A biosafety cabinet, also known as a biological safety cabinet or BSC, is an essential piece of equipment in the pharmaceutical industry. This specialized containment device provides a safe and controlled environment for handling hazardous biological materials, ensuring the protection of both laboratory personnel and the surrounding environment. Discover how biosafety cabinets facilitate aseptic techniques, prevent cross-contamination, and maintain sterility in pharmaceutical research, development, and production processes.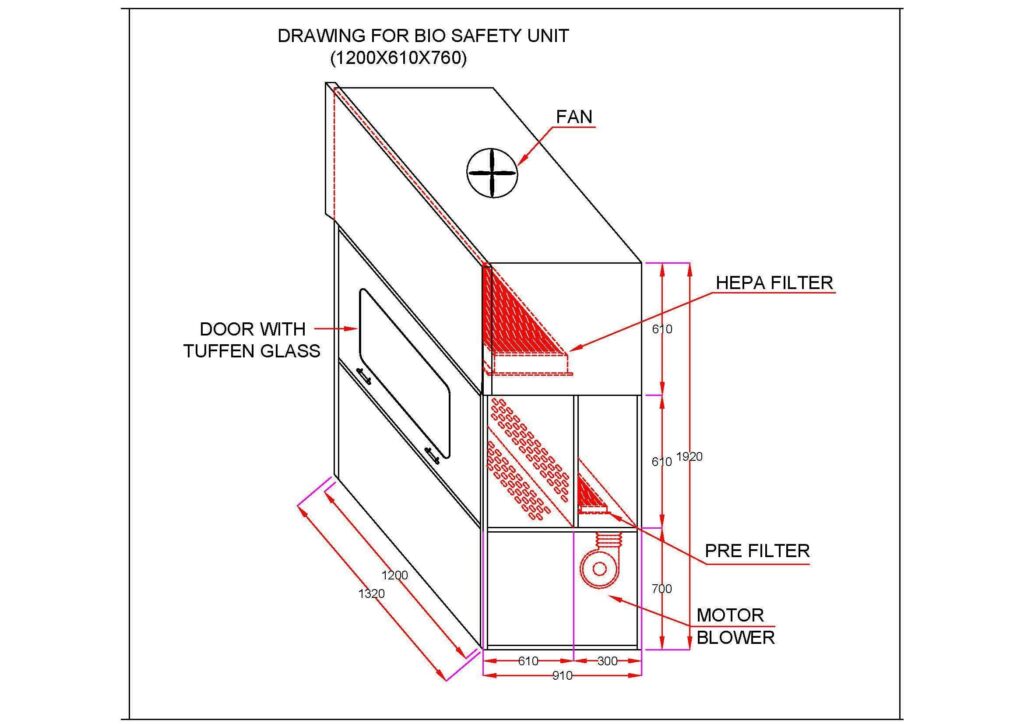
biosafety cabinet diagram
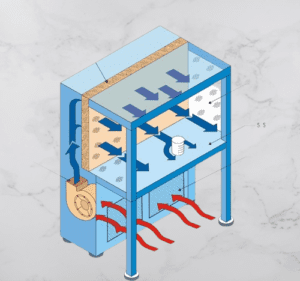
Biosafety cabinet principle
The working principle of a biosafety cabinet revolves around creating a controlled and safe environment to handle hazardous biological materials. Biosafety cabinets employ a combination of airflow patterns, filtration systems, and physical barriers to ensure the protection of personnel, the product, and the environment. Here is an original explanation of the working principle:
The biosafety cabinet functions by using a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration system to filter the incoming air and exhaust air, creating a controlled airflow within the cabinet. The airflow is typically unidirectional or turbulent, depending on the type of biosafety cabinet.
When an operator places their hands or equipment inside the cabinet, the inward airflow ensures that potentially contaminated air is drawn away from the operator’s breathing zone and directed through the HEPA filters, effectively capturing and removing microorganisms and particles.
The HEPA filters in the biosafety cabinet play a vital role in providing a sterile environment. These filters are designed to trap particles as small as 0.3 micrometers with a high efficiency of 99.97%. The filtered air is recirculated into the workspace, ensuring a clean and sterile environment for handling biological materials.
Biosafety cabinets also feature physical barriers, such as a sealed front sash or a glove box system, to prevent cross-contamination between different samples or materials. The cabinet’s interior is made of smooth and non-porous materials that are easy to clean and decontaminate.
