QMS in Pharma is a fundamental framework that organizations implement to ensure their products or services consistently meet or exceed customer expectations. It is a comprehensive set of processes, procedures, and policies meticulously designed to enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and bolster customer satisfaction. The implementation of a robust Quality Management System (QMS) is paramount. A QMS serves as the guiding light for ensuring that pharmaceutical companies adhere to stringent quality standards, regulations, and customer expectations. It is a comprehensive framework that encompasses various processes, procedures, and controls to safeguard the integrity, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Different Types of Quality Management Systems in Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, various types of Quality Management Systems (QMS) are implemented to ensure the highest standards of quality and compliance. Here are some different types of QMS commonly used in pharmaceuticals:
- Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP): GMP is a regulatory requirement that outlines specific quality standards and guidelines for the manufacturing, testing, and distribution of pharmaceutical products. It encompasses various aspects of quality assurance, including facility design, equipment validation, documentation control, process validation, and product quality testing.
- Good Laboratory Practice (GLP): GLP focuses on ensuring the quality and integrity of laboratory studies conducted during the development and testing of pharmaceutical products. It encompasses guidelines for laboratory operations, personnel training, equipment calibration, documentation, data integrity, and quality control.
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP): GCP is a set of internationally recognized guidelines for the conduct of clinical trials. It ensures the protection of human subjects participating in clinical studies and the reliability of data generated during these trials. GCP covers various aspects, including study design, participant recruitment, informed consent, safety monitoring, data collection and analysis, and reporting of results.
- Pharmacovigilance Systems: Pharmacovigilance is concerned with monitoring and evaluating the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle. It involves the collection, assessment, and reporting of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and other safety-related information. A robust pharmacovigilance system is essential for identifying and managing potential risks associated with pharmaceutical products.

- Quality Risk Management (QRM): QRM is a systematic process used to assess and manage risks that may impact the quality, safety, or efficacy of pharmaceutical products. It involves the identification of potential risks, their evaluation, and the implementation of risk mitigation strategies. QRM helps organizations prioritize resources and take proactive measures to prevent or minimize risks.
- Supplier Quality Management: Supplier Quality Management focuses on ensuring the quality and compliance of materials, components, and services supplied by external vendors. It involves establishing criteria for supplier selection, performing audits and assessments, conducting supplier qualification, and implementing processes to monitor and control supplier performance.
It’s important to note that these are just a few examples of the different types of Quality Management Systems employed in the pharmaceutical industry. The specific implementation and requirements may vary based on regulatory guidelines, organizational needs, and the nature of the pharmaceutical products being developed, manufactured, or distributed.
Elements of a Quality Management System QMS in Pharma
- Quality Policy: The Quality Policy is a statement of the organization’s commitment to quality. It outlines the overall quality objectives and sets the direction for the QMS implementation. The policy reflects the organization’s dedication to meeting customer requirements, complying with regulations, and continuously improving processes.
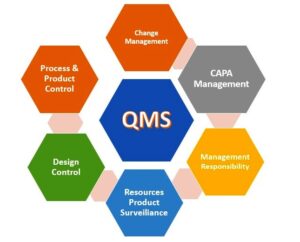
- Quality Planning: Quality Planning involves the development of strategies, procedures, and controls to achieve the desired level of quality. It includes defining quality objectives, determining quality criteria, establishing processes, and allocating resources necessary for meeting those objectives.
- Quality Assurance: Quality Assurance focuses on ensuring that processes and activities are performed in accordance with established requirements and standards. It involves implementing procedures, conducting audits, and performing inspections to verify compliance. Quality Assurance also encompasses training employees, maintaining documentation, and establishing quality metrics for monitoring performance.
- Quality Control: Quality Control involves the systematic measurement, analysis, and evaluation of processes, products, and services to ensure they meet specified requirements. It includes activities such as inspections, testing, sampling, and data analysis to identify and address deviations or non-conformities. Quality Control also involves the implementation of corrective and preventive actions to improve processes and prevent recurrence of issues.
- Management Review: Management Review is a critical element where top management evaluates the performance of the QMS and its effectiveness in achieving quality objectives. This includes reviewing data, analyzing trends, assessing customer feedback, and making informed decisions for improvement. Management Review serves as a platform for setting new goals, allocating resources, and driving continuous improvement initiatives.
- Continual Improvement: Continual Improvement is at the heart of a QMS. It involves an ongoing effort to enhance processes, products, and services based on feedback, data analysis, and best practices. Continual Improvement encourages innovation, the adoption of new technologies, and the pursuit of excellence in all aspects of the organization’s operations.
