Transport validation in pharmaceutical plants is a critical process that ensures the safe and compliant transportation of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished pharmaceutical goods. It is a vital aspect of the overall quality management system within the pharmaceutical industry.
The validation process involves verifying that the transportation methods and conditions maintain the integrity, safety, and efficacy of the products being transported. Here are the key steps involved in transport validation:
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the transportation process to identify potential hazards, risks, and critical control points. This assessment should consider various factors such as transportation routes, temperature, humidity, vibration, handling procedures, and potential exposure to external contaminants.
- Validation Plan: Develop a comprehensive validation plan outlining the scope, objectives, and acceptance criteria for the transport validation process. The plan should define the responsibilities of each stakeholder involved in the transportation process and specify the validation protocols to be followed.
- Qualification of Transport Providers: Ensure that transportation is carried out by qualified and reliable providers who have a proven track record of handling pharmaceutical products in a compliant manner. This may involve conducting audits and assessments of the transport providers’ facilities, processes, and documentation.
- Temperature Mapping and Monitoring: For temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals, perform temperature mapping studies on transportation vehicles or containers to assess temperature distribution and stability during transit. Implement continuous temperature monitoring systems to track and record temperature excursions throughout the journey.
- Packaging Validation: Validate the packaging used for transportation to ensure it provides adequate protection to the pharmaceutical products against external factors such as temperature variations, humidity, and physical damage.
- Shipping Validation: If applicable, validate the shipping process, including loading and unloading procedures, to prevent potential product damage during handling.
- Data Collection and Analysis: During the transportation process, collect relevant data, such as temperature records, humidity levels, and any incidents or deviations encountered. Analyze this data to ensure compliance with predefined acceptance criteria.
- Qualification of Reusable Containers: If reusable containers are used, ensure they undergo proper qualification, cleaning, and sterilization processes to avoid cross-contamination or degradation of the pharmaceutical products.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintain detailed documentation of the entire transport validation process, including protocols, reports, deviations, and corrective actions taken. Provide a comprehensive final report with conclusions and recommendations.
- Continuous Monitoring and Review: Transport validation is not a one-time activity; it requires periodic review and continuous monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
To ensure that the temperature controlled transport vehicle is capable of maintaining vehicle is capable for maintaining the temp. and RH within the specified limit throughout the transit time from plants to delivered destination.
Validation Protocol of Transport Validation
- SCOPE:
- This Validation protocol shall be applicable to the finished goods which are manufactured and supplied by Pharmaceutical Plant.
- This protocol shall be applicable for Domestic and Export market.
- Justification for the selection of products for transport validation are as follows, but not limited to:
- Changes in route of transportation.
- Changes in the port of destination.
- Changes in Environmental conditions of transport.
- Any recommendation by customers.
- Temperature and Humidity monitoring shows unexplained variability that is greater than normal.
- PROCEDURE for the Transport Validation:
- The warehouse officer shall inform the QA team about the information such as new transporter, transporter name, vehicle number and vehicle size, product details such as product name, batch number, and the number of packed shippers at least one day prior to delivery.
- The QA officer must verify the products and transport details and determine whether or not transport validation is required.
- If temperature mapping research is relevant on the transport vehicle, QA must notify all concerned parties from the site and depot.
- For Export: Data logger can be used as per the contract giver or customer consignment.
- The transport validation protocol must be approved by QA.
- The warehouse person shall arrange the shippers/ pallets/ drum of the product which is under transport validation.
- The warehouse person shall perform a visual inspection of all the containers to be shipped for cleanliness and any defects and record the observations in the report.
- If the transport container is unclean or damaged, wait until it is cleaned or repaired.
- QA shall ensure the pre-shipmen visual inspection of the container along with the warehouse person.
- Ensure that the packed products meet the required criteria.
