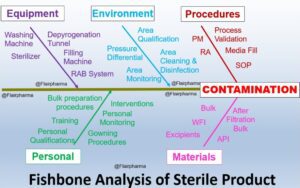
Pharma Industries 4.0 A Path for Quality & Safety, Will you be struggling for developing the contamination control strategy (CCS) for your organization? Our blog helps you to understand, analyze & generate a strategy for your organization. Now it’s time to introduce the pharmaceutical quality system (PQS) with all strategies. Introduction of Contamination control strategy (CCS) A contamination control strategy (CCS) is a self-defined system that protects the pharmaceutical product from all types of cross-contamination & provides 100 % qualitative products. In current practices, these quality issues are covered with quality risk management (QRM).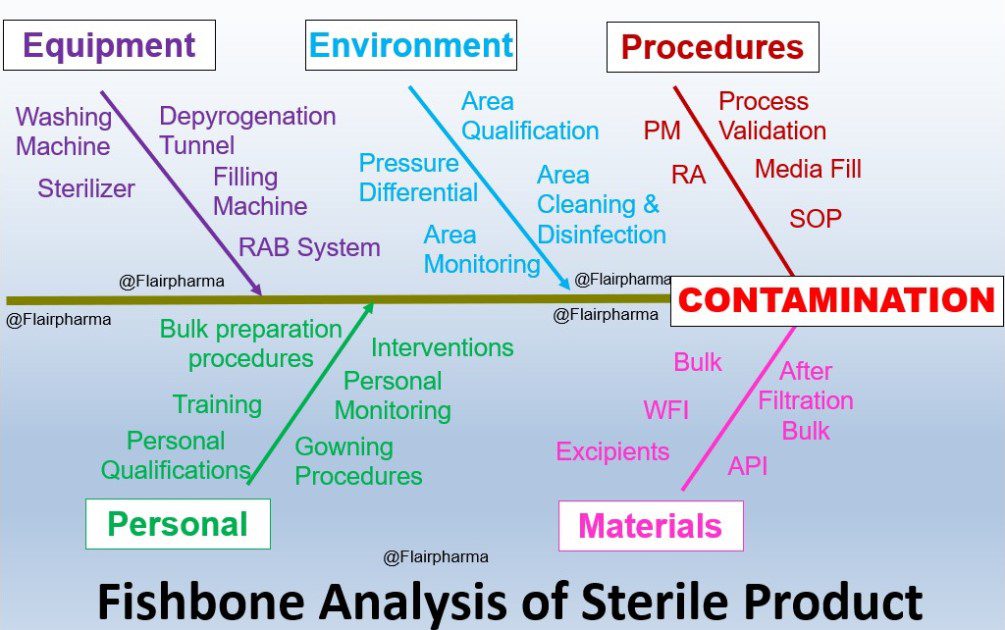
Key Elements which Impact the Quality of the Product:
The key elements for generating or developing the CCS are per pharmaceutical products we manufacture in that facility. the strategy will generate into consideration of following aspects: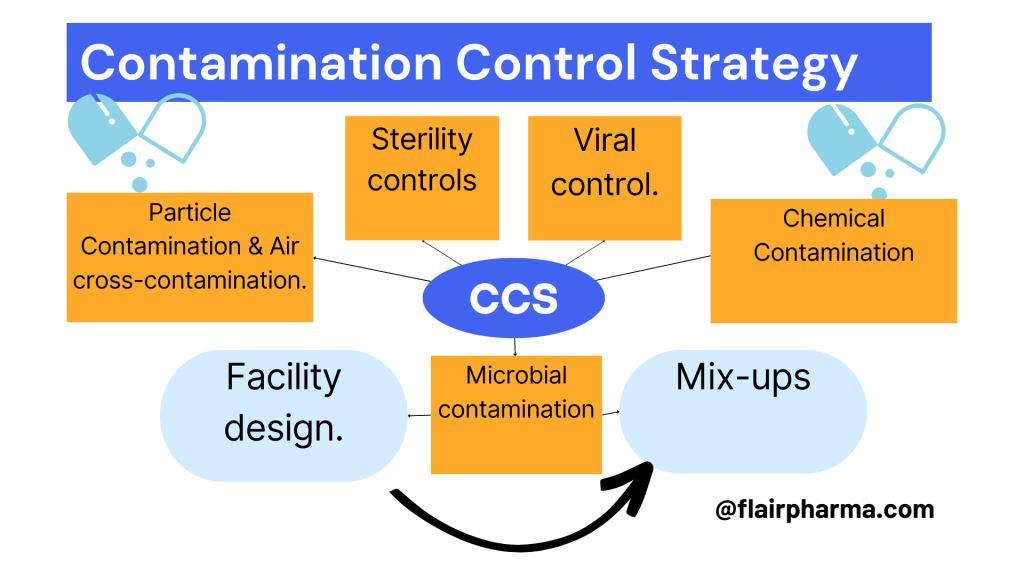
- Facility design.