- Customer Focus: Customer Focus is a fundamental element of a QMS. It involves understanding customer needs, expectations, and feedback, and aligning processes and activities to deliver products or services that consistently meet or exceed customer requirements. Customer satisfaction is a primary measure of the effectiveness of the QMS.
These core elements work together to establish a robust QMS that ensures quality objectives are met, customer expectations are fulfilled, and a culture of continuous improvement is fostered. By integrating these elements into their operations, organizations can strive for excellence, enhance their competitiveness, and build a reputation for delivering high-quality products or services.
Importance of Quality Management System (QMS) in quality assurance.
The importance of a Quality Management System (QMS) in quality assurance cannot be overstated. A QMS serves as the foundation upon which effective quality assurance practices are built, ensuring that products or services consistently meet or exceed predetermined quality standards. It provides a systematic and structured approach to managing quality, fostering a culture of excellence and continuous improvement within an organization.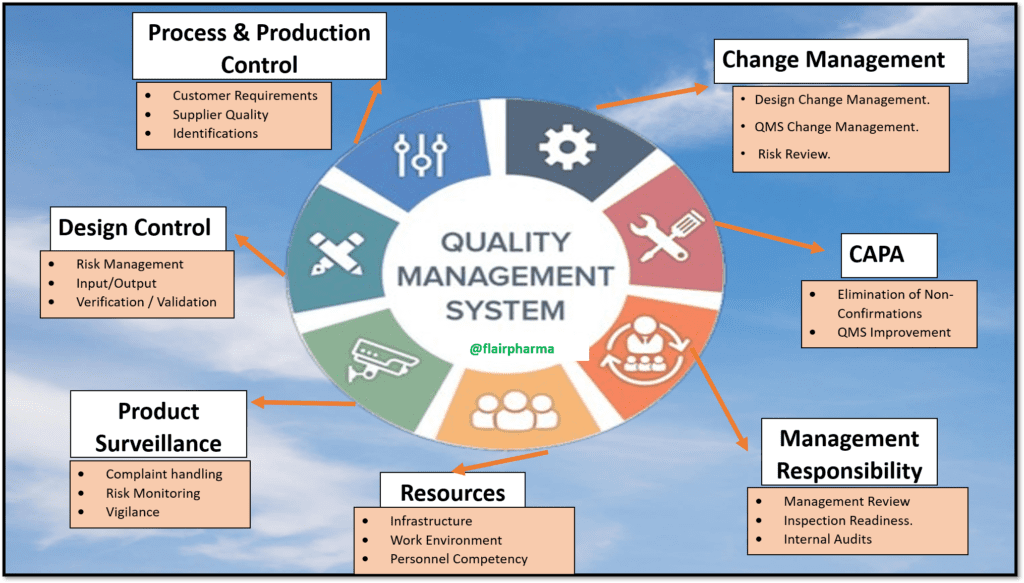
One key reason why QMS is essential in quality assurance is that it establishes a set of processes and procedures that guide the entire quality assurance lifecycle. From planning and development to implementation and monitoring, a QMS provides a framework for organizations to define and document their quality objectives, standardize processes, and ensure consistency in quality practices. This consistency is crucial for achieving reliable and predictable outcomes, as well as for meeting regulatory requirements and customer expectations.
Furthermore, a QMS helps in identifying and addressing potential quality issues proactively. It facilitates the implementation of preventive measures to minimize risks and deviations, ensuring that problems are detected and resolved early on. By having robust quality control mechanisms in place, organizations can effectively manage and mitigate risks, reducing the likelihood of defects, errors, and non-conformities. This proactive approach to quality assurance helps in enhancing customer satisfaction, protecting brand reputation, and avoiding costly rework or recalls.
Another significant aspect of QMS in quality assurance is the emphasis on data-driven decision-making. A well-designed QMS enables the collection, analysis, and utilization of quality-related data and metrics. This data provides valuable insights into the performance of processes, the identification of trends, and the measurement of key performance indicators (KPIs). By leveraging this information, organizations can make informed decisions, implement targeted improvements, and drive continuous quality enhancement across the board.
Moreover, a QMS fosters a culture of accountability and responsibility for quality throughout the organization. It clearly defines roles, responsibilities, and authorities related to quality assurance, ensuring that every individual understands their contribution to the overall quality objectives. By promoting a shared commitment to quality, a QMS encourages employee engagement, ownership, and empowerment, leading to a higher level of quality consciousness and a focus on continuous improvement.
