The significance of Spore Staining in the microbiology laboratory is multifaceted, playing a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of endospores and providing invaluable insights into the world of bacteria. Spore staining, an invaluable technique in the microbiology laboratory, offers a fascinating glimpse into the world of endospores, nature’s enigmatic microbial fortresses. This technique holds immense importance for researchers and healthcare professionals alike, as it offers a deeper understanding of microbial survival strategies and helps in various practical applications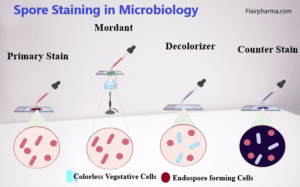
- Identification of Endospores: Endospores are highly resilient and dormant structures formed by certain bacteria to withstand unfavorable environmental conditions. Spore staining allows microbiologists to distinguish these endospores from vegetative cells, aiding in the identification and characterization of specific bacterial species. This knowledge is essential for diagnosing infectious diseases and determining appropriate treatment strategies.
- Study of Bacterial Survival Mechanisms: Endospore formation is a remarkable survival mechanism exhibited by some bacterial species. By staining and examining endospores, scientists can gain valuable insights into the conditions and triggers that lead to spore formation. Understanding these survival mechanisms can help in developing strategies to control bacterial infections and prevent disease outbreaks.

- Quality Control in Food and Pharmaceutical Industries: Endospores, particularly those of certain pathogenic bacteria, can be a concern in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Spore staining is instrumental in detecting and quantifying spores in food products and pharmaceutical preparations. This enables companies to maintain strict quality control measures, ensuring the safety and efficacy of their products.
- Environmental and Biotechnological Applications: Endospores are naturally present in the environment, and their study is essential for monitoring and assessing environmental contamination and microbial diversity. In biotechnological applications, spore staining aids in the identification and selection of bacteria that possess specific desirable characteristics, such as the ability to produce enzymes or metabolites of interest.
- Research and Fundamental Microbiology: Spore staining is an indispensable tool in microbiological research. It allows scientists to investigate various aspects of endospore biology, including germination, sporulation kinetics, and resistance to physical and chemical agents. Such research not only deepens our understanding of bacterial physiology but also contributes to the development of new antimicrobial strategies.
- Epidemiological Studies: In epidemiology, understanding the prevalence and distribution of bacterial pathogens is vital for disease surveillance and control. Spore staining helps in tracking the presence of spore-forming bacteria in clinical and environmental samples, aiding in the investigation of disease outbreaks and the implementation of targeted control measures.
The procedure for Spore Staining.
- SCOPE
- This SOP shall be applicable for Spore Staining in the Microbiology laboratory.
- RESPONSIBILITY
- Microbiology Personnel shall be responsible for carrying out the established procedure and maintaining its records.Officer Microbiology or above who is trained and well versed with the procedure shall be responsible for ensuring that the procedure is carried out correctly and checking documents for completeness of the content.
- Head – Microbiology/ Designee shall be responsible for the compliance of the SOP.
- ACCOUNTABILITY
- Head – Microbiology/ Designee shall be accountable for the proper implementation of the SOP.