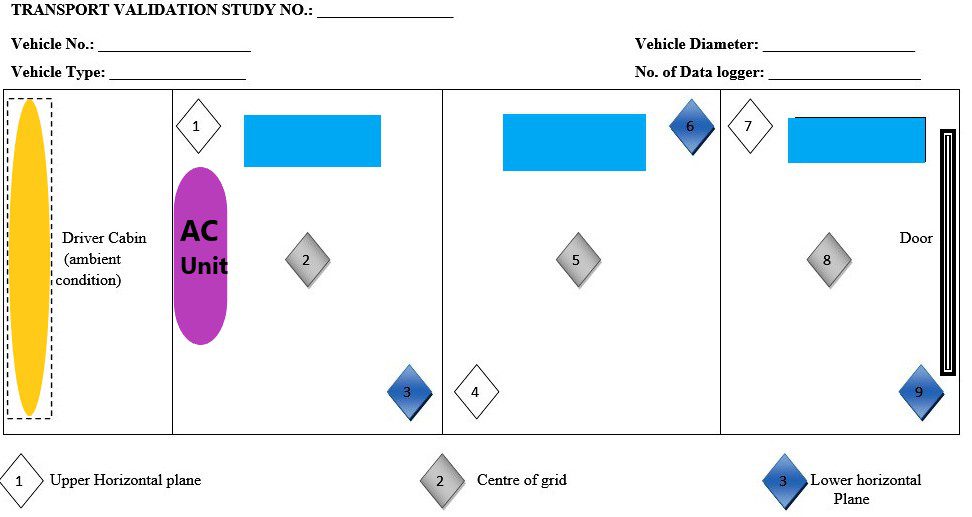
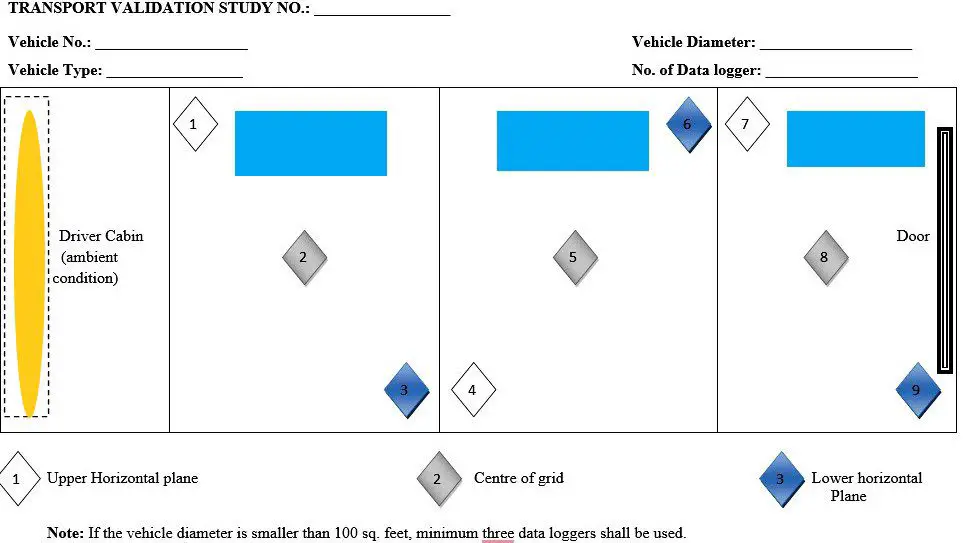
- QA shall measure the dimension of the vehicle (length and width) and divide the areas into the grid of approximately 10 ft X 10 ft. (100 sq. feet). If an area is smaller than 100 square feet, consider it as one grid.
- Arrangement of the data loggers in the grid as per the below-mentioned table example:
| Sr. No. | Grid No. | Data Logger Location | Centre Middle Level |
| 01 | I | Right side upper level | Behind the AC unit, difficult to achieve the desired temperature. |
| 02 | I | Centre Middle Level | The location is surrounded by shippers in all directions so the desired temperature is difficult to achieve. |
| 03 | I | Left side lower level | To demonstrate temperature distribution in the lower horizontal plane |
| 04 | II | Left side upper level | To demonstrate temperature distribution in the upper horizontal plane. |
| 05 | II | Right Side Upper Level | The location is surrounded by shippers in all directions so the desired temperature is difficult to achieve. |
| 06 | II | Right Side Lower level | To demonstrate temperature distribution in the lower horizontal plane. |
| 07 | III | Right Side upper Level | To demonstrate temperature distribution in the upper horizontal plane. |
| 08 | III | Centre middle level | The location is surrounded by shippers in all directions so the desired temperature is difficult to achieve. |
| 09 | III | Left Side- Lower level | To demonstrate temperature distribution in the lower horizontal plane and at location farthest away from the AC unit. |
- QA shall switch on the data loggers and set the program in data loggers to record the temperature and RH.