In summary, a Quality Management System (QMS) plays a crucial role in quality assurance by providing a structured framework for managing and improving quality practices. It ensures consistency, proactive risk management, data-driven decision-making, and a culture of accountability. By implementing a robust QMS, organizations can enhance their ability to deliver high-quality products or services, exceed customer expectations, and achieve sustainable business success.
Critical key features of the Quality Management System (QMS)
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Control | Effective management and control of documents and records |
| Process Standardization | Consistent and standardized processes across the organization |
| Risk Management | Identification, assessment, and mitigation of potential risks |
| Training and Competence | Ensuring employees have the necessary skills and knowledge |
| Corrective Actions | Addressing non-conformities and implementing corrective measures |
| Continuous Improvement | Promoting a culture of ongoing enhancement and innovation |
| Customer Focus | Understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations |
| Supplier Management | Establishing and maintaining reliable relationships with suppliers |
| Performance Metrics | Defining and tracking key performance indicators for quality |
| Management Review | Regular evaluation of the QMS by top management |
| Audits and Assessments | Systematic assessments to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement |
| Change Management | Controlled implementation of changes to prevent disruptions |
| Customer Feedback | Gathering and analyzing customer feedback for improvement |
| Root Cause Analysis | Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of issues |
| Calibration and Maintenance | Ensuring equipment and tools are accurate and well-maintained |
What are the 7 principles of QMS?
The 7 principles of a Quality Management System (QMS) are fundamental concepts that guide the development, implementation, and improvement of a QMS. These principles, as defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), are:
- Customer Focus: Organizations should understand and meet customer requirements, exceed their expectations, and strive to enhance customer satisfaction.
- Leadership: Top management should provide strong leadership, establish a clear vision, and create a supportive environment that fosters the engagement and involvement of all employees in achieving quality objectives.
- Engagement of People: People at all levels of the organization are the essence of the QMS. Their full involvement, competence, and empowerment are vital for achieving quality objectives.
- Process Approach: Consistent and predictable results are achieved more effectively and efficiently when activities are managed as interrelated processes within a coherent system.
- Improvement: Continual improvement is essential for enhancing the organization’s performance. This involves a systematic approach to identifying and implementing opportunities for improvement throughout the organization.
- Evidence-based Decision Making: Effective decisions are based on the analysis and evaluation of data and information. This principle emphasizes the importance of using factual information to make informed decisions.
- Relationship Management: An organization and its external providers (suppliers, partners) are interdependent and mutually beneficial. Managing these relationships effectively enhances the ability to create value.
These principles provide a foundation for developing a QMS Quality Management System that is focused on customer satisfaction, driven by strong leadership, and promotes employee engagement, process optimization, continual improvement, and data-driven decision-making.
Different Types of QMS
| Type of QMS | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 QMS | A QMS that conforms to the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard, focusing on quality management and customer satisfaction. |
| Six Sigma QMS | A QMS that utilizes the Six Sigma methodology to improve process efficiency, reduce defects, and enhance overall quality. |
| Lean Manufacturing QMS | A QMS that incorporates lean manufacturing principles to eliminate waste, optimize processes, and improve productivity. |
| TQM (Total Quality Management) QMS | A QMS that emphasizes the involvement of all employees in continuous improvement, customer satisfaction, and quality excellence. |
| Agile QMS | A QMS that applies agile principles and practices to manage quality in software development projects, focusing on flexibility and responsiveness to customer needs. |
| GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) QMS | A QMS designed specifically for the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and product quality. |
| HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) QMS | A QMS that focuses on identifying and controlling food safety hazards throughout the production process in the food industry. |
| ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) QMS | A QMS framework specifically designed for IT service management, providing best practices for delivering high-quality IT services. |
| Environmental Management System (EMS) QMS | A QMS that integrates environmental management practices to minimize the organization’s impact on the environment and comply with environmental regulations. |
| OHSAS 18001/ISO 45001 QMS | A QMS focused on occupational health and safety management, ensuring a safe and healthy work environment for employees and compliance with relevant standards. |
Difference Between QMS and QA Quality Assurance
| Details | Quality Management System (QMS) | Quality Assurance (QA) |
| Definition | A systematic framework that includes processes, policies, and procedures to ensure that products or services consistently meet customer requirements and comply with standards. | A set of activities implemented to ensure that quality requirements and standards are met throughout the product or service lifecycle. |
| Focus | Management and control of quality processes and systems. | Prevention of quality issues and assurance of product or service quality. |
| Scope | Encompasses the entire organization and its quality-related activities. | Primarily focuses on specific projects, products, or services. |