- Particle contamination & Air cross-contamination.
- Chemical contamination.
- Microbial contamination.
- Viral control.
- Sterility controls & their assurance.
- Mix-ups in different batches or mix-ups in primary, secondary packaging, or distribution systems.
The most recognized Cross-Contamination Control (CCS) will represent the infrastructural design, quality by design, standard procedures, regular manufacturing process risk identification & mitigations. It’s a forecast for contaminations or cross-contaminations.
Root Causes Analyses of Contamination:
Quality Risk Management (QRM) and Quality by Design (QbD) are both innately connected to knowledge of the process. Stages to perform a complete risk assessment of a process.
Current Practice vs. the Proposed CCS Concept:
Although the pharma plant has always been aware of the need to control contamination, it has a tendency to concentrate on evaluating specific sources and the methods to do so. This method hasn’t always been proactive, and it hasn’t always considered how all-important control points and controls interact with one another.
The pharmaceutical quality system and more robust and forceful QRM program in the pharma plants allow the CCS to achieve this goal through PQS. The current incorporation of the CCS concept aims to encourage businesses to think about and assess the risk and effects of numerous sources of contamination on drug quality and human safety. It proposes taking a more comprehensive approach to this issue and tackling it in an organized manner in order to assess the efficacy and interdependencies of the steps taken to control these risks. It enables the organization to make greater use of its knowledge of product and process risk as well as its competence in contamination control.
Even if the pharma plants presently evaluate, manage, and keep an eye on contamination sources individually with the help of the existing QMS tools, the introduction or modification suggests they consider how well they work together.
The advantages of an all-encompassing strategy are:
- Make a comprehensive program that guarantees equal focus on all important control points or CCP critical control points.
- Generate a comprehensive program that raises an understanding of different contamination sources, how they are connected, and how the risks they pose to humans and products as a whole.
- Reduction of individual subjectivities and ineffective control attempts, enabling improved resource allocation, optimal benefit, and continuous improvement
Reference: Sterile pharma product manufacturing facilities have a compulsion for the Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) as per FDA Aseptic Filling Guidance & EU GMP Annex 1.

Root Causes Analyses of Contamination:
Quality Risk Management (QRM) and Quality by Design (QbD) are both innately connected to knowledge of the process. Outlines the stages to perform a complete risk assessment of a process.
Current Practice vs. the Proposed CCS Concept:
Although the pharma plant has always been aware of the need to control contamination, it has a tendency to concentrate on evaluating specific sources and the methods to do so. This method hasn’t always been proactive, and it hasn’t always taken into account how all-important control points and controls interact with one another.
The pharmaceutical quality system and more robust and forceful QRM program in the pharma plants allow the CCS to achieve this goal through PQS. The current incorporation of the CCS concept aims to encourage businesses to think about and assess the risk and effects of numerous sources of contamination on drug quality and human safety. It proposes taking a more comprehensive approach to this issue and tackling it in an organized manner in order to assess the efficacy and interdependencies of the steps taken to control these risks. It enables the organization to make greater use of its knowledge of product and process risk as well as its competence in contamination control.
Even if the pharma plants presently evaluate, manage, and keep an eye on contamination sources individually with the help of the existing QMS tools, the introduction or modification suggests they consider how well they work together.
The advantages of an all-encompassing strategy are:
- Make a comprehensive program that guarantees equal focus on all important control points or CCP critical control points.
- Generate a comprehensive program that raises an understanding of different contamination sources, how they are connected, and how the risks they pose to humans and products as a whole.
