A media fill test is a critical quality control test conducted in the pharmaceutical industry. It involves simulating the production process by filling sterile growth media instead of the actual product into containers and subjecting them to the same manufacturing conditions. This test helps assess the sterility and integrity of the manufacturing process, ensuring the absence of microbial contamination. It plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality and ensuring the safety of pharmaceutical products.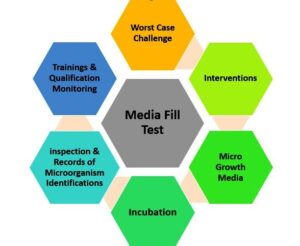
Media fill test steps
The media fill test in the pharmaceutical industry typically involves the following steps:

- Preparation of growth media: Prepare sterile growth media that mimic the composition and conditions used in the actual production process. This media should support the growth of microorganisms if any contamination occurs.
- Selection of containers: Choose containers that are representative of the actual production process, such as vials, ampoules, or bottles. Ensure they are properly cleaned and sterilized.
- Filling process simulation: Simulate the filling process by filling the containers with the prepared sterile growth media instead of the actual product. This should closely resemble the conditions and techniques used during regular production.
- Sealing and labeling: Properly seal and label the containers to prevent contamination and ensure traceability during the test.
- Incubation: Place the filled containers in appropriate incubation conditions, such as specified temperature and time, to promote microbial growth if any contamination exists.
- Examination and evaluation: After the incubation period, visually inspect the containers for any signs of microbial growth, such as turbidity, discoloration, or gas formation. Additionally, perform microbiological testing by sampling the filled containers to determine if any microorganisms are present.
- Interpretation of results: Analyze the test results to determine the overall sterility of the media fill process. If microbial growth is observed or if positive microbiological results are obtained, it indicates a potential contamination issue that needs to be investigated and addressed.
- Documentation and reporting: Document all the test procedures, observations, and results accurately and thoroughly. Report any deviations or findings that require corrective actions.
The media fill test is performed periodically to validate the aseptic manufacturing process and ensure the production of sterile pharmaceutical products.
Media fill Guidance
Media fill guidance can vary slightly between different regulatory guidelines and organizations. Here are some general sources of media fill guidance:
- FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration): The FDA provides guidance on media fill testing in its “Guidance for Industry: Sterile Drug Products Produced by Aseptic Processing – Current Good Manufacturing Practice” document. This guidance outlines the expectations for media fill testing, including considerations for media selection, container closure systems, incubation conditions, acceptance criteria, and data analysis.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA): The EMA provides guidance on media fill testing in its “Annex 1: Manufacture of Sterile Medicinal Products” document. This guidance covers various aspects of aseptic manufacturing, including media fill testing, and provides recommendations for test design, acceptance criteria, and monitoring of aseptic processes.
- Pharmacopoeias: Pharmacopoeias such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) may include specific requirements or recommendations for media fill testing. These compendia provide standards and guidelines for the quality control of pharmaceutical products and may provide specific methods or procedures for media fill testing.
why is 3% scdm used in media fill?
The use of 3% soybean casein digest medium (SCDM) in media fill tests is a common practice in the pharmaceutical industry. Here are a few reasons for its usage:

