Mass mixers play a critical role in the pharmaceutical industry, where precision and uniformity are of utmost importance. These versatile machines are extensively utilized for blending powders, ensuring consistent distribution of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients.
Let’s explore the significance of mass mixers in pharmaceutical applications:
- Tablet Production: Mass mixers are integral to tablet manufacturing processes. They facilitate the homogenous blending of APIs, excipients, disintegrants, lubricants, and other ingredients required for tablet formulation. Through efficient blending, mass mixers ensure uniform distribution of the components, resulting in tablets with consistent drug content and optimal dissolution characteristics.
- Capsule Formulation: In the production of capsules, mass mixers are employed to achieve a homogeneous mixture of powdered APIs and other formulation ingredients. By ensuring the uniform distribution of the active ingredients within the blend, mass mixers help maintain consistent dosage strength and enhance the efficacy of the capsules.
- Granulation: Mass mixers find application in wet granulation processes, which are commonly employed in pharmaceutical manufacturing. During wet granulation, the mass mixer facilitates the blending of APIs and excipients with a liquid binder, forming granules of uniform size. The uniformity achieved by the mass mixer ensures consistent drug content in each granule, contributing to the overall quality of the final product.
- Powder Blending: Mass mixers are also used for the blending of dry powders, allowing the combination of multiple powdered ingredients to create a homogeneous mixture. This is particularly useful for manufacturing specialized dosage forms, such as powder-filled sachets or orally disintegrating powders, where the uniform distribution of ingredients is crucial for dosing accuracy and patient convenience.
- Quality Control: Mass mixers play a vital role in quality control processes within pharmaceutical manufacturing. By ensuring uniform blending, these machines contribute to the consistency and reproducibility of drug products. They enable pharmaceutical companies to meet stringent regulatory requirements and maintain product efficacy and safety.
The utilization of mass mixers in pharmaceutical applications is driven by the need for precise blending, uniform distribution of ingredients, and overall product quality. These machines enhance process efficiency, reduce batch-to-batch variations, and contribute to the production of pharmaceutical products that meet the highest standards of efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction.
Working Principle of Mass Mixer
The working principle of a mass mixer unveils a captivating interplay of intricate movements and precise mechanisms. This ingenious machine operates on the principle of convection, transcending the boundaries of conventional mechanical mixing techniques.

At its core, a mass mixer employs a diverse array of components, including rotating blades, baffles, and choppers, to orchestrate a mesmerizing dance of powders. The process begins with the introduction of powders into the mixer, where they become enveloped in the whirlwind of complexity.
As the blades rotate, they create a vortex-like motion, generating a convection current within the mixer. This convective flow facilitates the intermingling of the powders, ensuring a thorough blending process. The baffles strategically positioned in the mixer further enhance the chaotic movement of the powders, promoting their intimate contact and preventing the formation of dead zones.
To further intensify the blending, choppers may be incorporated into the mass mixer. These choppers function as additional agitation elements, imparting a chopping action to the powders. This chopping motion aids in breaking down any agglomerates or lumps, ensuring a finer and more uniform blend.
The duration of the blending process is carefully controlled to strike a delicate balance between thorough mixing and maintaining the integrity of the powders. This control allows for the desired level of blending complexity and ensures that the resulting mixture achieves the desired uniformity.
Mass Mixer Design
When it comes to the design of a mass mixer, careful consideration is given to various elements to ensure optimal functionality and efficient blending of powders. The design of this ingenious machine encompasses several key aspects that contribute to its effectiveness and versatility.
- Structure and Construction:
- Mass mixers are typically constructed using high-quality stainless steel, known for its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. The robust structure provides stability and withstands the forces exerted during the blending process. The interior surfaces are often polished to prevent powder adherence and facilitate easy cleaning, ensuring hygienic operation.
- Mixing Chamber:
- The mixing chamber is the heart of the mass mixer. It is designed to accommodate the desired batch size of powders. The shape and size of the chamber may vary depending on the specific application and production requirements. The geometry of the chamber is carefully engineered to promote efficient movement of powders and prevent the formation of dead zones, ensuring uniform blending.
