Types of Biological indicators (BIs) play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical industry by ensuring the effectiveness of sterilization processes. They are used to validate the sterility of equipment, medical instruments, and pharmaceutical products. These indicators contain known populations of highly resistant microorganisms to assess whether sterilization procedures meet regulatory standards.
Sterility is a cornerstone of pharmaceutical manufacturing, where even the slightest microbial contamination can compromise product safety and efficacy. To ensure stringent sterilization standards, biological indicators (BIs) serve as critical validation tools. These indicators contain highly resistant microorganisms designed to assess the effectiveness of sterilization processes in pharmaceutical settings.
Unlike chemical indicators, which only measure physical parameters like temperature and pressure, biological indicators provide direct proof of microbial inactivation. By incorporating spore-forming bacteria with known resistance levels, BIs help pharmaceutical industries confirm that sterilization methods—such as steam, dry heat, ethylene oxide, radiation, and hydrogen peroxide—meet regulatory standards.
In this highly regulated industry, biological indicators act as microbial sentinels, detecting potential failures in sterilization protocols. Their precise application and interpretation not only safeguard patient health but also uphold the integrity of pharmaceutical production worldwide.
Types of Biological Indicators in Pharmaceuticals
Biological indicators in the pharmaceutical industry are classified based on the sterilization methods they validate:

Properties of Biological Indicators in Pharmaceuticals
Biological indicators must possess specific properties to ensure their reliability in sterilization validation:
- High Resistance: Must withstand extreme sterilization conditions.
- Standardized Population: Must contain a known concentration of spores.
- Reproducibility: Should provide consistent results under identical conditions.
- Easy Detection: Must allow simple and rapid verification of sterility.
- Shelf Stability: Should maintain viability over prolonged storage.
Applications of Biological Indicators in Pharmaceuticals
Biological indicators serve various critical functions in the pharmaceutical industry:
| Application | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Validation of Sterilization | Ensures sterilization processes are effective. |
| Equipment Monitoring | Verifies sterility of pharmaceutical manufacturing tools. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets global sterilization standards (FDA, WHO, USP, EU GMP). |
| Process Control | Identifies potential failures in sterilization methods. |
| Quality Assurance | Ensures the safety and sterility of pharmaceutical products. |
Importance of Biological Indicators in Pharmaceuticals
- Regulatory Requirement: Compliance with sterilization validation standards is mandatory.
- Product Safety: Ensures patient safety by preventing contamination.
- Process Optimization: Helps improve sterilization procedures for better efficiency.
- Early Detection: Identifies sterilization failures before product distribution.
Challenges in Using Biological Indicators in Pharmaceuticals
Despite their advantages, biological indicators present certain challenges:
- Variability in Resistance: Some strains may exhibit inconsistent resistance levels.
- Testing Time: Some BI tests require extended incubation periods for results.
- Contamination Risks: Improper handling may lead to false positives.
Biological indicators (BIs) are vital tools in ensuring sterilization processes are effective across multiple industries. These indicators provide a direct and reliable measure of whether sterilization conditions have successfully eliminated harmful microorganisms. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what biological indicators are, their key benefits, common applications, different types, and where to source high-quality BIs for your needs.
What Are Biological Indicators?
Biological indicators are specialized testing systems that contain highly resistant bacterial spores, such as Geobacillus stearothermophilus or Bacillus atrophaeus. These spores are more resistant to sterilization than most microbes, making them ideal for verifying whether a sterilization process has been successful.
Unlike chemical indicators, which only show that sterilization conditions (like temperature or pressure) were reached, BIs confirm that the process was actually lethal to microorganisms. This makes them the gold standard for sterilization validation.
Key Benefits of Using Biological Indicators
Biological indicators offer several advantages over other sterilization monitoring methods:
- Accuracy: BIs provide direct evidence of microbial kill, ensuring sterilization effectiveness.
- Reliability: They are more dependable than chemical indicators, reducing the risk of false positives.
- Safety Assurance: By confirming sterilization, BIs protect patients, consumers, and workers from infections.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries require BIs to meet strict sterilization standards (e.g., FDA, ISO, AAMI).
- Process Validation: Essential for quality control in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and healthcare.
