Fluidized Bed Dryer (FBD) or Fluid Bed Processor (FBP)
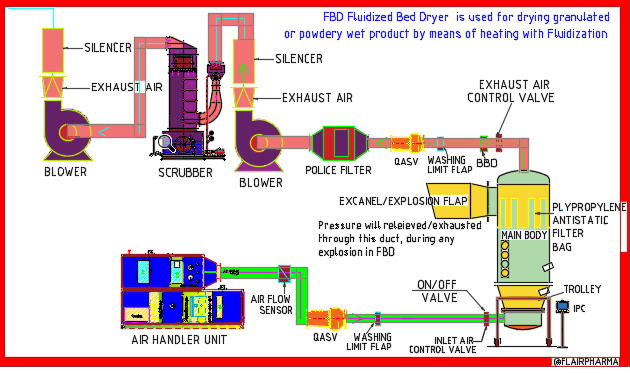
The full form of fbd is Fluidized bed dryers are widely used equipment in pharmaceutical industries. These dryers or processors are installed in the granulation section of the pharmaceutical company. This is a well-known machinery i.e. fluidized bed dryer (FBD) in the granulation stage of pharmaceutical manufacture. The material is dried throughout the granulation process to get the optimum moisture content in the tablet formulation granules needed for effective tablet compression.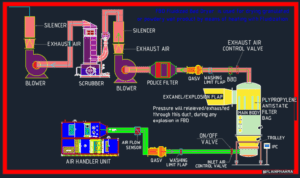
Nowadays in pharmaceutical plants, fluidization is carried out with solution coating of granules that’s why FBD is also modified & called FBP (Fluid Bed Processor, FBE (Fluid Bed Equipment), or Wurster coatings or Fluid bed Multifunctional Processor.
fluid bed processor is also integrated with top spray, bottom spray tangent spray for granulation, drying, coating, and pelletizing.
Types of FBD:
FBD Machines used in Industries basis on safety design are of two types:
- Vented Fluid Bed machines (2 bar Pressure Shock Resistant machine).
- Non – Vented Fluid Bed machines (12 bar Pressure Resistant machine).
Working Principles of the FBD:
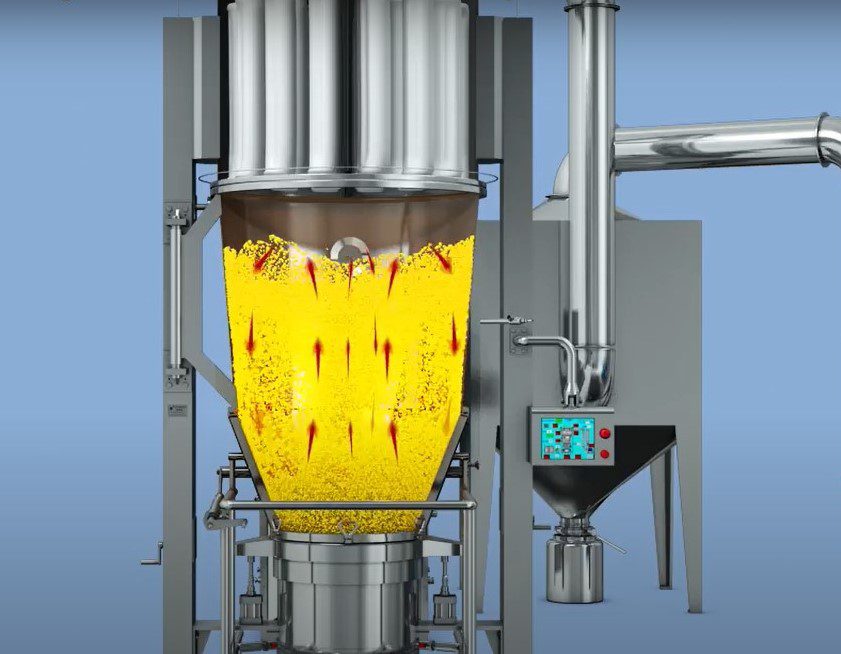
The working principle of the Fluid bed processor is based on fluidization. Fluidization In a flow of gas or liquid, solid particles are kept floating upward by a process known as fluidization. When similar-sized and-shaped particles are exposed to an upward stream of cold air during freezing, fluidization takes place. States that solid particles will be blown up and suspended in the air stream if the air is allowed to pass through a bed of solid powdered material in an upward direction at a velocity greater than the particles’ rate of settling.