Mass mixer diagram
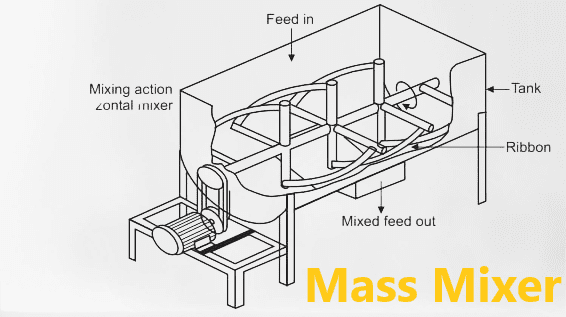
- Blades and Agitation Elements:
- The design of the blades plays a crucial role in the blending process. The blades are strategically positioned and designed to generate an intense convection current within the mixing chamber. This convective flow facilitates the thorough intermingling of powders, promoting homogeneity. The number, shape, and orientation of the blades are optimized to ensure effective powder movement and prevent particle segregation.
- Drive Mechanism:
- The drive mechanism is responsible for powering the rotation of the mixing blades. It consists of a motor and a power transmission system. The motor is selected based on the required speed and torque, considering the characteristics of the powders being blended. The power transmission system efficiently transfers the power from the motor to the mixing blades, ensuring smooth and consistent rotation.
- Controls and Safety Features:
- Modern mass mixers are equipped with advanced control systems that allow operators to adjust parameters such as mixing speed and duration. These controls enhance process flexibility and enable customization based on specific powder characteristics and blending requirements. Additionally, safety features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and interlocking mechanisms are integrated to ensure operator safety and prevent accidents.
Technical calculations & key critical points of mass mixture
| Technical Calculations | Key Critical Points |
|---|---|
| Capacity | – Determine the required batch size to meet production demands effectively. |
| Mixing Time | – Calculate the optimal duration for achieving the desired blend uniformity while considering the characteristics of the powders being mixed. |
| Mixing Speed | – Determine the appropriate rotational speed of the mixing blades based on the powder properties and desired blending efficiency. |
| Power Requirements | – Calculate the power needed to drive the motor based on the mixing load, rotational speed, and equipment efficiency. |
| Blade Design | – Optimize the number, shape, and orientation of the blades to ensure efficient powder movement and prevent particle segregation. |
| Chamber Geometry | – Design the mixing chamber with consideration for preventing dead zones and ensuring uniform powder flow. |
| Energy Consumption | – Determine the appropriate rotational speed of the mixing blades based on the powder properties and desired to blend efficiency. |
| Particle Size Distribution | – Analyze the particle size distribution of the powders before and after blending to evaluate the mixing effectiveness. |
| Homogeneity | – Evaluate the uniformity of the mixture using statistical techniques or sampling methods to ensure consistent product quality. |
| Cleaning and Hygiene | – Design the mass mixer to facilitate easy cleaning, prevent cross-contamination, and adhere to hygiene standards. |
| Safety Measures | – Incorporate safety features, such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and interlocking mechanisms, to ensure operator safety during operation. |
Mass mixer specifications
- Capacity: Mass mixers come in various capacities, ranging from small-scale laboratory models to large-scale industrial units. The capacity is usually measured in terms of the maximum volume or weight of powders that can be accommodated in a single batch.
- Mixing Speed: The mixing speed refers to the rotational speed of the mixing blades within the mass mixer. It is typically adjustable to accommodate different types of powders and achieve the desired blending efficiency.
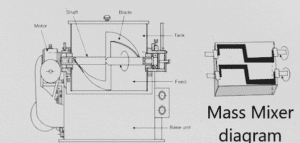
- Motor Power: The motor power specifies the electrical power required to drive the mixing blades. It is determined based on factors such as the volume of the mixture, the characteristics of the powders being blended, and the desired mixing speed.
- Construction Material: Mass mixers are predominantly constructed using stainless steel due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. The quality of stainless steel used can vary, with higher-grade materials being more suitable for demanding applications.
- Control System: Modern mass mixers are equipped with advanced control systems that allow operators to adjust parameters such as mixing speed and duration. These systems offer flexibility and precision in controlling the blending process.
- Safety Features: Mass mixers incorporate safety features to ensure operator safety during operation. These features may include emergency stop buttons, overload protection, interlocking mechanisms, and safety guards to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Mass mixers are designed to facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. Smooth and polished interior surfaces, detachable components, and easy access to critical areas enhance the cleaning process and reduce downtime.
- Certification and Compliance: Depending on the industry and specific requirements, mass mixers may need to comply with relevant regulations and certifications, such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or other industry-specific standards.
It is important to note that specific specifications may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and intended application of the mass mixer. Therefore, it is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or contact them directly for detailed specifications specific to a particular mass mixer model.
