Lab refrigerators play a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry, where stringent temperature control and storage conditions are essential for preserving the integrity and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. These specialized refrigerators provide a controlled environment that ensures the stability and longevity of various pharmaceutical materials, including medications, vaccines, biological samples, and sensitive chemicals.
Pharmaceutical laboratory refrigerators are designed with specific features to meet the unique requirements of the pharmaceutical industry. Here are some key aspects:
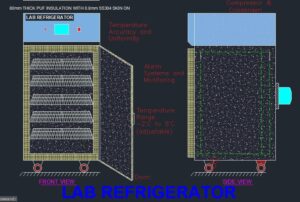
- Temperature Accuracy and Uniformity: Precise temperature control is vital in pharmaceutical storage. Lab refrigerators used in pharmaceuticals typically offer a narrow temperature range, such as 2°C to 8°C, which is suitable for preserving most medications and vaccines. These refrigerators employ advanced temperature control systems to maintain consistent and accurate temperatures throughout the storage compartment, minimizing temperature fluctuations that could compromise the quality of pharmaceutical products.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Pharmaceutical lab refrigerators adhere to strict regulatory guidelines, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Storage Practices (GSP). These standards ensure that pharmaceutical products are stored under appropriate conditions, maintaining their stability and efficacy. The refrigerators may be designed with features like temperature monitoring, data logging capabilities, and alarm systems to comply with these regulations.
- Secure Storage and Access Control: Lab refrigerators used in pharmaceuticals are equipped with robust security features. This includes secure locking mechanisms, access control systems, and audit trails to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of stored pharmaceutical products. Controlled access helps maintain a strict chain of custody and minimizes the risk of tampering or contamination.
- Alarm Systems and Monitoring: To safeguard pharmaceutical materials, lab refrigerators incorporate alarm systems that alert personnel in case of temperature deviations, power failures, or door openings. These alarms help ensure timely intervention to mitigate any risks to the stored pharmaceutical products. Additionally, some refrigerators may have monitoring capabilities, allowing remote monitoring of temperature and other critical parameters.
- Storage Capacity and Organization: Pharmaceutical Lab refrigerators come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate the storage needs of different pharmaceutical facilities. They are designed with adjustable shelves, compartments, and storage options to maximize space utilization and facilitate the proper organization of pharmaceutical products. This enables efficient storage and easy retrieval of medications and vaccines.
Components of Lab Refrigerators
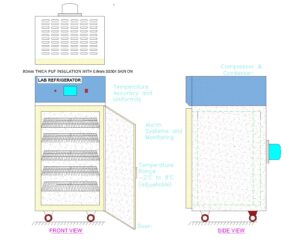
- Compressor: The compressor is the heart of the refrigeration system and is responsible for circulating refrigerant and maintaining the desired temperature inside the refrigerator.
- Condenser: The condenser facilitates heat transfer by converting high-pressure refrigerant vapor into a high-pressure liquid, releasing heat in the process.
- Evaporator: The evaporator helps cool the interior of the refrigerator by absorbing heat from the stored materials and converting the liquid refrigerant into a vapor.
- Expansion Valve: The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, allowing it to expand and cool down.
- Temperature Control System: This system monitors and controls the internal temperature of the refrigerator, ensuring it remains within the desired range.
- Insulation: Insulation materials line the walls and doors of the refrigerator, minimizing heat transfer between the internal and external environment.
- Shelving: Lab refrigerators feature adjustable shelves or storage compartments to accommodate various sizes of containers and facilitate organized storage.
- Door: The refrigerator door provides access to the interior and is often equipped with a sealing gasket to maintain a tight seal when closed.
- Alarm System: Some Lab refrigerators come with built-in alarm systems that alert users in the event of temperature deviations, power failures, or door openings, helping to protect stored materials.
- Lighting: Interior lighting allows users to easily view and locate stored items within the refrigerator.
- Control Panel: The control panel houses the temperature control settings and may include additional features such as alarm settings and temperature display.
- Air Circulation System: Lab refrigerators often incorporate a fan or air circulation system to ensure uniform cooling and temperature distribution throughout the storage compartment.
- Drainage System: In refrigerators with automatic defrosting capabilities, a drainage system collects and removes excess water resulting from the defrosting process.
