Data integrity in CCS plays a potential role, as we are already discussed in detail about the Contamination control strategy. Perhaps it won’t come as a surprise to you to realize that data integrity is essential to a cleanroom’s smooth operation. We strongly advise you to read on and make notes if you are surprised by this. But for many cleanroom or particle counter workers, the concept of “data integrity” has been so thoroughly ingrained in our minds that we occasionally lose sight of its genuine significance. Aside from that, we neglect its potential contribution to our contamination control strategies (CCSs).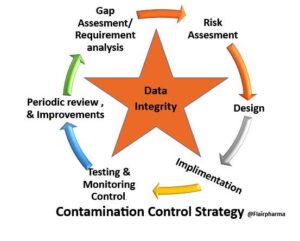
Recent revisions to GMP Annex 1 have placed a strong emphasis on Quality Risk Management (QRM) via an extensive CCS. Your CCS ought to be founded on a risk assessment and start by addressing the following:
- Full Integration across the entire product life cycle.
- Personnel with the necessary knowledge to determine when sterility is in danger.
- Protocols for investigating equipment failures, including corrective and preventive measures (CAPA).
- Follow risk management guidelines to prevent contamination.
- Engaged senior management in frequent evaluations as well as monitoring.
- Risk-free product finishing, storage, and transportation.
- Techniques and equipment for contamination monitoring.
- Monitoring of contaminated points.
- The cleanroom’s design and the materials utilized in its construction.
- The management and usage of utilities.
- Staff members receive regular and thorough training, particularly on gowning.
Above is only a brief description of some of the updates made to Annex 1, Data Integrity in CCS but one thing is certain, you need a thorough contamination control strategy that establishes the layout and use of your cleanroom and the plant equipment and processes. The HVAC, cleanroom, Plant Equipment, Quality Instruments, production procedures, Quality procedure, and everything that goes with it, must be planned with this in mind, it cannot be an afterthought.
Where, therefore, does data integrity fit into this plan? We’re so happy you inquired about Data Integrity in CCS.
One component of the larger picture of current good manufacturing practices (cGMPs), which have been defined for the protection of human health, is Data integrity in environmental monitoring (EM).
The measurement of potential contamination has previously been focused on using particle counters, active air samplers, Petri dishes, and swabs for surface monitoring. In order to improve the ability to detect microbial contamination throughout the production process, filter integrity and bioburden of the bulk products were also examined. To stop and manage any contamination before it gets to the product—the point of no return—this strategy has been modified. Determining the origins is crucial since once contamination occurs, there is no affordable removal strategy to resume production. This is done through:
Quality by Design implementation in the manufacturing sector.
Brief of Data Integrity:
Before discussing about the DI in CCS, let’s quickly define data integrity so that everyone is on the same page. If someone in the USA brings up laws pertaining to data integrity, they most likely mean 21 CFR 11. This pertains to Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations, Part 11, of the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Data integrity is described by the FDA as “the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of data. Attributable, legible, contemporaneously documented, original / a true copy, & accurate (ALCOA) data is present.
Data integrity has many uses in every stage of pharmaceutical processes, but for regulatory agencies, it primarily serves one purpose: to confirm that you are creating safe products according to best practices.
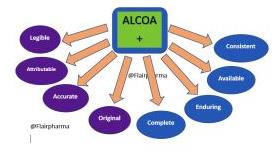
Following ALCOA+ is one of those best practices. This abbreviation means:
- Attributable: With a signature and date, it must be obvious who entered the date.
- Legible: The information must be plainly understandable and free of cryptic symbols.
- Contemporaneous: Information should be documented as soon as it is produced.
- Original: Either the original data or a verified copy should be used.
- Accurate: Information should accurately depict the observed phenomenon or circumstance.
- Complete: Records should cover testing and retesting and should leave nothing out.
- Consistent: Time stamps ought to appear in the anticipated order. Data generation should be uniform across the board. Data should only be entered into systems that are no longer in operation (or if unavailable, controlled worksheets in laboratory notebooks).
- Available: The record must be easily accessible for inspection and audits during the duration of the record.
When you incorporate technology and resources to help with complaints, adhering to ALCOA+ is significantly easy. The 21 CFR 11 regulations were created particularly to make sure you can retain the greatest level of data integrity while yet being flexible.
Role of Data Integrity in Contamination Control Strategy
The main nerve system of CCS in general is the integrity of your data. Your systems’ information flow is what tells you whether everything is operating normally and whether there are any anomalies. It eliminates any possibility of contamination and cross contaminations, while also acting as the basis for audits and classification, which keeps the space operating properly. Data Integrity in CCS drives all documentation trails.
The process of developing your CCS is similar in that you must start by thinking about how to protect data integrity. To work effectively, pass audits, and keep classification, your system and plant must handle all data with the highest integrity. The systems necessary to make this procedure seamless won’t exist if your CCS was not designed with data integrity in mind. You’ll have to allocate man-hours where they shouldn’t have to because you’ll wind up with messy paper trails and challenging audits.
Instead, if you base your Data Integrity in CCS, you’ll find that the process runs smoothly, audits are easier, and you have more confidence and security in your plant.
For Data Integrity in CCS, you may also read the best book on Developments in Surface Contamination and Cleaning, Volume 12: Methods for Assessment and Verification of Cleanliness of Surfaces and Characterization of Surface Contaminants
FAQ Data Integrity in CCS :
What is data integrity in CSS?
Answer: The consistency and accuracy of the data utilized in a strategy that is referred to as data integrity in CSS. This requires that the data be accurate, current, and clear of mistakes or discrepancies that might affect how the pharma factory is a workout.
The best practices, such as utilizing acceptable syntax, avoiding duplicating rules of DI, and maintaining well-organized and documented stylesheets, are crucial for ensuring data integrity in CSS. Also, it’s critical to frequently validate the CSS and check the mistakes and inconsistencies as well as to ensure that the CCS complies with the most recent standards.
What is meant by data integrity?
What is the definition of data integrity?
What is data integrity and why is it important?
Answer: Data integrity is directly proportional to the accuracy, reliability & consistency of data for the entire lifecycle. It ensures that the data is complete, correct, and trustworthy. Maintaining data integrity is critical for any organization that relies on data to make business decisions or for any application that stores and processes data.
The importance of data integrity can be summarized as follows:
1. Reliable decision-making: When data is accurate and consistent, organizations can rely on it to make informed decisions, which can lead to better outcomes and more efficient processes.
2. Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulatory compliance requirements that mandate the accuracy and completeness of data. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and legal penalties.
3. Cost savings: Data integrity can help avoid costly errors and rework by ensuring that data is accurate and consistent, reducing the risk of lost time and resources.
4. Customer trust: Customers expect the organizations they do business with to protect and manage their data with integrity. By maintaining data integrity, organizations can build and maintain trust with their customers.
5. System efficiency: Data integrity helps prevent errors and inconsistencies in data, which can reduce the workload on systems and improve system performance.
Overall, data integrity is critical for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data, which in turn supports effective decision-making, regulatory compliance, cost savings, customer trust, and system efficiency.