In addition, biosafety cabinets may incorporate a variety of safety features, including alarms, airflow indicators, and interlocking mechanisms to ensure proper operation and alert operators to any deviations or malfunctions.
Overall, the working principle of a biosafety cabinet involves creating a controlled airflow environment combined with HEPA filtration and physical barriers to safeguard both the personnel and the surrounding environment from potential biohazards.
Biosafety Cabinet Types
Biosafety cabinets are available in different types, each designed to meet specific safety requirements and provide appropriate containment levels for different applications. Here is an original description of the common types of biosafety cabinets:
-
Class I Biosafety Cabinet:
- Class I cabinets provide personnel and environmental protection, but they do not protect the product being handled. These cabinets have an open front with inward airflow, creating a barrier between the operator and the hazardous materials. The air is then filtered through HEPA filters before being exhausted.
-
Class II Biosafety Cabinet:
- Class II cabinets are the most commonly used type and offer both personnel and product protection. They provide a highly controlled sterile environment and are classified into four subtypes: A1, A2, B1, and B2. Class II cabinets have a partially enclosed work area, and the inward airflow protects the operator. The air passes through HEPA filters, providing sterile air for both personnel and product protection. Class II cabinets also recirculate a portion of the filtered air to maintain a sterile environment.
-
Class III Biosafety Cabinet:
- Class III cabinets, also known as glove boxes or glove bags, provide the highest level of containment and protection. They are completely enclosed and airtight, with glove ports or glove sleeves for operators to handle the materials. Class III cabinets maintain a negative pressure within the cabinet, and all the air is HEPA filtered before being exhausted to ensure the complete containment of hazardous materials. These cabinets are typically used for working with highly infectious agents or biohazardous materials requiring maximum containment.
-
Animal Biosafety Cabinets:
- Animal biosafety cabinets, also referred to as containment ventilated caging systems (CVCS), are designed specifically for housing laboratory animals. They provide a controlled environment to prevent the spread of allergens and protect both the animals and personnel from potential biological hazards. These cabinets feature HEPA-filtered supply and exhaust air to maintain the required ventilation and air quality standards.
Each type of biosafety cabinet offers specific features and containment capabilities, allowing users to select the appropriate level of protection based on their specific applications and the types of hazardous materials being handled. It is essential to consider the biosafety guidelines and regulatory requirements when choosing the appropriate biosafety cabinet type for a particular laboratory or facility.
Critical Points of biosafety cabinet
- Operator Protection: A biosafety cabinet should provide effective protection to the operator by maintaining a barrier between the operator and the biohazardous materials. It should prevent exposure to aerosols, droplets, and contaminants generated during the handling process.
- Product Protection: The biosafety cabinet should ensure the protection of the product or experiment being handled. It should prevent cross-contamination and maintain the sterility and integrity of the materials inside the cabinet.
- Environmental Protection: The cabinet should prevent the release of biohazardous materials into the surrounding environment. It should have proper filtration systems and exhaust mechanisms to capture and contain contaminants, ensuring the safety of the external environment.
- Airflow Control: An essential aspect of a biosafety cabinet is the control of airflow patterns. The cabinet should have a well-designed airflow system that maintains proper air balance, prevents air turbulence, and ensures the correct direction of airflow within the cabinet.
- HEPA Filtration: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are critical components of a biosafety cabinet. They should be properly installed, regularly maintained, and periodically tested to ensure their efficiency in capturing particles as small as 0.3 micrometers.
- Biosafety Level Compliance: Biosafety cabinets should comply with the appropriate biosafety level requirements, as specified by regulatory agencies and guidelines such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) or the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Proper Training and Usage: Users of biosafety cabinets should receive appropriate training on the safe and correct operation of the cabinet. This includes understanding the cabinet’s features, airflow patterns, maintenance requirements, and proper decontamination protocols.
- Regular Maintenance and Certification: Biosafety cabinets should undergo regular maintenance and certification to ensure their continued performance and compliance with safety standards. This includes filter replacement, airflow calibration, and certification by qualified technicians.
- Emergency Situations: Biosafety cabinets should have proper emergency features and protocols in place. This includes alarms for airflow failure, power outage backup systems, and clear guidelines for handling spills, leaks, or other emergency situations.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: It is important to maintain proper documentation of biosafety cabinet installation, maintenance, certification, and usage records. This helps in tracking and verifying compliance, troubleshooting issues, and ensuring the cabinet’s ongoing performance and safety.
