A colony counter is a specialized device used in microbiology laboratories to facilitate the enumeration and analysis of microbial colonies grown on agar plates. It simplifies and automates the process of counting colonies, which are visible clusters of microorganisms that have multiplied and formed distinctly visible spots on the agar surface.
The colony counter typically consists of a digital imaging system that captures high-resolution images of the agar plates. These images are then analyzed using advanced software algorithms designed to accurately identify, count, and measure the colonies.
Type of Colony Counter
Manual Colony Counters:
These are traditional handheld devices equipped with a magnifying lens or grid system. Microbiologists manually count and record the number of colonies visible through the lens or by marking the grid. While manual colony counters offer a basic counting solution, they are more susceptible to human errors and may lack the advanced features of automated systems.
Digital Imaging Colony Counters:
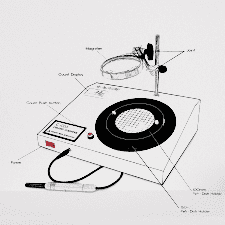
These modern colony counters employ digital imaging technology to capture high-resolution images of agar plates. The images are then analyzed using specialized software that automatically detects and counts colonies based on predefined criteria. Digital imaging colony counters offer improved accuracy and efficiency compared to manual methods, as they eliminate human subjectivity and allow for faster analysis of larger sample sizes.
Automated Colony Counters:
These advanced colony counters utilize robotic systems and sophisticated algorithms to automate the entire colony counting process. They can handle a large number of agar plates, reducing labor-intensive tasks and saving time. Automated colony counters often integrate image capturing, colony detection, counting, and data analysis into a seamless workflow. These systems offer high accuracy, reproducibility, and increased throughput, making them well-suited for high-volume microbiological analysis in pharmaceutical plants.
Image Analysis Software:
In addition to dedicated colony counters, image analysis software can be utilized alongside digital imaging systems to assist with colony counting and analysis. This software allows microbiologists to manually or semi-automatically count colonies by processing the images captured by digital cameras. It provides features such as image enhancement, customizable colony recognition algorithms, and data management capabilities.

The choice of colony counter in pharmaceutical plants depends on factors such as sample volume, required accuracy, throughput, and budget considerations. Each type of colony counter offers its own advantages and limitations, and selection should be based on specific laboratory needs and objectives. It is important for pharmaceutical plants to ensure that the selected colony counter complies with regulatory requirements and provides accurate and reliable results, as microbiological analysis plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and quality of pharmaceutical products
Colony counter principle
The principle of a colony counter is based on the detection and enumeration of microbial colonies grown on agar plates. It involves the use of technology, such as digital imaging or manual counting methods, to accurately determine the number of visible colonies present on the agar surface.
In the case of digital imaging colony counters, the principle involves capturing high-resolution images of agar plates using a digital camera or imaging system. These images are then processed and analyzed using specialized software algorithms. The software applies image processing techniques to enhance the visibility of colonies and differentiate them from other artifacts or background elements on the plate.
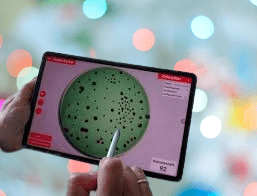
The software employs predefined criteria to detect and identify colonies based on their size, shape, color, or other characteristics. Once the colonies are identified, the software counts them automatically and provides the user with the final colony count. Some advanced systems may offer additional features, such as the ability to measure colony size or calculate other statistical parameters.
For manual colony counters, the principle involves visual inspection of the agar plates through magnifying lenses or grids. The microbiologist manually counts the visible colonies by observing the agar surface and recording the count either directly or by marking the colonies on a grid. This method requires careful attention to detail and may be more prone to human errors or subjectivity.
The principle underlying both digital imaging and manual colony counters is to provide an efficient and accurate means of quantifying microbial colonies. The technology aims to streamline the process, improve accuracy, and reduce the time and effort required for colony enumeration compared to traditional manual counting methods.
By utilizing the principle of colony counting, pharmaceutical plants and other microbiology laboratories can effectively monitor microbial growth, assess the quality of products or environmental samples, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. The accurate determination of colony counts is crucial for making informed decisions, implementing corrective actions, and maintaining the safety and integrity of pharmaceuticals and related products.
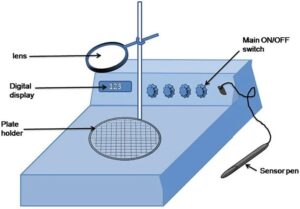
Parts of the colony counter
| Part/Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Base | Provides stability and support for the colony counter. |
| Illumination Source | Light source positioned beneath the agar plate for colony visibility. |
| Stage/Plate Holder | Processes images, identify colonies, and provides data analysis. |
| Magnifying Lens/Imaging System | Securely holds the agar plate in place during the counting. |
| Display | Shows the colony count or other relevant information. |
| Controls | User interface elements for adjusting counting parameters. |
| Software (for digital colony countrs) | Processes images, identify colonies and provides data analysis. |
| Power Source | Processes images, identify colonies, and provides data analysis. |
| Optional Accessories | Additional features or attachments, e.g., grid overlays. |
Colony counter diagram
Applications of the colony counter
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Microbial Colony Enumeration | Accurate counting and quantification of microbial colonies on agar plates for various research purposes. |
| Quality Control and Assurance | Monitoring and assessing microbial growth in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries. |
| Environmental Monitoring | Analyzing and monitoring microbial contamination in air, water, soil, and other environmental samples. |
| Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing | Assisting in determining the effectiveness of antibiotics against specific microbial strains. |
| Microbiological Research | Supporting scientific investigations and experiments related to microbiology and microbial ecology. |
| Veterinary Diagnostics | Assessing microbial growth and identifying pathogens in veterinary samples for disease diagnosis. |
| Food Safety and Hygiene | Detecting and quantifying microbial contamination in food samples, ensuring safety and quality. |
| Water and Wastewater Analysis | Monitoring and assessing microbial populations in water sources and wastewater treatment processes. |
| Pharmaceutical Development | Evaluating the efficacy of antimicrobial agents and studying the growth characteristics of microorganisms. |
| Epidemiological Studies | Investigating the spread and prevalence of infectious diseases through colony analysis. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a colony counter?
Answer: A colony countr is a device or software used to accurately count and analyze microbial colonies on agar plates.
How does a digital imaging colony counter work?
Answer: A digital imaging colony countr captures high-resolution images of agar plates and uses specialized software to automatically detect and count colonies based on predefined criteria.
What are the advantages of using a digital imaging colony counter?