- PROCEDURE
- Precautions:
- Wear a nose mask and gloves before performing the staining.
- This process is for in vitro diagnostic use only and it is to be used adequately by a qualified microbiology person.
- Proper disposal procedures are to be followed after the completion of testing.
- Sterilize all biohazard waste before disposal.
- Requirements:
- 5% aqueous solution of malachite green
- Safranin (counter stain)
- Purified Water
- Microscope
- Methodology:
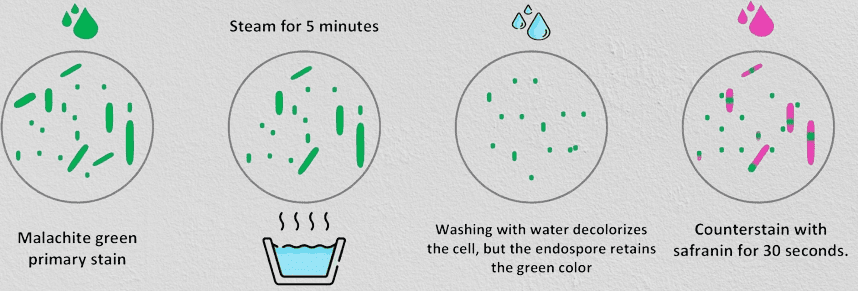
- Prepare a smear of the isolated pure culture in the culture handling room.
- Dry the smear in the air and fix it with heat.
- Place the slide on a small beaker, containing boiling water, kept on the hot plate.
- Cover the smear with a small piece of filter paper; keep the filter paper saturated with a 5% aqueous solution of malachite green for about 30 minutes.
- Wash the slide gently with water.
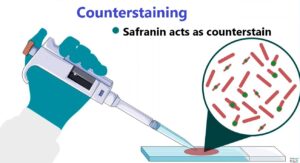
- Counter stain with safranin for 30 seconds.
- Wash the slide with water and blot dry with Whattman filter paper.
- Observe the slide under a microscope 100X using immersion oil.
- The spores are stained green whereas the vegetative cells are stained pink.
- Observe the location of the spore within the cell (e.g. central spore, sub-terminal spore, terminal spore with swollen sporangium).
- Precautions:
- ABBREVIATIONS
- SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
- MB : Microbiology
- % : Percentage
- ANNEXURES
- Annexure-I : Spore Staining Report
SPORE STAINING REPORT
| Type of Sample | Batch No. / A.R. No. | ||
| Date | Microscope ID | ||
| Area | Sample |
| Colony Characters on Agar plate (Sub-culture if the growth medium is broth) | ||
| Colony Characteristics | Observation | |
| Color | ||
| Shape | Punctiform Circular Rhizoid Irregular Filamentous | |
| Pigmentation | Pigmented/ Non-pigmented | |
| Opacity | Opaque/ Transparent | |
| Elevation | ||
| Surface | Smooth/ Rough/ Wrinkled/ Dry/ Sticky | |
| Margin | Entire Undulate Lobate Filamentous Curled | |
| Microscopic observation | ||
| Test | Observation | |
| Cell shape | Cocci/ Bacilli/ Coco bacilli | |
| Spore Staining | Green Colored cells/ Pink colored cells | |
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is Spore Staining in the microbiology laboratory?
Answer: Spore staining is a specialized staining technique used to differentiate endospores, dormant and resilient structures formed by certain bacteria, from vegetative cells. It is a valuable tool for studying bacterial survival mechanisms and identifying specific bacterial species.
Why is Spore Staining important in microbiology?
Answer: Spore staining is crucial in microbiology as it allows researchers to distinguish endospores from vegetative cells, providing insights into bacterial survival strategies, aiding in disease diagnosis, and facilitating research on fundamental microbiological processes.
How is Spore Staining performed?
Answer: Spore staining involves several steps. A bacterial smear is prepared on a glass slide, heat-fixed to secure the cells. Malachite green, the primary stain, is applied and heat is used to facilitate stain penetration. After rinsing and decolorization, the slide is counterstained with safranin to visualize endospores and vegetative cells under a microscope.
What is the purpose of using Malachite Green in Spore Staining?
Answer: Malachite green is the primary stain in spore staining. It imparts a vibrant green color to the bacterial cells, effectively staining endospores. The stain’s unique characteristics and the heat treatment help it penetrate the tough cell walls of endospores, revealing their presence.
How are endospores different from vegetative cells?
Answer: Endospores and vegetative cells are two distinct stages of certain bacterial species. Endospores are dormant, highly resistant structures formed under adverse conditions, whereas vegetative cells are metabolically active and actively growing bacteria.
What information can be gained from Spore Staining?
Answer: Spore staining provides valuable information about bacterial survival mechanisms, the presence of specific bacterial species, and the distribution of endospores in various samples. It aids in diagnosing infectious diseases, assessing environmental contamination, and conducting epidemiological studies.
How is Spore Staining applied in practical settings?
Answer: Spore staining finds applications in healthcare for diagnosing infectious diseases, in the food and pharmaceutical industries for quality control, in environmental studies for monitoring microbial diversity, and in biotechnology for selecting bacteria with desired characteristics.
Why is it essential to study endospores in microbiology?
Answer: Studying endospores is vital in understanding bacterial resilience and survival strategies. Endospores’ ability to withstand harsh conditions makes them a significant concern in various fields, such as medicine, industry, and environmental monitoring.
What are the benefits of Spore Staining in epidemiological studies?
Answer: Spore staining assists in epidemiological studies by allowing researchers to track the presence of spore-forming bacteria in clinical and environmental samples. This information is critical for investigating disease outbreaks and implementing targeted control measures.
How does Spore Staining contribute to biotechnological research?
Answer: In biotechnological applications, spore staining aids in identifying and selecting bacteria with specific desirable characteristics, such as the production of enzymes or metabolites of interest. This helps in advancing biotechnological processes and applications.
Can Spore Staining be used to identify specific bacterial species?
Answer: Yes, Spore Staining is an effective method for identifying certain bacterial species that are capable of forming endospores. The presence of endospores in the stained sample can help narrow down the potential bacterial species and aid in their accurate identification.
How does the process of heat fixation contribute to Spore Staining?
Answer: Heat fixation plays a crucial role in Spore Staining by securing the bacterial cells to the glass slide. This process not only preserves the natural arrangement of cells for microscopic examination but also enhances cellular permeability, allowing the subsequent staining agents to penetrate the cells effectively.
What are the advantages of using Safranin as the counterstain in Spore Staining?
Answer: Safranin serves as the counterstain in Spore Staining due to its brilliant crimson color, which provides a striking contrast to the green-stained endospores. This contrast allows researchers to distinguish between endospores and vegetative cells easily, facilitating accurate observations under the microscope.
Can Spore Staining be used to assess the effectiveness of sterilization processes?
Answer: Yes, Spore Staining can be utilized to assess the effectiveness of sterilization processes in various industries, such as healthcare and food production. Endospores, being highly resistant, act as biological indicators to evaluate the success of sterilization methods.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with Spore Staining?
Answer: One limitation of Spore Stain is that it can only identify endospore-forming bacteria and may not provide information about other types of bacteria. Additionally, interpreting spore staining results requires expertise, as false positives or negatives can occur if the staining process is not conducted accurately.
How does Spore Staining contribute to the overall understanding of bacterial life cycles and survival strategies?
Answer: Spore Stain provides critical insights into the life cycles and survival strategies of bacteria, especially those capable of forming endospores. By studying the formation, germination, and behavior of endospores, researchers gain a deeper understanding of bacterial adaptation to harsh environmental conditions, which is essential for diverse applications, including healthcare, agriculture, and environmental management.

2 thoughts on “SOP for Spore Staining Strategy in Microbiology 2023”