Technical Specifications of Biosafety Cabinet
| Technical Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Biosafety Cabinet Type | Class I, Class II (A1, A2, B1, B2), Class III, or Animal Biosafety Cabinet |
| Airflow Velocity | Typically 0.3 to 0.6 meters per second (60 to 120 feet per minute) |
| Airflow Pattern | Unidirectional or turbulent airflow patterns |
| HEPA Filters | High-Efficiency Particulate Air filters for supply and exhaust air |
| Filtration Efficiency | Minimum 99.97% efficiency for capturing particles of 0.3 micrometers or larger |
| Work Surface Material | Stainless steel or other non-porous, easy-to-clean material |
| Lighting | Integrated lighting system for adequate illumination |
| Front Access Opening | Adjustable sash or door for operator access and protection |
| Physical Barriers | Gloves, glove ports, or glove sleeves for handling materials |
| Noise Level | Low noise emissions for a comfortable working environment |
| Control System | User-friendly controls for adjusting airflow, alarms, and lighting |
| Pressure Differentials | Maintains negative pressure within the cabinet (Class III) or inward airflow (Class I/II) |
| Power Requirements | Complies with electrical safety standards and power supply requirements |
| Size and Configurations | Available in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different applications |
| Compliance | Conforms to relevant biosafety guidelines and regulations |
fume hood vs biosafety cabinet
| Aspect | Fume Hood | Biosafety Cabinet |
| Purpose | To remove hazardous chemical fumes and vapors | To provide a controlled environment for handling biohazardous materials |
| Protection Level | Protects the user from chemical exposure | Protects the user, product, and environment from biological hazards |
| Airflow | Unidirectional airflow (from the front to the back) | Unidirectional or turbulent airflow patterns (depending on the type) |
| Filtration System | Typically uses activated carbon filters for chemical fume removal. | Uses High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters for both supply and exhaust air |
| Particulate Filtration | Limited or no particulate filtration | HEPA filters capture particles as small as 0.3 micrometers with high efficiency |
| Containment | Provides limited containment for chemical vapors | Provides containment for biohazardous materials to prevent release and protect the environment |
| Biological Protection | Does not provide protection from biological hazards | Provides protection from biological hazards and maintains a sterile environment |
| Work Surface | Typically made of chemical-resistant materials | Made of non-porous, easy-to-clean materials |
| Lighting | Adequate lighting for visibility | Integrated lighting system for proper illumination |
| Access | Front sash or door for operator access | Front sash or glove ports for operator access |
| Application | Suitable for handling chemicals and non-biological substances | Suitable for working with biohazardous materials, microorganisms, and cell cultures |
| Compliance | Conforms to relevant safety standards and guidelines | Conforms to biosafety guidelines and regulations |
Difference between biosafety cabinet and laminar airflow.
difference between laf and biosafety cabinet.
| Aspect | Biosafety Cabinet | Laminar Airflow |
| Purpose | Provides a controlled environment for handling biohazardous materials | Provides a controlled flow of clean air |
| Types | Class I, II, III, or Animal Biosafety Cabinet | Horizontal or Vertical Laminar Airflow |
| Containment | Provides containment for biohazardous materials | Provides clean and particle-free air to a specific area |
| Protection Level | Protects the user, product, and environment from biological hazards | Provides protection for sensitive processes or equipment from airborne contaminants. |
| Airflow Pattern | Unidirectional or turbulent airflow patterns | Unidirectional airflow in a straight line |
| Filtration System | HEPA filters for both supply and exhaust air | HEPA filters for supply air (in some cases) |
| Applications | Suitable for working with biohazardous materials, microorganisms, and cell cultures | Suitable for applications requiring a sterile or controlled environment, such as cleanrooms or critical manufacturing processes. |
| Work Surface | Made of non-porous, easy-to-clean materials | Provides a clean work surface for processes or equipment |
| Access | Front sash or glove ports for operator access | Typically has a pass-through window or access panel |
| Compliance | Conforms to biosafety guidelines and regulations | Conforms to cleanroom standards and requirements |
Major components of the biosafety cabinet
The biosafety cabinet consists of several major components that work together to provide a safe and controlled environment for handling biohazardous materials. Here are the major components of a biosafety cabinet:
- Work Area: The work area is the main space where the operator performs tasks. It typically includes a work surface made of stainless steel or other non-porous materials that are easy to clean and decontaminate. The work area may also have built-in accessories such as sinks, electrical outlets, or waste disposal systems.