Industries That Rely on Biological Indicators
Biological indicators are used in various fields where sterility is critical:
1. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Ensures sterility of drug production equipment and packaging.
- Required for compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
2. Medical Device Sterilization
- Validates sterilization of surgical tools, implants, and disposable devices.
- Used in ethylene oxide (EO), steam, and hydrogen peroxide sterilization.
3. Healthcare & Hospitals
- Confirms sterility of surgical instruments and medical equipment.
- Prevents healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).
4. Food & Beverage Industry
- Ensures safety in packaged and processed foods.
- Used in canning and ultra-high-temperature (UHT) processing.
5. Research & Laboratory Settings
- Validates sterilization of lab equipment, media, and biosafety cabinets.
6. Dental Practices
- Guarantees sterility of dental instruments to prevent cross-contamination.
Types of Biological Indicators
Different sterilization methods require specific types of BIs:
| Type of BI | Sterilization Method | Common Spore Used |
|---|---|---|
| Steam Biological Indicators | Autoclaving (moist heat) | Geobacillus stearothermophilus |
| Ethylene Oxide (EO) BIs | EO gas sterilization | Bacillus atrophaeus |
| Hydrogen Peroxide BIs | Vaporized hydrogen peroxide (VHP) | Geobacillus stearothermophilus |
| Dry Heat BIs | Dry heat sterilization | Bacillus atrophaeus |
Among these, steam biological indicators are the most widely used due to the prevalence of autoclaves in labs, hospitals, and manufacturing.
Do Biological Indicators Expire?
Yes—BIs have a defined shelf life (typically 12-24 months) and must be used before their expiration date. Expired indicators may lose spore viability, leading to inaccurate results. Always store BIs according to manufacturer guidelines (usually at controlled room temperature).
Where to Buy Reliable Biological Indicators?
Choosing a trusted supplier is crucial for accurate sterilization monitoring. Mesa Labs is a leading provider of high-quality biological indicators, offering:
- A wide range of BIs for different sterilization methods.
- Industry-compliant products (ISO 11138, USP, FDA-approved).
- Reliable performance and consistent results.
Other reputable suppliers include STERIS, 3M, and Cantel Medical. When selecting a BI supplier, consider:
✔ Certifications (ISO, FDA, CE)
✔ Product range (compatibility with your sterilization method)
✔ Customer support & technical assistance
Conclusion
Biological indicators are vital in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring sterility and compliance with regulatory requirements. By selecting appropriate biological indicators and maintaining stringent validation processes, pharmaceutical companies can guarantee the safety and efficacy of their products. Continuous monitoring and advancements in BI technology further enhance the reliability of sterilization validation.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ):
What are biological indicators in pharma?
Biological indicators (BIs) are test systems containing highly resistant microorganisms, primarily bacterial spores, used to verify the effectiveness of sterilization processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing. They help ensure that sterilization methods eliminate all microbial life, confirming compliance with regulatory standards.
How many types of biological indicators are there?
Biological indicators are categorized based on sterilization methods. The major types include:
- Steam Sterilization BIs (Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- Dry Heat Sterilization BIs (Bacillus atrophaeus)
- Ethylene Oxide (EO) Sterilization BIs (Bacillus atrophaeus)
- Radiation Sterilization BIs (Bacillus pumilus)
- Hydrogen Peroxide Vapor BIs (Geobacillus stearothermophilus)
- Chemical Sterilization BIs (Bacillus atrophaeus)
What are examples of biological indicators?
Common biological indicators include:
- Spore Strips – Paper strips inoculated with bacterial spores.
- Self-Contained BIs – Vials with spores and growth media.
- Ampoules – Liquid-based BIs for steam sterilization.
- Suspension BIs – Directly inoculated bacterial suspensions.
What is a type 4 sterilization indicator?
A Type 4 sterilization indicator is a multi-parameter chemical indicator that reacts to two or more sterilization parameters, such as temperature and time, confirming exposure to the sterilization process. However, it does not replace biological indicators for sterility validation.
What is the biological indicator principle?
The principle of biological indicators relies on the use of highly resistant bacterial spores to challenge sterilization efficiency. If sterilization is successful, the spores will be killed; otherwise, they will germinate and grow in a nutrient medium, signaling sterilization failure.