Technical Specifications of Laboratory Refrigerators
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -2°C to 8°C (adjustable) |
| Cooling Mechanism | Forced air circulation or fan-assisted cooling |
| Temperature Control | Digital or analog control systems |
| Capacity | Various sizes, ranging from XX liters to XX liters |
| Door Type | Solid door or glass door |
| Locking Mechanism | Key lock or electronic lock |
| Shelves | Adjustable shelves or storage compartments |
| Alarm System | Various sizes are available, ranging from XX liters to XX liters |
| Energy Efficiency | High-quality insulation and efficient compressor |
| Defrosting Mechanism | Automatic or manual defrosting |
| Exterior Material | Stainless steel or durable coated steel |
| Power Supply | Standard electrical outlet (AC) |
Quality Control Laboratory
GA drawing for Lab Refrigerator
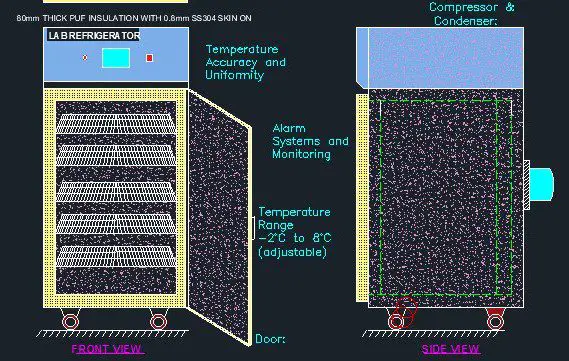
Applications of Laboratory Refrigerators
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Storage | Lab refrigerators are used to store medications, vaccines, and other pharmaceutical products at controlled temperatures to maintain their stability and efficacy. |
| Biological / Microbiological Samples | Lab refrigerators are utilized to store biological samples, such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and cell cultures, at specific temperatures to prevent degradation and preserve their integrity for research and diagnostic purposes. |
| Chemical Reagents | Lab refrigerators provide a controlled environment for storing chemical reagents, ensuring their stability and minimizing the risk of chemical reactions or degradation that could affect experimental outcomes. |
| Clinical Trials | Refrigerators are used in clinical trial settings to store investigational drugs and specimens collected from study participants, adhering to regulatory requirements and maintaining sample integrity for analysis. |
| Forensic Storage | Refrigerators play a crucial role in forensic science by providing appropriate temperature-controlled storage for biological samples, DNA evidence, and toxicological samples, ensuring their integrity and viability for forensic analysis. |
| Food and Beverage | Refrigerators are employed in food and beverage industries for quality control and shelf-life studies. They help store perishable food samples, beverages, and ingredients at specific temperatures to maintain freshness, prevent spoilage, and preserve product quality. |
| Environmental Testing | Industrial Refrigerators are used in environmental testing laboratories to store samples, such as water, soil, and air samples, at controlled temperatures to preserve their integrity and prevent contamination before analysis. |
| Research Laboratories | Industrial refrigerators find extensive use in various research settings, including biology, chemistry, and medical laboratories, for storing samples, specimens, chemicals, and reagents at specific temperatures to support ongoing experiments and studies. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the temperature range typically offered by laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Industrial refrigerators typically offer a temperature range of -2°C to 8°C, which is suitable for preserving a wide range of sensitive materials.
How is temperature control achieved in laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Temperature control in Industrial refrigerators is achieved through advanced control systems that regulate the operation of the compressor and cooling mechanisms, maintaining the desired temperature set by the user.
What cooling mechanism is commonly used in laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Laboratory Industrial refrigerators often utilize forced air circulation or fan-assisted cooling to ensure uniform temperature distribution and optimal cooling performance within the storage compartment.
How do laboratory refrigerators ensure temperature uniformity throughout the storage compartment?
Answer: Laboratory Industrial refrigerators employ internal fans or air circulation systems that promote even distribution of cool air, minimizing temperature variations and ensuring uniform cooling across all areas of the storage compartment.
What security features are commonly found in laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Laboratory refrigerators typically have sturdy doors with reliable locking mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. Some models may also include alarm systems that alert users in case of temperature deviations, power failures, or door openings.
What is the defrosting mechanism used in laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Laboratory refrigerators may have either automatic or manual defrosting mechanisms. Automatic defrosting systems periodically remove ice buildup to maintain optimal cooling efficiency, while manual defrosting requires users to manually remove ice and frost buildup as needed.
How is energy efficiency achieved in laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Energy efficiency in laboratory refrigerators is achieved through features like high-quality insulation, efficient compressors, and LED lighting. These elements help minimize energy consumption while maintaining the desired temperature inside the refrigerator.
What capacity options are available for laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Laboratory refrigerators come in various capacity options, ranging from smaller units with capacities of around 100 liters to larger models with capacities exceeding 1000 liters. The choice depends on the specific storage needs of the laboratory.
Can laboratory refrigerators be monitored remotely?
Answer: Some laboratory refrigerators offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing users to monitor temperature, alarms, and other critical parameters through a computer or mobile device. This feature enhances convenience and provides real-time updates on storage conditions.
What are the considerations for maintenance and calibration of laboratory refrigerators?
Answer: Regular maintenance, including cleaning, defrosting, and inspection of seals and gaskets, is crucial for the optimal performance of laboratory refrigerators. Calibration should be performed periodically to ensure accurate temperature control and compliance with regulatory standards.