- HEPA Filters: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are crucial components of a biosafety cabinet. They are responsible for filtering the incoming air and exhaust air to remove airborne particles, microorganisms, and contaminants. HEPA filters have a minimum efficiency of 99.97% for capturing particles as small as 0.3 micrometers.
- Blower/Motor Assembly: The blower or motor assembly is responsible for creating the necessary airflow within the cabinet. It draws in ambient air, passes it through the HEPA filters, and circulates it within the cabinet. The blower/motor assembly ensures a consistent and controlled airflow pattern, maintaining the desired containment and sterility levels.
- Airflow System: The airflow system controls the direction and pattern of airflow within the biosafety cabinet. Depending on the type of cabinet, the airflow can be unidirectional (from the front to the back) or turbulent. The airflow system ensures that potentially contaminated air is contained and properly filtered to protect the operator and the environment.
- Front Access Opening: The front access opening of the biosafety cabinet allows the operator to interact with the work area. It may consist of a sash or a door that can be adjusted to control the size of the opening. The front access opening is designed to prevent the escape of biohazardous materials and to maintain the integrity of the controlled environment.
- Control Panel: The control panel is typically located on the front or side of the biosafety cabinet. It houses the controls for adjusting airflow, lighting, alarms, and other operating parameters. The control panel allows the operator to monitor and adjust the cabinet’s settings to ensure proper operation and safety.
- Lighting System: An integrated lighting system provides adequate illumination within the biosafety cabinet’s work area. It ensures visibility and facilitates accurate and safe handling of biohazardous materials. The lighting system is designed to minimize shadows and glare that could hinder the operator’s visibility.
- Alarms and Safety Features: Biosafty cabinets often include alarms and safety features to alert operators of potential issues or deviations. These may include alarms for low airflow, filter saturation, or improper sash position. Interlocking mechanisms may also be present to ensure proper use and prevent accidental exposure.
These major components create a controlled and safe environment for handling biohazardous materials in a biosafety cabint. They contribute to the containment, filtration, airflow, and operator safety aspects of the cabinet’s operation.
Operation and Cleaning of Laminar Air Flow
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Class I, Class II, and Class III biosafety cabinets?
Answer :
- Class I biosafety cabinets provide personnel and environmental protection but do not protect the product being handled.
- Class II biosafety cabinets offer both personnel and product protection and are further classified into subtypes (A1, A2, B1, B2) based on airflow patterns and exhaust systems.
- Class III biosafety cabinets provide the highest level of containment, fully enclosing the work area and providing maximum protection for the operator, product, and environment.
How often should I replace the HEPA filters in a biosafety cabinet?
Answer: HEPA filters should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry standards. Typically, they are recommended to be replaced every 1 to 3 years, depending on usage and environmental conditions. Regular filter integrity testing should also be conducted to ensure their effectiveness.
What is the recommended airflow velocity for a biosafety cabinet?
Answer: The recommended airflow velocity for a biosafty cabinet is typically between 0.3 to 0.6 meters per second (60 to 120 feet per minute). This velocity ensures proper containment and maintains a sterile environment within the cabinet.
How should I clean and decontaminate the interior of a biosafety cabinet?
Answer: Cleaning and decontamination procedures may vary depending on the specific biosafety cabint and the biohazardous materials being handled. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and industry best practices. Generally, a disinfectant approved for use in biosafety cabints is applied to all surfaces, including the work area, followed by thorough cleaning and rinsing.
What should I do if the airflow alarm is triggered on the biosafety cabinet?
Answer: If the airflow alarm is triggered, it indicates a potential issue with the airflow system. The operator should stop working, assess the situation, and check for any blockages or disruptions to the airflow. If the issue cannot be resolved, the biosafety cabint should be taken out of service and serviced by a qualified technician.
Can I use a biosafety cabinet for handling chemicals?
Answer: Biosafety cabints are primarily designed for handling biohazardous materials, not chemicals. If chemicals are being used, a chemical fume hood or other appropriate containment device should be utilized.
What are the electrical requirements for a biosafety cabinet?
Answer: Biosafety cabints typically require a dedicated electrical circuit with appropriate voltage and amperage as specified by the manufacturer. It is important to ensure compliance with local electrical codes and regulations.

2 thoughts on “Biosafety Cabinet 2023”