What are type 5 sterilization indicators?
Type 5 indicators are integrating indicators, meaning they react to all critical sterilization parameters (temperature, time, pressure, and humidity). They provide results similar to biological indicators but do not replace them in sterility assurance.
What is autoclave tape for?
Autoclave tape is a chemical indicator that changes color when exposed to high temperatures, confirming that the item has undergone the sterilization process. However, it does not verify sterility.
What is a CSSD indicator?
CSSD (Central Sterile Supply Department) indicators include chemical and biological indicators used to monitor sterilization processes in hospital sterilization units. These indicators ensure the sterility of surgical instruments and medical supplies.
What are key biological indicators?
Key biological indicators include:
- Geobacillus stearothermophilus (Steam, Hydrogen Peroxide)
- Bacillus atrophaeus (EO, Dry Heat, Chemical)
- Bacillus pumilus (Radiation)
How to dispose of a biological indicator?
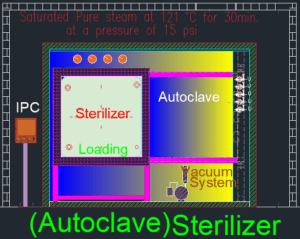
After use, biological indicators should be autoclaved at 121°C for 30 minutes to ensure complete microbial destruction before disposal. They can then be discarded as non-hazardous waste.
What bacteria is in a biological indicator?
Common bacterial spores used in biological indicators include:
- Geobacillus stearothermophilus – Resistant to moist heat and hydrogen peroxide.
- Bacillus atrophaeus – Resistant to dry heat and ethylene oxide.
- Bacillus pumilus – Resistant to radiation sterilization.
How to use a biological indicator?
- Place the BI inside the sterilizer along with the test load.
- Run the sterilization cycle as per protocol.
- Incubate the BI at the specified temperature.
- Check for growth – No growth indicates successful sterilization, while growth signals failure.
What are the best bioindicators?
The best bioindicators depend on the sterilization method:
- Steam & Hydrogen Peroxide: Geobacillus stearothermophilus
- Dry Heat & EO Gas: Bacillus atrophaeus
- Radiation: Bacillus pumilus
How to check sterilization?
Sterilization is checked using:
- Biological Indicators (spore testing)
- Chemical Indicators (tape, strips)
- Physical Indicators (temperature, pressure readings)
What is a biological indicator example?
A spore strip containing Geobacillus stearothermophilus used to verify autoclave sterilization is a common biological indicator example.
How do you store biological indicators?
Biological indicators should be stored in a cool, dry environment at temperatures between 2°C and 25°C, away from direct light and humidity.
What is the best indicator for an autoclave?
The best indicator for an autoclave is a biological indicator with Geobacillus stearothermophilus spores, as they are highly resistant to moist heat sterilization.
How many minutes to autoclave?
Autoclaving typically requires 15–30 minutes at 121°C under 15 psi pressure, depending on the load type.
Why biological indicators?
Biological indicators provide direct evidence of microbial inactivation, making them the most reliable method for confirming sterilization efficacy.
What is the temperature for sterile storage?
Sterile storage areas should maintain a temperature between 18°C and 24°C, with relative humidity below 60%.
How to spore test an autoclave?
- Place a biological indicator inside the autoclave.
- Run the sterilization cycle.
- Incubate the indicator to check for bacterial growth.
- If no growth occurs, sterilization is successful.
What is the minimum temperature for flash sterilization?
Flash sterilization requires a minimum temperature of 132°C (270°F) for 3–10 minutes, depending on the load.
What causes sterilization failures?
Common causes include:
- Incorrect loading of the sterilizer.
- Insufficient exposure time or temperature.
- Equipment malfunction.
- Improper packaging of items.
What is the humidity limit in pharma?
Pharmaceutical cleanrooms should maintain humidity levels below 60%, with some areas requiring even lower levels to prevent microbial growth.
Do sterile items expire?
Yes, sterile items have an expiration date based on storage conditions, packaging integrity, and regulatory guidelines.
What is a sterile temperature?
A sterile temperature typically ranges between 121°C and 134°C, depending on the sterilization method used.