Critical parameters of fluid bed:
when fluidization is in the process following parameters are critical:
- AHU motor RPM/speed.
- Inlet air temperature in the body. ( having max. tolerance of ±2 degree)
- Bulk temperature.
- LOD of Bulk.
Main Structure:
Every FBD has below parts as per requirements:
- Movable product container.

- Expansion chamber
- Filter chamber or Finger bag
- Food-grade silicon gaskets.
- Top spray
- Bottom spray.
- Screen mesh.
- Temperature Sensor.
- Inlet damper opening & closing.
- CIP/WIP system.
- Differential pressure transmitter.
- Product Contact parts are of (metallic) SS 316L.
- Solid flow Monitor (SFM)/ Broken Bag Detector BBD.
Processes:
- Gentle drying: Drying of solids through fluidization is the most effective way in pharmaceutical industries, the moisture is carried away by the drying air by exchanging heat through the air to the product in a specific ideal tie.
- Granulating: Granulating is the method of creating granules by spraying aqueous or organic solvents on the mixed powder.
- Coating or Layering on Drug for pellets: This process needs very high precision to laying active substance on the starter core granule this is called powder layering technology.
- Direct pelletizing: This process is also very critical, in this API is in powder form other materials are directly transferred to the pellet without the addition of a starter core. API can be formulated into the matrix of pellets using different excipients, with a targeted release of the API.

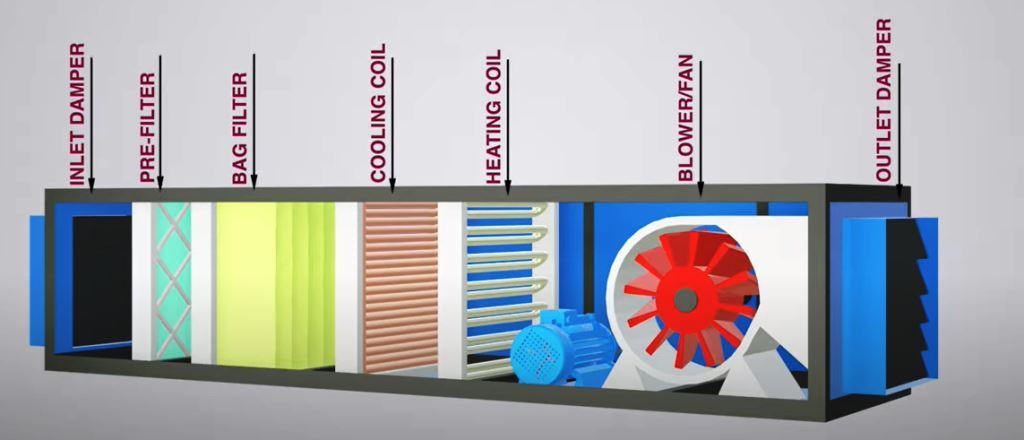
Air Handling Unit (AHU) of FBP
The Air Handling Unit Consists of the following:
- Pre-filter G4
- Intermediate Filter F8
- Dehumidification (Dehumidifier)
- Chilled water coil
- Steam Coil
- Blower & Motor (Flameproof)
- Final filtration with EU 13 HEPA filter (99.97% efficiency down to 0.3 microns)
- Differential gauges
The Exhaust Air Handling Unit Consists
- Police filter
- Stainless Steel 304 Impulse Back Blow Dust Collection.
- Differential pressure meter
- Exhaust Air Recycling
- Wet Scrubber
Critical Parameters of FBD.
- Product temperature
- Exhaust air temperature
- Air flow rate
- The humidity of inlet air
- Utility controls
- Alarm set points
- Temperature Variation against the set point. (Temp overshooting (±1 °C))
In pharmaceutical applications, the critical parameters of a fluidized bed processor may include:
- Particle size and distribution: The size and distribution of the drug particles in the bed can affect the flow behavior and the uniformity of the final product.
