For accurate endotoxin detection, heating blocks serve as steadfast allies. These purpose-built devices maintain precise and uniform temperatures, creating an optimal environment for endotoxin-lysate reactions. By ensuring consistent thermal conditions, heating blocks minimize variability and elevate the reliability of BET testing results.
The Bacterial Endotoxin Test (BET) stands as a critical assay to detect and quantify bacterial endotoxins, also known as pyrogens. However, precision and accuracy are key in this life-saving process, and that’s where the indispensable heating blocks come into play. In this article, we explore the vital role of heating blocks in advancing BET testing and safeguarding public health.
The Significance of BET Testing
Bacterial endotoxins, derived from the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, can trigger severe immune responses and pyrogenic reactions in humans. These toxic substances pose a significant threat to patients, making BET testing an essential step in pharmaceutical quality control and medical device validation. The detection and quantification of endotoxins require a delicate balance of conditions, and heating blocks emerge as crucial facilitators in this endeavor.
Heating Blocks: Precise Temperature Control for BET Testing
In the quest for accurate endotoxin detection, heating blocks serve as steadfast allies. These purpose-built devices maintain precise and uniform temperatures, creating an optimal environment for endotoxin-lysate reactions. By ensuring consistent thermal conditions, heating blocks minimize variability and elevate the reliability of BET testing results.
- OBJECTIVE
- To define the technique for operating the Heating Block.
- SCOPE
- This SOP shall be applicable for the operation of the Heating Block used in Microbiology.
- RESPONSIBILITY
- Microbiology Personnel shall be responsible for the operation of Heating Block as per established procedure, maintaining its documents, recording observations and reporting the results.
- Officer Microbiology or above who is trained or well versed with the procedure shall be responsible for ensuring that the same is carried out correctly and checking of documents for completeness of content.
- Head – Microbiology/ Designee shall be responsible for the compliance of the SOP.
- ACCOUNTABILITY
- Microbiology – Head/ Designee shall be accountable for the proper implementation of SOP.
- DEFINITIONS
- Nil
- PROCEDURE
- Equipment Details:
| S. No. | Equipment Name | Equipment ID | Make |
| 1. | Heating Block | ||
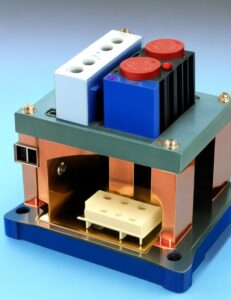
- Operation:
- Connect the instrument to the power supply ensuring that the temperature compensation knob is at minimum position. Switch ON the main power supply.
- Switch ON the mains of the instrument.
- Set the required temperature by pressing the set button.
- Switch the instrument after use.
- Precautions:
- Handle the instrument carefully.
- Always keep the instrument clean.
- Do not make erratic movements of the temperature control knob.
- After setting the temperature lock the instrument.
- Calibration Frequency:– Once in a 6 month (Outside Party)
- Precautions:
- ABBREVIATIONS
- SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
- BET : Bacterial Endotoxin Test
- mL : Microliter
- WFI : Water For Injection
- ºC : Degree Centigrade
- MB : Microbiology

- REFERENCES
- Nil
- ANNEXURES
- Annexure-I : Log Book of Heating Block Usages
- DISTRIBUTION DETAILS
- SOP shall be distributed to Quality Assurance and Microbiology Department.
LOGBOOK OF HEATING BLOCK USAGE
| Date | Name of Material | Batch No. | Start Time | End Time | Operated By | Checked By |
List of components of the Heating Block
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Heating Element | The heating element is the core component responsible for generating and regulating heat within the heating block. It ensures the uniform distribution of temperature throughout the block. |
| Temperature Control | The temperature control system is responsible for setting and maintaining the desired temperature for the heating block. It ensures precise and accurate temperature control during experiments. |
| Temperature Display | The temperature display provides real-time information about the current temperature inside the heating block. This allows researchers to monitor and adjust the temperature according to their experimental needs. |
| Block Surface | The block surface is the flat, heated area where samples or containers are placed. It comes in various configurations and can accommodate different types of vessels, such as tubes, vials, or microplates. |
| Lid | Some heating blocks come with a lid that covers the block surface, providing additional insulation and maintaining temperature stability. The lid also prevents contamination and evaporation during experiments. |
| Control Panel | The control panel houses the user interface, including buttons or touchscreen controls, for setting temperature, timer, and other parameters. It allows researchers to program and customize their experiments with ease. |
| Safety Features | Heating blocks often include safety features like overheat protection and automatic shutoff mechanisms to prevent accidents and ensure user safety. These features are crucial for preventing equipment damage and potential hazards. |
| Power Source | The power source supplies the necessary electricity to the heating element, enabling the block to reach and maintain the desired temperature levels. Heating blocks can operate using standard electrical outlets or batteries in portable models. |
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a heating block in the context of a microbiology lab?
Answer: A heating block is a specialized device used in the microbiology lab to maintain precise and uniform temperatures for various processes and assays. It plays a crucial role in providing a stable thermal environment, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experimental results.
What is the primary purpose of using a heating block in the microbiology lab?
Answer: The primary purpose of using a heating block is to create and maintain a controlled temperature for specific procedures, such as Bacterial Endotoxin Testing (BET), culture media preparation, enzyme reactions, and other temperature-sensitive assays. By providing consistent thermal conditions, heat blocks optimize the efficiency and accuracy of these laboratory processes.
How does a heating block contribute to Bacterial Endotoxin Testing (BET) in microbiology?
Answer: In Bacterial Endotoxin Testing, heat blocks are essential for precisely controlling the temperature during the reaction between endotoxin-lysate and coagulase. The heat block ensures uniform heating, facilitating accurate detection and quantification of bacterial endotoxins, which are crucial for assessing the safety of pharmaceutical products and medical devices.
What are the advantages of using heating blocks in microbiology experiments?
Answer: Heat blocks offer several advantages in microbiology experiments. They provide precise temperature control, reducing variability and improving the reproducibility of results. The ability to swiftly adjust temperatures also enhances efficiency in time-sensitive assays, saving valuable laboratory time. Additionally, the versatility of heat blocks extends their application beyond BET testing to various other processes in the microbiology lab.
Are there different types of heating blocks available for microbiology applications?
Answer: Yes, there are various types of heat blocks designed for different applications in microbiology. Some heat blocks are specifically tailored for BET testing, featuring multiple wells or vials to accommodate multiple samples simultaneously. Other heat blocks may be used for general laboratory purposes, such as maintaining specific temperatures for enzymatic reactions or incubating bacterial cultures.

How do heating blocks ensure the safety of pharmaceutical products and medical devices?
Answer: Heat blocks play a vital role in BET testing, a critical quality control measure for pharmaceutical products and medical devices. By accurately detecting and quantifying bacterial endotoxins, heat blocks help ensure that these products and devices are free from pyrogenic substances that could trigger harmful immune responses in patients, thus safeguarding their safety and efficacy.
Can heating blocks be used in other scientific disciplines outside of microbiology?
Answer: Yes, heat blocks have applications beyond microbiology and are commonly used in various scientific disciplines. They are employed in chemistry, biochemistry, molecular biology, and other fields where precise temperature control is essential for conducting experiments and assays.
What precautions should be taken while using heating blocks in the microbiology lab?
Answer: When using heat blocks, it is crucial to follow safety guidelines and protocols. Proper calibration and maintenance of the equipment are essential to ensure accurate and reliable temperature control. Users should avoid overheating and regularly check for any signs of malfunction or wear. Additionally, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn to prevent any accidental exposure to heated surfaces during experiments.