Applications of Mass mixer
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Mass mixers are extensively used in the pharmaceutical industry for blending powders to produce tablets, capsules, and other dosage forms. They ensure uniform distribution of active ingredients and excipients, enhancing product quality and consistency. |
| Food Processing | Mass mixers find application in the food processing industry for mixing ingredients in the production of various food products, such as bakery items, confectionery, spices, and seasonings. They enable efficient and homogeneous blending, improving the overall quality and taste of the final products. |
| Chemical Processing | Mass mixers find applications in the food processing industry for mixing ingredients in the production of various food products, such as bakery items, confectionery, spices, and seasonings. They enable efficient and homogeneous blending, improving the overall quality and taste of the final products. |
| Cosmetics | Mass mixers play a vital role in the cosmetics industry for blending ingredients in the formulation of creams, lotions, ointments, and other cosmetic products. They ensure the proper dispersion of pigments, emulsification of ingredients, and uniform distribution of additives, enhancing product consistency and appearance. |
| Nutraceuticals | In the chemical industry, Mass mixtuer machines are employed for blending different powders or granules to create homogeneous mixtures for chemical reactions, catalyst preparations, and the production of specialty chemicals. They ensure precise and uniform distribution of ingredients, optimizing process efficiency and product quality. |
| Veterinary | In the veterinary sector, Mass mixtuer machine are used to blend powdered medications for animal health applications. They ensure precise and homogeneous mixing of active pharmaceutical ingredients, facilitating accurate dosing and improving the palatability of veterinary medicines. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a mass mixer?
Answer: A Mass mixtuer machineis a machine used in the pharmaceutical industry for blending powders and granules to achieve a uniform mixture of ingredients.

How does a mass mixer work?
Answer: A Mass mixtuer machine works by utilizing rotating blades or agitators to create a convection current within the mixing chamber, promoting the intermingling and blending of powders.
What are the main components of a mass mixer?
Answer: The main components of a Mass mixtuer machine include the mixing chamber, blades or agitators, drive mechanism, control panel, and safety features.
What is the purpose of baffles in a mass mixer?
Answer: Baffles are strategically positioned in a Mass mixtuer machine to enhance the chaotic movement of powders, prevent dead zones, and promote efficient blending.
What is the role of choppers in a mass mixer?
Answer: Choppers in a Mass mixtuer machine function as additional agitation elements that break down agglomerates and improve the uniformity of the mixture.
How is the mixing speed adjusted in a mass mixer?
Answer: The mixing speed in a Mass mixtuer machine is typically adjustable using a control panel, allowing operators to set the desired rotational speed of the blades.
What are the factors to consider when selecting a mass mixer for a pharmaceutical application?
Answer: Factors to consider include the desired capacity, mixing speed range, motor power, construction material, and compliance with regulatory standards.
How is the cleaning process performed in a mass mixer?
Answer: The cleaning process typically involves disassembling the removable components, manually cleaning them, and ensuring thorough removal of any residual powders or residues.
What are some safety features incorporated in mass mixers?
Answer: Safety features may include emergency stop buttons, overload protection, interlocking mechanisms, safety guards, and warning indicators.
How is the blending homogeneity assessed in a mass mixer?
Answer: Blending homogeneity can be assessed by sampling the mixture and performing tests such as sieve analysis or content uniformity testing.
What are the considerations for selecting the appropriate mass mixer for granulation processes?
Answer: Considerations include the desired batch size, wet or dry granulation requirements, suitability for the specific formulation, and ease of cleaning for product changeovers.
How is the energy consumption of a mass mixer calculated?
Answer: The energy consumption of a Mass mixtuer machine can be calculated by multiplying the motor power rating by the blending time and taking into account the efficiency of the equipment.
Can a mass mixer handle heat-sensitive materials?
Answer: Yes, certain Mass mixtuer machine are designed to handle heat-sensitive materials by incorporating features such as jacketed mixing chambers for temperature control.
How can mass mixers contribute to process efficiency in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: Mass mixtuer machine ensure consistent blending, reduce batch-to-batch variations, and enhance overall production efficiency by achieving uniform mixtures of pharmaceutical ingredients.
What are some maintenance practices for mass mixers?
Answer: Maintenance practices may include regular lubrication of moving parts, inspection and replacement of worn components, calibration of controls, and periodic cleaning to prevent product contamination.