- Bed temperature: The temperature of the bed is a critical parameter in determining the rate of drying or other processing steps. The temperature must be carefully controlled to prevent degradation or other changes in the drug substance.
- Airflow rate: The airflow rate is an important parameter in determining the degree of fluidization of the bed and the mixing of the particles. The airflow rate must be high enough to suspend the particles, but not so high as to cause excessive attrition or entrainment of particles.
- Humidity: The humidity of the processing environment can affect the drying rate and the stability of the drug substance. The humidity must be carefully controlled to prevent moisture uptake or loss.
- Inlet air temperature and humidity: The temperature and humidity of the inlet air can affect the efficiency of the fluidized bed dryer. The inlet air temperature and humidity must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired drying rate and minimize the risk of degradation or other changes in the drug substance.
- Bed depth: The bed depth is an important parameter in determining the residence time of the drug particles in the bed and the overall capacity of the fluidized bed processor. The bed depth must be carefully controlled to prevent overloading or underutilization of the equipment.
- Material properties: The material properties of the drug substance, including its melting point, density, and hygroscopicity, can affect the processing behavior in the fluidized bed processor. The material properties must be carefully considered to achieve optimal process performance and final product quality.
Calculation factors in fluidized bed processor:
The capacity check for a fluidized bed processor in pharmaceutical manufacturing typically involves several calculations, including:
- Minimum fluidization velocity: This calculation determines the minimum velocity of the fluidizing gas required to achieve fluidization of the particles in the bed. The minimum fluidization velocity can be calculated using empirical correlations or experimental data.
- Bed expansion: The degree of bed expansion is a function of the fluidizing gas velocity and the size and density of the particles in the bed. Bed expansion can be calculated using empirical correlations or experimental data.
- Residence time: The residence time of the particles in the bed is an important parameter in determining the processing capacity of the fluidized bed processor. Residence time can be calculated using the bed height, the particle size, and the fluidizing gas velocity.
- Drying rate: The drying rate of the material being processed is a function of the fluidizing gas temperature, humidity, and velocity, as well as the material properties such as moisture content and particle size. The drying rate can be calculated using experimental data or theoretical models.
- Capacity calculation: Once the above parameters are determined, the capacity of the fluidized bed processor can be calculated using the following formula:
Capacity = (Bed volume) x (Bulk density of particles) x (Residence time) / 3600
where bed volume is the volume of the fluidized bed, bulk density of particles is the mass per unit volume of the particles in the bed, the residence time is the time that particles spend in the bed, and 3600 is a conversion factor to convert seconds to hours.
These calculations can be used to determine the optimal operating conditions for a fluidized bed processor, as well as to assess the potential processing capacity and throughput of the equipment.
Safety Features or Requirements in fbd
-
-
- The motor and blower shall be flameproof in fbd.
- NEMA Rating of enclosures.
- Emergency switch and safety interlocks/features, for safe operation and maintenance.
- Earthing relay with interlocks is provided in fbd.
- Bursting disc/ Below details.
-
- Explosion prevention: Fluidized bed processors can create an environment that is conducive to explosions if proper precautions are not taken. It is important to implement explosion prevention measures, such as using inert gas, maintaining proper ventilation, and avoiding the use of ignition sources.
- Material handling: Handling and processing of pharmaceutical materials can pose a hazard due to their potentially toxic or reactive properties. It is important to follow appropriate handling procedures, including the use of personal protective equipment, to minimize the risk of exposure to hazardous materials.
- Temperature control: The temperature of the fluidized bed processor must be carefully controlled to prevent overheating and the risk of fire or thermal degradation of the materials being processed. Temperature sensors and automatic shut-off systems can help to prevent temperature-related hazards.
- Pressure control: The fluidized bed processor must be operated within safe pressure limits to prevent over-pressurization and the risk of explosion. Pressure sensors and relief valves can help to prevent pressure-related hazards.
- Electrical safety: The fluidized bed processor contains electrical components and must be operated in compliance with electrical safety standards to prevent electrical hazards. Grounding, circuit protection, and lockout/tagout procedures are important measures for electrical safety.
