14644-3 -2019.
- Segregation test- ISO 14644-3 -2019.
- Viable- Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Products.
- ISO-14644-1,2, ISO 14644-3 2019.
AUTOCLAVE :
- HTM-2010- Health Technical Memorandum-TR-48.
- HTM-2016- Health Technical Memorandum.
- EN-285 2015- European standard norms.
- PDA-Technical Monograph no. 1, 2002 revision- industrial moist heat sterilization in autoclaves.
- USP CHAPTER 1228.
- USP Chapter <85> recommended de-pyrogenation temperature is 250 ºC for 30 min.
- European pharmacopoeia 10.3.
Pure Steam and its Generation:
- HTM-2010- Health Technical Memorandum-TR-48.
Temperature mapping of Cold rooms, Storage area & Deep freezer:
- World Health Organization WHO (2015). The Technical Supplement number 08 to the WHO Technical Report of Series, WHO No. 961, dated 2011 for the Temperature mapping of the warehouse and stores.
- ISPE-total number of sensor place –volume bases.
Media fill:
- (PDA) Technical Report No. 22 (Revised 2011) for the Parenteral Drug Association.
- USFDA September 2004 Sterile Drug Products Produced aseptic techniques in Aseptic area — the U.S. department of Health & Human Services of the FDA.
- PIC/S PHARMACEUTICAL INSPECTION CO-OPERATION SCHEME PI 007-6 1 January 2011.
- EU (EUROPEAN COMMISSION) Annex-1 25 November 2008 Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products.
Cleaning validation:
- ACTIVE PHARMACEUTICAL INGREDIENTS COMMITTEE (APIC)- guidance on aspects of cleaning validation in API plants-sept-2016.
- PDA-TR NO-29-2012.
- ISPE-cleaning validation life cycle -2020.
- USFDA guideline on cleaning validation (a guide to inspections validation of cleaning process FDA-1993).
Visual inspection:
- USP- the General Chapters 〈1790〉 Visual Inspection of Injections.
- IPA-visual inspection of sterile products best practices document-2021.
Compressed Air Gas Qualification:
- ISO: 8573 -1:2010 (International Organization for Standardization).
- ISPE -for good practice guide: PROCESS GASES-2011.
- BP (British pharmacopoeia)-2021).
- EN12021(European standard norms).
Nitrogen Air Gas Qualification:
- ISPE -for Good practice guide: PROCESS GASES-2011.
- BP (British pharmacopoeia)-2021).
- European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) 10th Edition.
Guidelines for the Good Aseptic Practices:
- US FDA guideline for industry, sterile drug product by aseptic processing current good manufacturing practice, September-2004-Good aseptic practices (pharmaceutical injection).
- PICS GMPPE-009-16-guide to good manufacturing practices for medical product annexure”.
Guidelines for Data integrity:
- USFDA-Data Integrity and Compliance with Drug CGMP Questions and Answers.
- Guidance for Industry- December 2018- MHRA-2015-data integrity definition and guidance for industry.
- WHO-2015 the guidance on good data & data record management procedures.
- PIC/S-2016-good practice for data management and integrity.”
- “Data integrity: data integrity will talk about the ALCOA. i.e. Attribute, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate. ALCOA removes data consistency, completeness, and errors. Attributable, readable, and contemporaneously documented data must be consistent, complete, correct, and original or A true Copy, and Accurate (ALCOA).
- The Metadata”- The value of the data is itself meaningless without the additional information about the data- FDA will allow checking at the electronic records”
Computer System Validation (CSV):
- Good Automated manufacturing processes i.e. GAMP 5- derived by risk-based approach to compliant Gxp computerized systems(Industrial PC, HMIs, and SCADA).
Self-Inspection, Batch Record Review
- World Health Organization Annex-2 for the Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharma Products.
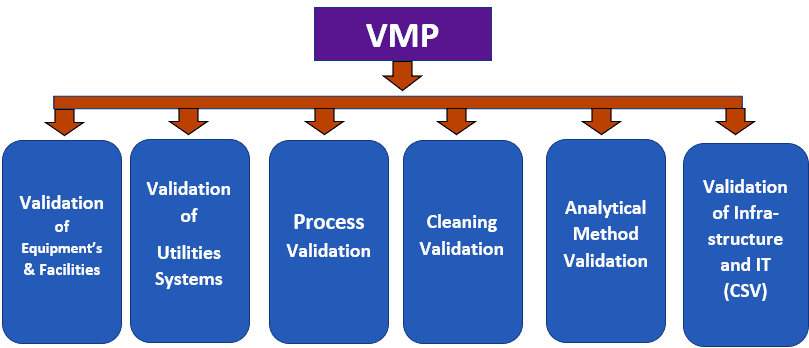
“Quality Assurance of Pharmaceuticals”
- WHO Volume 2, 2nd updated edition –For Quality assurance of pharmaceuticals
- Q1A: The Stability study and testing of fresh drug substances and products.
- Q1B: Stability testing and the photostability study of new drug substances and products.
- Q1C: Stability testing of the fresh dosage forms.
- Q1D: Testing the stability of new medicinal compounds and products using the bracketing and matrixing designs.
- Q1E: Evaluation and analysis of stability data.
- Q2: Validation of analytical procedures text and methodology.
- Q3A: Impurities in new drug substances.
- Q3B: Study of Impurities of new drug products.
- Q3C: Study of Impurities guideline of residual solvents.
- Q4: Pharmacopoeias.
- Q5B: Quality of biotechnological products: analysis of the expression construct in cells used for the production of r-DNA derived protein products.
- Q5C: Quality of biotechnological products: stability testing of biotechnological/biological products.
- Q5D: Derivation and characterization of cell substrates used for the production of biotechnological/biological products.
- Q5E: Comparison of biological and biotechnological goods is subject to modifications in their manufacturing process.
- Q6A: Specifications of the Chemical Substances and the Procedures for Evaluating New Drug Substances and New Drug Products and Acceptance Criteria.
- Q6B: Specifications of the test analysis procedures and Assessment Criteria for biotechnological/biological finish products.
- Q7: Good Manufacturing Practice for Active Pharma Ingredients i.e. (GMP).
- Q8: Pharmaceutical development and its studies.
- Q9: Quality Risk Management for the pharmaceuticals (QRM).
- Q10: Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS) for Pharma plants.
- Q11: (DMDS) Development and Manufacture of the Drug substance in the pharma world.
- Q12: Technical and Regulatory Considerations for Pharmaceutical, throughout the entire Product Lifecycle Management and its study.
- Q13: Drug Products and Drug Substances are manufactured continuously.
- Q14: Development of the analytical procedure i.e. AMV and revision of the Q2 (R1) analytical validation
For more technical details, or any type of documentation (SOP, DQ, IQ, OQ, PQ etc.) Please contact us at: admin@flairpharma.com