- Nutrient-rich medium: SCDM is a nutrient-rich medium that supports the growth of a wide range of microorganisms. It contains soybean digest and casein, which provide a variety of nutrients necessary for microbial growth. This composition ensures that if any microbial contamination is present, it will have the necessary nutrients to grow and be detected during the media fill test.
- Simulates product conditions: The goal of a media fill test is to simulate the actual manufacturing process and conditions. By using a medium that closely resembles the composition and conditions encountered during production, such as SCDM, provides a representative environment for the microorganisms that may be encountered in the real process.
- Regulatory acceptance: The use of 3% SCDM in media fill testing has gained regulatory acceptance and is referenced in various guidelines and pharmacopeias. It has been widely used and demonstrated its effectiveness in detecting microbial contamination, making it a common choice for media fill tests.
It’s worth noting that while 3% SCDM is a commonly used medium, specific variations or alternative media formulations may be used depending on the product being manufactured and the regulatory requirements of a particular region or organization.
Critical Parameters of the media fill in aseptic filling
During a media fill test in aseptic filling, several critical parameters need to be considered and controlled to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the test. These parameters include:
- Sterility of components: All components used in the media fill test, such as containers, closures, filters, and equipment, must be properly sterilized. This ensures that any microbial growth observed during the test is a result of potential process deviations rather than initial contamination from the components.
- Aseptic technique: The media fill test should closely mimic the aseptic filling process. Strict adherence to aseptic techniques, including personnel gowning, environmental control, and proper disinfection procedures, is essential to minimize the introduction of contaminants during the test.
- Process simulation: The media fill should accurately simulate the actual filling process, including the filling equipment, line speed, and other critical parameters. This ensures that the test accurately represents the potential risks and challenges faced during routine production.
- Media selection: The choice of growth media is crucial in media fill testing. The selected media, such as 3% SCDM, should provide appropriate nutrients to support the growth of a wide range of microorganisms that may be present in the manufacturing environment.
- Incubation conditions: The filled containers should be incubated under appropriate conditions to promote the growth of any potential contaminants. The temperature, duration, and other factors should be set to mimic the intended storage conditions of the actual product.
- Sampling plan: A well-defined sampling plan should be established to ensure representative sampling of the filled containers. This includes determining the number of samples, locations, and sampling frequency. It is important to capture potential variations and identify any localized contamination issues.
- Data analysis: Thorough analysis of the test results is crucial. Visual inspection of the filled containers, as well as microbiological testing of the samples, should be conducted. The data obtained should be carefully reviewed and evaluated against predefined acceptance criteria to determine the overall sterility assurance of the aseptic filling process.
By closely monitoring and controlling these critical parameters, the media fill test can provide valuable insights into the sterility and integrity of the aseptic filling process, helping ensure the production of safe and sterile pharmaceutical products.
Section procedure of media in media fill
| Procedure Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Preparation of Growth Media | Prepare sterile growth media, such as 3% Soybean Casein Digest Medium (SCDM), following the specified formulation and sterilization method. Ensure appropriate quality control measures are in place. |
| Selection of Containers | Choose representative containers (vials, ampoules, bottles) used in the actual production process. Ensure they are properly cleaned, sterilized, and ready for filling. |
| Aseptic Gowning and Setup | Follow the aseptic gowning procedure, including the use of sterile gloves, gown, mask, and head cover. Set up the aseptic area, including the sterile workbench and necessary equipment. |
| Filling Process Simulation | Simulate the actual filling process by filling the prepared growth media into the selected containers using the designated aseptic filling equipment, following the specified process parameters. |
| Container Sealing and Labeling | Properly seal and label the filled containers according to the standard labeling requirements. Ensure traceability and prevent any potential contamination during the test. |
| Incubation | Transfer the sealed and labeled containers to the designated incubation area or equipment. Set the appropriate temperature and duration based on the intended storage conditions of the product. |
| Visual Inspection | After the incubation period, visually inspect each container for any signs of microbial growth, such as turbidity, discoloration, or gas formation. Record observations accurately. |
| Microbiological Testing | Conduct microbiological testing by aseptically sampling a subset of the filled containers. Perform appropriate microbial analysis, such as plating, membrane filtration, or other suitable methods. |
| Data Analysis and Reporting | Analyze the test results, including visual inspection and microbiological data, against the predefined acceptance criteria. Document all observations, deviations, and test outcomes in the report. |
| Deviation Investigation | Investigate any deviations, out-of-specification results, or abnormalities observed during the media fill test. Identify root causes, implement corrective actions, and document the investigation process. |
Media fill acceptance criteria
| Acceptance Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| No Visible Growth | Visual inspection of the filled containers should show no signs of microbial growth, such as turbidity, discoloration, or gas formation. |
| Microbiological Limits | Microbiological testing should be performed on the sampled containers. The results should comply with specified limits, including total viable count, absence of specified pathogens, or other relevant criteria. |
| No Positive Controls | Positive control samples, containing a known number of microorganisms, should demonstrate growth as a control measure to validate the effectiveness of the testing method. |
| Compliance with Regulatory Requirements | The media fill test should comply with applicable regulatory guidelines, such as those from the FDA, EMA, or pharmacopeias. |
| Consistency and Reproducibility | The results of the media fill test should be consistent and reproducible over multiple runs, indicating the reliability and robustness of the aseptic filling process. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a media fill test in aseptic filling?
Answer: The purpose of a media fill test is to simulate the aseptic filling process using growth media instead of actual product, to evaluate the sterility and integrity of the process and detect any potential contamination risks.
What is the significance of using 3% Soybean Casein Digest Medium (SCDM) in media fill testing?
Answer: 3% SCDM is commonly used in media fill testing as it provides a nutrient-rich medium that supports the growth of a wide range of microorganisms, helping to detect potential contamination.
What parameters should be considered during the selection of containers for a media fill test?
Answer: Containers selected for the media fill test should closely resemble those used in the actual production process, ensuring representative conditions. Factors such as size, closure type, and sterilization method should be considered.
How should aseptic technique be maintained during the media fill test?
Answer: Aseptic technique should be maintained through proper gowning, environmental control, and adherence to disinfection procedures to minimize the introduction of contaminants during the test.
Why is incubation necessary after the media fill test?
Answer: Incubation is necessary to provide optimal conditions for the growth of any potential contaminants that may have been introduced during the filling process, allowing for their detection.
What are the key aspects of visual inspection during the media fill test?
Answer: Visual inspection involves examining the filled containers for any signs of microbial growth, such as turbidity, discoloration, or gas formation, which may indicate contamination.
What types of microbiological testing can be conducted during the media fill test?
Answer: Microbiological testing methods such as plating, membrane filtration, or other suitable methods can be employed to assess the presence of microorganisms in the filled containers.
What are the typical acceptance criteria for a media fill test?
Answer: Acceptance criteria may include no visible growth in the filled containers, compliance with specified microbiological limits, absence of specified pathogens, and consistency with regulatory requirements.
How can the reproducibility of the media fill test be ensured?
Answer: Reproducibility can be ensured by conducting multiple runs of the media fill test and demonstrating consistent results, indicating the reliability and robustness of the aseptic filling process.
What are positive controls in the media fill test?
Answer: Positive controls are samples deliberately contaminated with a known number of microorganisms, serving as a control measure to validate the effectiveness of the testing method.
What documentation is required for a media fill test?
Answer: Documentation should include detailed records of test procedures, observations, test results, deviations, corrective actions, and a final report summarizing the outcomes of the test.
How often should media fill tests be performed?
Answer: The frequency of media fill tests should be determined based on regulatory requirements, risk assessments, and the history of the aseptic filling process. Typically, they are conducted at predefined intervals.
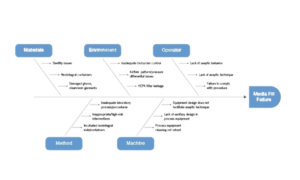
What are the potential challenges or sources of errors in media fill testing?
Answer: Challenges or errors in media fill testing can arise from improper aseptic technique, inadequate sterilization of components, inaccurate media preparation, or deviations in filling process parameters.
How can deviations or out-of-specification results in the media fill test be addressed?
Answer: Deviations or out-of-specification results should be thoroughly investigated

1 thought on “Media Fill Test 2023”