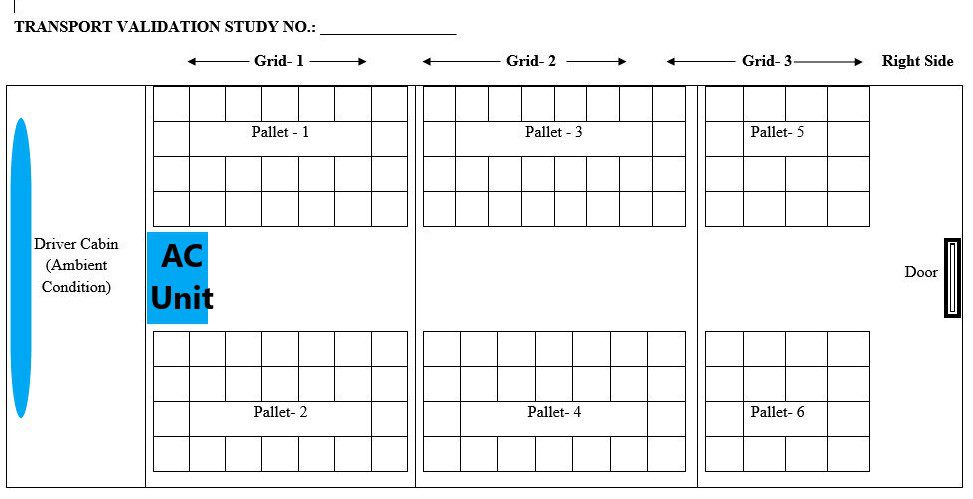
- Data loggers shall be placed while loading shippers and the same shall be recorded in Annex.
- In case of without pallet, the warehouse person shall place the data loggers in identified shippers/ drum (upper corner of shipper drum) of the consignment in the presence of QA.
- In the case of with pallets, the warehouse person shall place the data logger on the upper corner of half of the total pallets and on the lower corner on half of the pallets of the consignment in the presence of QA.
- The warehouse person shall label the outer surface on each side of the shipper/ pallet/ drum which contains the loggers as “contains data logger” as per site SOP for labeling.
- QA shall verify the functioning and placement of the data logger in the shipper/ pallet/ drum.
- A real-time photograph of the loading pattern shall be attached with a validation report by WH person.
- Diagrammatic representation of the position of data logger in the vehicle and data logger number to be recorded in Annex II for without pallets and in Annex with pallets.
- QA shall intimate the export department/ consignee/ customer to return the data logger immediately on receipt or through mail or both by the warehouse person.
- After completion of packing the shipment shall be sent to the customer destination from the manufacturing unit.
- Upon receipt of shipment at the customer destination, a customer representative shall checks / confirms the physical conditions of the shipment and fills the details in the data loggers tracking sheet.
- Verification of physical condition and product integrity includes (but not limited to):
- Damaged Products.
- Tempered products.
- Withdraw the samples (if required) from the shippers/ pallet/ drum in which the data logger is placed (quantity required for two times analysis).
- Customer representatives shall stop the data logger and shall send the data logger to the manufacturing site along with Annex and COA of analyzed products (if samples are withdrawn by customer representatives).
- Upon receipt of the data logger to the manufacturing site along with Annex and COA of analyzed samples withdrawn by customer representatives. QA shall collect the data from data loggers.
- QA shall attach these documents (data from the data logger, data logger tracking sheet, and COA of analyzed samples) with the report.
- QA shall review the results of analyzed samples and evaluate compliance.
- The analytical results and data from the data logger shall be compiled in a report and attached to the protocol.
- After review and evaluation of data, a summary of transport validation shall be approved and shared to the customer.
- In case the data logger is provided by the customer then temp. & relative humidity data shall be provided to the manufacturing site.
- Any deviation such as temperature excursion or product damage that has occurred during transportation, and departure from protocol instruction shall be recorded and investigated as per the current version of SOP for handling of deviation.
- Product stability data must demonstrate the acceptable temperature excursion time during transport.
- Risk Assessment of delivery routes shall be used to determine where temperature controls are required.
Transport Validation Report with Temperature Mapping During Transit of Drug Products
- OBJECTIVE:
- To ensure that the temperature-controlled transport vehicle is capable of maintaining the vehicle is capable for maintaining a temperature within the specified limit throughout the transit duration from the plant to the customer depot.
- SCOPE:
- This Validation report shall be applicable for the finished goods which are manufactured and supplied by the Pharmaceutical Plant.
- Justification for selection of products for transport validation:
- Recommended by the authority to perform the transport validation.
- Site of Validation:
- Manufacturing Site: Complete Address.
- Customer Depot: Address of the Product destination.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- A representative from the manufacturing plant from the below departments:
- Engineering.
- QA
- Warehouse
- A representative from the manufacturing plant from the below departments:
- DETAILS OF TRANSPORT VEHICLE AND PRODUCT:
- Items
- Name of the Transporter:
- Agreement Number:
- Vehicle Number:
- 4 Vehicle Size (length in ft.):
- Details of the Products:
- Name of the Product:
- Batch Number:
- Storage conditions: Store protected from light and moisture, or Temperature Range, Do not freeze etc.
- The number of shippers: Nos.
- Loading Pattern:
- CONTROLS: Calibration details of Data logger:
| Sr. No. | Data Logger ID | Sr. No | Calibration Done on | Calibration due on |
- ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA:
- There must not be any damage of the product during transport.
