Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in water is a type of impurity. TDS meter is used to the collective measurement of the concentration of all dissolved organic & inorganic substances or molecules present in the water. These substances can include minerals, salts, metals, cations, anions, and other chemical compounds that have dissolved into the water from various sources.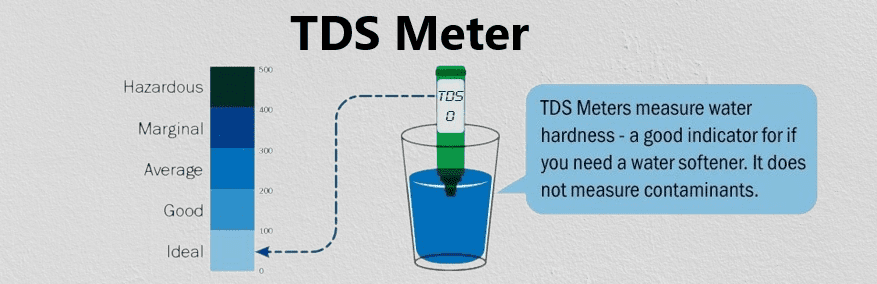
TDS is typically measured in parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per liter (mg/L) and is an essential parameter in water quality assessment. It provides valuable insights into the purity and composition of water, indicating the presence of different dissolved substances that can affect its taste, safety, and suitability for various purposes.
Natural sources, such as mineral-rich aquifers and springs, can contribute to elevated TDS levels in water. Additionally, human activities and pollution can introduce TDS into water bodies through agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and improper waste disposal.

TDS can impact the taste, odor, and appearance of water. High TDS levels might result in a salty or bitter taste and cloudy appearance, making the water less desirable for drinking, cooking, or other domestic uses. Moreover, excessive TDS can also have adverse effects on industrial processes, agricultural irrigation, and aquatic ecosystems.
To ensure water quality and safety, it’s crucial to monitor and regulate TDS levels. Water treatment methods like reverse osmosis and distillation can effectively reduce TDS, improving the water’s taste and overall suitability for consumption and specific applications.
TDS Meter Working Principle:
The working principle of a TDS meter revolves around the concept of electrical conductivity. These ingenious devices are designed to measure the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) in a liquid sample by assessing its ability to conduct electricity. The underlying principle is founded upon the fact that dissolved ions and molecules in water contribute to its electrical conductivity.
The intricacies of the TDS meter’s working principle:
- Conductivity Measurement: TDS meters use a pair of electrodes, typically made of metals like platinum or graphite, that are immersed into the liquid sample. When an electric current is applied between these electrodes, it creates a closed circuit. The presence of dissolved ions and other charged particles in the liquid allows the electric current to flow more easily, increasing the conductivity of the sample.

- Dissolved Solids and Conductivity: The dissolved solids in the liquid, such as salts, minerals, metals, and other ionic compounds, enhance the ability of the liquid to conduct electricity. This is because the charged particles (ions) present in the dissolved solids facilitate the movement of electrons, enabling a higher electrical conductivity.
- Conversion to TDS Value: The TDS meter measures the electrical conductivity of the liquid sample, which is usually displayed as microsiemens per centimeter (μS/cm) or millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm). To obtain the TDS value, the meter uses a conversion factor that relates electrical conductivity to the concentration of dissolved solids.
- Temp. & Calibration Compensation: Before use, TDS meters need to be calibrated using standard solutions of known TDS values to ensure accurate readings. Additionally, temperature can significantly impact the electrical conductivity of the liquid. Therefore, many advanced TDS meters incorporate temperature sensors and offer temperature compensation to provide more precise and reliable TDS measurements across various temperatures.
- Digital Display: The TDS meter processes the electrical conductivity data and displays the corresponding TDS value on a digital screen. Users can easily read and interpret the TDS measurement, allowing for quick assessment of water quality and the presence of dissolved substances.