- Reduction of individual subjectivities and ineffective control attempts, enabling improved resource allocation, optimal benefit, and continuous improvement
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding CCS :
-
What is contamination control strategy?
Answer: A planned set of controls for microbes, pyrogens, and particles that are drawn from current product and process understanding and ensure process performance and product quality is known as a contamination control strategy (CCS). The parameters and characteristics of the active ingredient, excipient, and drug product materials and components, the operating conditions of the facility and equipment, the in-process controls, the specifications for the finished product, and the associated techniques and frequency of monitoring and control are all examples of controls. The facility should execute a Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) to establish all essential control points, evaluate the efficacy of all controls (design, procedural, technical, and organizational), and monitor the hazards associated with contamination. The manufacturing and control processes should be constantly improved under the direction of the CCS.
-
What is contamination control in aseptic processing operation?
Answer: The goal of the contamination control strategy should be to safeguard the product from microbial contamination during the time when the risk is the highest. Aseptic filling involves fitting a sterile stopper and oversealing the sterile product once it has been filled into dehydrogenated glassware. The process of injecting the product into the vial with a filling needle is the most dangerous.
-
How a contamination control program impacts product sterility?
Answer: Manufacturers of aseptically filled products must develop a contamination control strategy to devote the majority of their resources to, with a stronger emphasis on control than just monitoring using techniques with built-in limits. Importantly, if contamination management is inadequate, a string of zero counts found during environmental monitoring or sterility test passes may not provide much solace.
Sterile assurance and the creation of a sterile product are the goals of a contamination control plan for aseptically filled products (a product absolutely devoid of viable microorganisms). This result is inextricably linked to a procedure designed to dependably impart the intended state. Aseptic processing, where the priority is to prevent microbiological infiltration, cannot offer the same statistical confidence as terminal sterilization, where the Sterility Assurance Level can provide a statistical understanding of the probability of non-sterility. As a result, the manufacturer depends on an effective contamination control plan.
-
What are the 5 control strategies?
Answer: Following are the control strategies for the CCS:
- Avoidance: When most firms are aware of the prospect of a dangerous or unpredictable occurrence occurring, they instinctively take precautions to reduce risk. Forward-thinking and thorough planning are crucial to reducing danger. You can frequently completely avoid a problem if you have quick access to information that detects risk.
- Acceptance: The acceptance of risk also rests on a foundation of information and understanding. Accepting the risk may be the best course of action if your analysis indicates that it is relatively negligible compared to the potential rewards of a particular situation.
- Mitigation: To minimize the impact of a bad occurrence happening by thorough planning is to mitigate risk. The next logical step is mitigation if you are unable to completely eliminate the risk or if you cannot afford to accept it entirely. Risk reduction strategies frequently include precautions like insurance. You have plans in place to lessen the impact of the unfavorable event if it should occur.
- Transferal: Risk transfer includes transferring the risk to a party whom you believe to be more capable of handling the circumstance. Delegating the responsibility for handling an approaching danger to a department or employee who is more competent or experienced might assist transfer the risk. A company’s chances of suffering permanent harm from unplanned losses are decreased when financial risk is distributed among multiple different organizations. The key to successful risk transfer is identifying the entity that is most suited to handle the circumstance.
-
How can we control contamination in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: One of the biggest issues facing the pharmaceutical industry today is contamination. Making safe and high-quality products can be facilitated by locating the source of contamination and upholding strict hygiene standards. In the pharmaceutical sector, contamination can have disastrous effects on anything from patient safety to the viability of the company. For any firm to adhere to legal requirements and guarantee the safety of the general public, contamination prevention during manufacturing and the production of sterile products is essential. The requirements and methodology used by state and federal regulatory authorities for testing pharmaceutical items for contamination are very strict. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and prevent the emergence of contaminants that pose a major threat to a drug product or facility. Merely regulating the bio-burden levels through good cleaning is not sufficient.
Worldwide there are many Pharma Consultants who help in working for the contamination control strategy, if you want to know more about the CCS or related activities please feel free to contact: admin@flairpharma.com
Copyright @Flairpharma

1 thought on “CCS Contamination Control Strategy Tricks 2023”