- The analytical results of the product must comply with the release specification.
- The temperature must be within the specified range.
- SUMMARY OF OBSERVATION OF VALIDATION:
- During the Transport validation study, following observations are as follows:
- Physical verification of the vehicle was done and found complies as per the checklist.
- Data loggers are placed in vehicles and tracked from the manufacturing site to the customer depot.
- “Contains Data Logger” labels are affixed on the shippers as mentioned in Annexure.
- The physical condition and its integrity of the transported material have been checked and found complies. No any damage found and the tempered condition of the shippers was satisfactory during the material transportation.
- All these data reports are collected and reviewed and found to be satisfactory.
- During the Transport validation study, following observations are as follows:
- CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION:
- Finished goods are transferred from manufacturing site to the customer depot/ site as per maintaining the product storage condition. (at temperature not exceeding 250C). Data loggers were placed in the consignment at specified locations and temperature found within the limit. Product condition was good, no damaged was observed.
- Hence, we conclude that the transit of drug products is validated.
Check List for the Pre- shipment visual inspection of containers
Transport Validation Study Number: _____________
| Sr. No. | Check points | Vehicle No. – | Vehicle No. – | Vehicle No. – |
| 1. | Transporter Name | |||
| 2. | Vehicle Type | AC/ Non AC/ Cold Van | AC/ Non AC/ Cold Van | AC/ Non AC/ Cold Van |
| 3. | Vehicle Temperature | Before Loading _________0C | Before Loading _________0C | Before Loading _________0C |
| After Loading _________0C | After Loading _________0C | After Loading _________0C | ||
| 4. | Check Cleanliness of floor (below the tarpaulin in case of non AC vehicle) | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK |
| 5. | Check cleanliness of vehicle from inside (ceiling roof, walls & floor) | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK |
| 6. | Check cleanliness of vehicle from outside | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK |
| 7. | Vehicle is free from odor | Yes/ No | Yes/ No | Yes/ No |
| 8. | Check absence of any abnormal fitting, foreign material | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK | OK/ Not OK |


Advantages of the Transport Validation in the Pharmaceutical Plants
| Ensures product integrity and quality during transportation |
| Reduces the risk of product contamination and degradation |
| Complies with regulatory requirements and industry standards |
| Increases patient safety by delivering effective and safe medications |
| Minimizes product losses and waste due to transportation issues |
| Provides data-driven insights for process improvement and optimization |
| Builds trust with customers and stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry |
| Enables identification and mitigation of transportation-related risks |
| Facilitates smoother logistics and supply chain management |
| Demonstrates commitment to quality assurance and compliance |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is transport validation in pharmaceutical plants?
Answer: Transport validation in pharmaceutical plants is the process of verifying and ensuring that the transportation of pharmaceutical products is conducted in a manner that maintains product integrity, safety, and efficacy throughout the journey.
Why is transport validation essential in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Transport validation is crucial to guarantee that pharmaceutical products reach their destination in a safe and compliant condition, ensuring that they remain effective and free from contamination or degradation.
What factors are considered during the risk assessment phase of transport validation?
Answer: Factors considered during the risk assessment phase include transportation routes, temperature, humidity, vibration, handling procedures, and potential exposure to external contaminants.
How is the qualification of transport providers conducted during transport validation?
Answer: Qualification of transport providers involves conducting audits and assessments of their facilities, processes, documentation, and track record in handling pharmaceutical products.
What is temperature mapping, and why is it important in transport validation?
Answer: Temperature mapping involves studying the temperature distribution and stability within transportation vehicles or containers. It is vital for ensuring that temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals are protected from temperature excursions that could compromise their quality.
How does continuous temperature monitoring contribute to transport validation?
Answer: Continuous temperature monitoring provides real-time data on temperature variations during transportation, allowing for immediate corrective actions if any temperature excursions occur.
Why is packaging validation essential in transport validation?
Answer: Packaging validation ensures that the containers used for transportation provide adequate protection to pharmaceutical products against environmental factors, preventing damage and maintaining product integrity.
What is shipping validation, and why is it relevant in transport validation?
Answer: Shipping validation involves validating the loading and unloading procedures to prevent potential product damage during handling, further ensuring the quality of the pharmaceutical products upon arrival.
How does data collection and analysis contribute to transport validation?
Answer: Data collection and analysis provide insights into the conditions encountered during transportation, enabling the identification of potential risks and the assessment of compliance with predefined acceptance criteria.
Why is documentation and reporting crucial in transport validation?
Answer: Documentation and reporting serve as evidence of a well-documented validation process, helping pharmaceutical plants demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices during audits or inspections.


2 thoughts on “Transport Validation Protocol & its advantage for Pharma Products 2025”