- Maintenance and inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of the fluidized bed processor can help to identify and prevent potential hazards. It is important to follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance and to conduct periodic inspections of the equipment.
- Emergency preparedness: In the event of an emergency, such as a fire, explosion, or chemical release, it is important to have appropriate emergency response procedures in place. This may include evacuation plans, emergency shut-off procedures, and training for personnel in emergency response procedures.
Difference between the Vented (2 bar) and Non vented (12Bar) machine
Non-Vented FBD |
Vented FBD |
| 12 bar Pressure Resistant | 2 bar pressure shock resistant |
| Higher thickness material having MOC – Stainless steel Duplex Grade SS 318 or SS 316L) | MOC – Stainless Steel SS316L |
| Explosion relief vent/duct not required | An explosion relief vent/duct is required |
| In case of an explosion, all the dust and gases are contained within the equipment. | In case of an explosion, the pressure is relieved to the atmosphere, and all gases, smoke, and product dust are also released into the atmosphere. |
Control & Operating systems:
- Industrial PC in fbd.
- 21 CFR compliance Software in fdb.
- Different levels of users with individual IDs and Passwords in fbd.
Utility Requirements:
- Electrical Supply
- Compressed Air
- Raw Steam for Heating
- Pure Steam for humidification
- Purified Water
WIP System:
- High-pressure Pump
- Valve Group / Manifold
- Process Piping & Spray Nozzles.
- Compressed Air System
- Electrical Control.
Breakdown possibility in fluidized bed processor
The breakdowns that may occur in a fluidized bed processor during pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
- Heating and cooling system failure: The heating and cooling system within the fluidized bed processor can experience failures due to issues such as clogging, leakage, or component failure.
- Pump failure: Pumps used for fluidization, spraying, or product transfer can fail due to issues such as clogging, wear, and tear, or mechanical failure.
- Instrumentation failure: Failure of critical sensors or instrumentation, such as temperature sensors or pressure transmitters, can result in process deviations and product quality issues.
- Power supply failure: Power supply failures, such as tripped breakers or blown fuses, can result in a complete or partial shutdown of the fluidized bed processor.
- Mechanical failure: Mechanical components within the fluidized bed processor, such as the blower, air distributor, or product discharge mechanism, can experience issues such as wear and tear, misalignment, or component failure.
- Control system failure: Failure of the control system, including the programmable logic controller (PLC) or human-machine interface (HMI), can result in loss of process control and product quality issues.
- Material handling issues: Issues with material handlings, such as product buildup, bridging, or blockage, can result in equipment failure and downtime.
It is important to have a robust maintenance program in place for the fluidized bed processor, including routine inspections, preventative maintenance, and quick response to issues to minimize downtime and prevent product quality issues.
Certification & Documentations:
- GA Drawing & P&ID for FBD, AHU, Exhaust unit, Wet scrubber, Complete set of Top, Side & Elevation view.
- Ladder logic drawings.
- Motor certificates along with a flameproof certificate.
- MOC certificates of all contact & major non-contact parts including gaskets.
- Certificate of filter bag, pressure test certificate, or each component certificate.
- Document for WIP/CIP system for In FBD chamber and duct cleaning document.
- Complete set of DQ, and IQ Documents.
- All documents are as per URS
Best Manufacturer (OEM)of FBD/FBP worldwide:
There are thousands of manufacturers worldwide who manufacture this granulation equipment many of then are provide full-line setups for the pharma plant, here we are providing some of the best OEMs below:
- GEA Process equipment.
- ACG Group
- Glatt GmbH – Integrated Process Solutions
- Bowen and Archer
- Anchor mark
- Ganson Pvt ltd.
- Anish Pharma equipment.
Advantages of Fluidized bed processors
Fluidized bed processors offer several advantages in pharmaceutical manufacturing, including:
- Improved process efficiency: Fluidized bed processors can provide efficient and continuous processing of pharmaceutical materials, with rapid heat and mass transfer rates. This can reduce processing times and increase productivity.
- Precise process control: Fluidized bed processors allow for precise control of process parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and airflow, which can help to ensure consistent product quality and reduce process variability.
- Uniform product quality: Fluidized bed processors can provide uniform drying, granulation, and coating of pharmaceutical materials, resulting in consistent product quality and reduced variation between batches.