In summary, the working principle of a TDS meter centers around electrical conductivity. By utilizing a pair of electrodes immersed in the liquid sample, these devices measure the ease with which an electric current passes through the sample. The dissolved solids, consisting of ions and molecules, contribute to the electrical conductivity, allowing the TDS meter to infer the total concentration of dissolved substances. Through accurate calibration and temperature compensation, TDS meters provide valuable insights into water quality, making them indispensable tools in various applications, from monitoring drinking water to assessing industrial processes and environmental studies.
Types of the TDS Meters
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) meters, also known as conductivity meters or salinity meters, come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and environments. These meters are essential tools in water quality assessment and other industries where the measurement of TDS is crucial. Here are some common types of TDS meters:
- Handheld TDS Meters:
- Handheld TDS meters are portable and user-friendly devices commonly used for quick on-site measurements. They consist of a probe attached to a compact electronic unit with a digital display. Users can immerse the probe into the water sample, and the meter will display the TDS reading. Handheld meters are widely used in laboratories, swimming pools, aquariums, and for testing the quality of drinking water.

- Benchtop TDS Meters:
- Benchtop TDS meters are more sophisticated instruments designed for precise and accurate measurements in a laboratory setting. They offer advanced features, such as data logging, temperature compensation, and customizable calibration settings. Benchtop meters are commonly used in research facilities, educational institutions, and industries where precise TDS measurements are required.
- Online/Continuous TDS Meters:
- Online or continuous TDS meters are built for real-time monitoring of TDS levels in a water system or industrial process. These meters are installed directly into pipelines or water treatment systems, providing continuous readings to ensure consistent water quality. Online TDS meters are crucial in water treatment plants, industrial processes, and environmental monitoring systems.
- Pocket TDS Testers:
- Pocket TDS testers are compact and affordable devices ideal for casual users and homeowners. These testers are simple to use, often resembling a pen or small stick with an integrated probe. They are primarily used for basic water quality checks in household applications, such as checking the TDS of tap water or filtered water.
- Multiparameter Water Quality Meters:
- Some advanced water quality meters offer multiparameter capabilities, which include TDS measurement along with other important parameters like pH, temperature, conductivity, and dissolved oxygen. These versatile instruments are valuable in environmental studies, field research, and aquatic ecosystem monitoring.
- Laboratory-grade TDS Meters:
- Laboratory-grade Total Dissolved Solids meters are high-precision instruments used in research, scientific laboratories, and industrial applications where accuracy is paramount. They often feature advanced calibration options, multiple measurement modes, and compatibility with various types of electrodes for specialized measurements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does TDS stand for in TDS meters?
Answer: TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids.
What is the primary function of a TDS meter?
Answer: The primary function of a Total Dissolved Solids meter is to measure the concentration of dissolved solids in a liquid sample.
How does a TDS meter measure the concentration of dissolved solids?
Answer: Total Dissolved Solids meters measure the electrical conductivity of the liquid sample, which is directly related to the concentration of dissolved solids.
What units are commonly used to express TDS measurements?
Answer: TDS measurements are commonly expressed in parts per million (ppm) or milligrams per liter (mg/L).
What types of applications are TDS meters used for?
Answer: Total Dissolved Solids meters are used in various applications, including testing the quality of drinking water, monitoring industrial processes, assessing agricultural irrigation water, and evaluating the health of aquatic ecosystems.
How do you calibrate a TDS meter?
Answer: To calibrate a Total Dissolved Solids meter, you need to use standard calibration solutions with known TDS values. The meter is adjusted to match the TDS value of the calibration solution.
Can TDS meters measure the specific types of dissolved solids present in water?
Answer: No, Total Dissolved Solids meters provide a total measurement of all dissolved substances. They do not differentiate between specific types of dissolved solids.
Do TDS meters require temperature compensation?
Answer: Yes, temperature can affect the electrical conductivity of the liquid, so many Total Dissolved Solids meters offer temperature compensation to provide accurate readings across different temperatures.
What are some factors that can influence TDS measurements?
Answer: Factors that can influence TDS measurements include temperature, the presence of specific dissolved ions, and the level of contamination or impurities in the water.
Can TDS meters be used to assess the safety of drinking water?
Answer: Yes, Total Dissolved Solids meters are commonly used to assess the general quality of drinking water. However, they do not provide information about specific contaminants or pathogens present in the water, so additional testing may be required for a comprehensive analysis of drinking water safety.
(Good Laboratory Practices) GLP in Microbiology Laboratory