| Objective | Establish and maintain a structured approach to quality management, driving continuous improvement. | Ensure that quality standards, requirements, and customer expectations are met throughout the project or product lifecycle. |
| Emphasis | Systematic processes, documentation, standardization, and continual improvement. | Planning, prevention, adherence to quality standards, and verification of quality throughout the project or product lifecycle. |
| Implementation | Implemented through the establishment and maintenance of a comprehensive quality management system. | Implemented through quality planning, quality control, and quality assurance activities. |
| Components | Includes processes, policies, procedures, documentation management, risk management, training, and continuous improvement. | Includes quality planning, quality control, quality audits, process reviews, and verification activities. |
| Goal | Ensure that products or services consistently meet customer requirements and achieve customer satisfaction. | Prevent defects, ensure product or service conformance to requirements, and enhance overall quality. |
| Role | Provides a framework for managing quality across the organization and driving continuous improvement. | Ensures that quality requirements are planned, implemented, and verified throughout the project or product lifecycle. |
| Relationship | Quality assurance activities are part of the broader quality management system. | Quality assurance is an integral component of a comprehensive QMS. |
Benefits of QMS in Pharma
| Benefits of Quality Management System (QMS) |
|---|
| Ensures consistent quality of products or services |
| Enhances customer satisfaction |
| Reduces defects and non-conformities |
| Improves efficiency and productivity |
| Facilitates compliance with regulatory requirements |
| Minimizes risks and prevents issues |
| Provides a systematic approach to problem-solving |
| Promotes continuous improvement |
| Enhances organizational reputation and credibility |
| Supports effective decision-making based on data |
| Fosters a culture of quality and accountability |
| Increases employee engagement and motivation |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Quality Management System (QMS)?
what is qms?
Answer: A QMS Quality Management System is a set of processes, policies, and procedures implemented by an organization to ensure that products or services consistently meet customer requirements and comply with applicable standards and regulations.
What is the purpose of a QMS?
Answer: The purpose of a QMS Quality Management System is to establish a framework for managing quality, driving continuous improvement, and achieving customer satisfaction.
What are the key elements of a QMS?
Answer: The key elements of a QMS Quality Management System include quality policy, organizational structure, documentation management, process management, risk management, training and competence, supplier management, monitoring and measurement, non-conformity management, and continuous improvement.
What is the role of top management in implementing a QMS?
Answer: Top management plays a crucial role in providing leadership, establishing quality objectives, allocating resources, and creating a culture of quality within the organization.
What is the difference between a QMS and quality control?
Answer: A QMS Quality Management System is a comprehensive system that encompasses all aspects of managing quality, while quality control focuses specifically on inspecting, testing, and evaluating products or services to ensure they meet specified requirements.
How can a QMS help in achieving regulatory compliance?
Answer: A well-implemented QMS provides the necessary processes and controls to ensure compliance with applicable regulations and standards. It includes documentation management, training programs, audits, and procedures for addressing non-conformities.
What is the role of risk management in a QMS?
Answer: Risk management in a QMS Quality Management System involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that may impact the quality of products or services. It helps organizations proactively address potential issues and prevent quality-related problems.
How can a QMS support continuous improvement?
Answer: A QMS Quality Management System promotes a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging the identification of opportunities for enhancement, implementing corrective actions, measuring performance indicators, and conducting regular management reviews.
What is the importance of supplier management in a QMS?
Answer: Supplier management ensures that external suppliers meet quality requirements and deliver reliable materials or services. It involves supplier qualification, performance monitoring, and audits to maintain a consistent supply chain.
How can a QMS help in achieving customer satisfaction?
Answer: A QMS Quality Management System focuses on meeting customer requirements, addressing their feedback, and consistently delivering high-quality products or services. By establishing processes and controls, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction.
What is the role of documentation in a QMS?
Answer: Documentation in a QMS Quality Management System provides guidelines, procedures, work instructions, and records to ensure standardized processes, traceability, and compliance. It helps in training employees, audits, and ensuring consistency.
How can data analysis contribute to a QMS?
Answer: Data analysis allows organizations to monitor and measure performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions for improvement. It helps in identifying areas of non-conformance, root cause analysis, and decision-making based on data.
What is the process for addressing non-conformities in a QMS?
Answer: Non-conformities are identified, documented, and investigated to determine their root causes. Corrective actions are then implemented to address the non-conformities, and their effectiveness is verified through follow-up actions.
What is the role of audits in a QMS?
Answer: Audits in a QMS are conducted to assess compliance with established processes, procedures, and standards. They provide an independent evaluation of the QMS Quality Management Systems.

3 thoughts on “QMS in Pharma 2023”