- Reduced production costs: Fluidized bed processors can help to reduce production costs by minimizing material waste and reducing processing times, which can result in lower energy consumption and labor costs.
- Versatility: Fluidized bed processors can be used for a wide range of pharmaceutical processing applications, including drying, granulation, and coating of particles, as well as for powder mixing and particle size reduction.
- Reduced environmental impact: Fluidized bed processors can help to reduce the environmental impact of pharmaceutical manufacturing by reducing waste and emissions, and by using more efficient and sustainable processing methods.
- Reduced risk of contamination: Fluidized bed processors are designed to minimize the risk of contamination, with enclosed processing chambers and sealed processing systems, which can help to ensure product purity and reduce the risk of product recalls.
Disadvantages of Fluidized bed processors
fbd also has some disadvantages, including:
- High initial investment cost: The initial capital cost of a fluidized bed processor can be relatively high compared to other types of pharmaceutical processing equipment, which can be a barrier to adoption for some manufacturers.
- Complex operation: Fluidized bed processors require a high degree of operator expertise and training to operate effectively and safely, which can be challenging for some organizations.
- Limited capacity: Fluidized bed processors typically have a limited processing capacity compared to other types of equipment, which can result in longer processing times for larger batches.
- Limited particle size range: Fluidized bed processors are typically most effective for processing particles within a specific size range, and may not be suitable for processing very fine or very coarse particles.
- Potential for particle attrition: The high shear forces within a fluidized bed processor can result in particle attrition, which can reduce product quality and increase the risk of contamination.
- Risk of material agglomeration: Material agglomeration can occur within a fluidized bed processor, particularly during granulation or coating processes, which can result in uneven product quality and reduced process efficiency.
- Risk of fluidization instability: Fluidized bed processors can be prone to instability, particularly if process parameters are not carefully controlled, which can result in uneven product quality and an increased risk of equipment failure.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ) about Fluidized Bed Processors:
What is fluid bed equipment?
Answer: Fluid bed equipment is used to lower the moisture content of pharmaceutical granules or powder. Additionally, you can employ fluid bed equipment for coating or granulating various particle types.
What is the difference between FBP and FBD?
Answer: FBP is the fluid bed processor used for drying as well as coating the granules of the bulk drug. But FBD only has a facility for drying the granules of the bulk drug.
What is fluidised bed technology?
Answer: This is the technology i.e. the drying of the granules through passing hot air penetrating from the granules.
What is the purpose of a fluidized bed dryer FBD?
Answer: The main purpose of this equipment is the drying granules.
For more technical details, best equipment vendor comparison, or any type of documentation. (SOP,DQ,IQ,OQ,PQ etc.) Please contact: admin@flairpharma.com

Check set point it should be 5Drgree tolerance.
Dear viewer
Thanks for your comment.
Dear flair pharma team,
I felt delighted and refreshed my concept after reading your article on FBD.
Would like to b in regular touch..
Dear Rahul Ji
Your feedback is highly important to us. We are working on getting in touch with our viewers. We will notify you soon for regular notification on new topics.
Thanks
Team Flair
dear flair pharma team plese about fbd duct cleaning procedure how to clean fbd duct
Dear Mohit
thanks for your query!
Duct cleaning is the hottest point in most USFD-approved plants. So as far as the procedure of duct cleaning, there are multiple designs available in the markets for example the inlet and outlet ducting has detachable spray nozzles with WIP skid for duct cleaning. to ensure the cleaning we have to put a conductivity sensor at the drain point and also have view glasses in the ducts for verification of the duct cleaning. And all the systems are validated through cleaning validation protocol and report.
Thanks!.
Team flair.
If any other query you may write us at flairpharma28@gmail.com
We are very thankful for this great information. Provided information is very clear, simple and understandable. That why always I suggests to my juniors for flairpharma….
Dear Mr. Mahender
“Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that you find the information clear, simple, and understandable. Your recommendation to your juniors means a lot to us. If there’s anything more we can help you with or improve upon, please feel free to let us know. We appreciate your support and value your feedback!”
you may contact us on Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/flair-pharma-027b91252/