Answer: The advantages include increased accuracy, faster analysis, elimination of human subjectivity, and the ability to handle larger sample sizes.
How does a manual colony counter work?
Answer: A manual colony countr typically consists of a magnifying lens or grid system, allowing microbiologists to visually count and record the number of colonies on agar plates.
What are the limitations of manual colony counting?
Answer: Manual counting can be subjective and prone to human errors, and it may be less efficient for high-volume analysis compared to digital methods.
What are some key features to consider when selecting a colony counter?
Answer: Considerations include counting accuracy, ease of use, compatibility with different plate sizes, data management capabilities, and integration with laboratory workflows.
Can a colony counter differentiate between different types of colonies?
Answer: Some advanced colony countrs and software systems can differentiate colonies based on size, shape, color, or other characteristics, providing additional analysis capabilities.
Can a colony counter measure the size of individual colonies?
Answer: Yes, certain colony countrs offer the ability to measure colony size, providing valuable data for research or quality control purposes.
How is the accuracy of a colony counter determined?
Answer: The accuracy is typically assessed by comparing the colony count obtained using the colony countr with manual counting by multiple trained microbiologists.
Can a colony counter handle different agar plate sizes?
Answer: Many colony countrs offer adjustable plate holders or grids to accommodate various plate sizes commonly used in microbiology labs.
Can a colony counter store and export data?
Answer: Yes, most modern colony countrs have data storage capabilities and allow for exporting data in various formats for further analysis or documentation.
Is it possible to integrate a colony counter with other laboratory equipment or software?
Answer: Yes, some colony countrs offer integration capabilities with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) or other software for seamless data transfer and analysis.
How often should a colony counter be calibrated?
Answer: Calibration frequency depends on the manufacturer’s recommendations and laboratory quality control procedures, but it is typically done annually or as specified by the manufacturer.
Can a colony counter be used for counting colonies on selective or differential media?
Answer: Yes, colony counters can be used for counting colonies on various types of media, including selective or differential media.
Are colony counters suitable for high-throughput analysis?
Answer: Yes, automated and digital colony countrs are particularly well-suited for high-throughput analysis, as they offer faster and more efficient colony enumeration compared to manual methods.

Great insights on the Colony Counter 2023! I found the comparison between different models particularly helpful. It’s always a challenge to determine which features are truly essential. Looking forward to more updates on advancements in this area!