A pharmaceutical quality system is a set of processes, procedures, and practices that ensure pharmaceutical products are consistently manufactured to meet the required quality standards. The system includes a range of activities, such as product development, manufacturing, testing, and distribution. The primary goal of the system is to ensure patient safety by preventing product defects, deviations, and failures.
The pharmaceutical quality system includes various elements, such as quality control, quality assurance, and quality risk management. It also involves continuous improvement through monitoring, analysis, and corrective actions.
An effective pharmaceutical quality system is critical for compliance with regulatory requirements, such as the Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines, and for maintaining product quality and integrity. By implementing a comprehensive quality system, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their products meet the required quality standards, are safe and effective, and consistently meet the needs of patients and healthcare professionals.
What is a Pharmaceutical Quality System?
A pharmaceutical quality system encompasses the organizational processes, procedures, and resources employed by pharmaceutical companies to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of their products. It involves a systematic approach to managing and controlling various aspects of pharmaceutical operations, including manufacturing, testing, documentation, and regulatory compliance.
Importance of a Pharmaceutical Quality System
A robust pharmaceutical quality system is essential for pharmaceutical companies to adhere to regulatory requirements, maintain product quality, and ultimately safeguard patient safety. By implementing a comprehensive quality system, companies can ensure that their products consistently meet established standards, minimize the risk of defects or contamination, and build trust among healthcare professionals and patients.
Key Elements of a Pharmaceutical Quality System
To develop an effective pharmaceutical quality system, it’s important to understand its key elements. These elements work together to ensure compliance with regulations and the delivery of high-quality pharmaceutical products. Let’s explore them in detail:
1. Quality Management
Quality management is the foundation of a pharmaceutical quality system. It involves establishing a quality policy, setting quality objectives, and implementing processes to achieve those objectives. The quality management system should be supported by a robust organizational structure, clearly defined responsibilities, and effective communication channels.
2. Document Control
Document control is a crucial aspect of the pharmaceutical quality system. It involves the creation, revision, approval, and distribution of documents such as standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, and product specifications. Document control ensures that the most up-to-date and accurate information is available to employees, helping them perform their tasks consistently and according to established guidelines.
3. Risk Management
Risk management plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical industry, where the potential impact of product failures or quality issues can be significant. A systematic approach to risk management helps identify, evaluate, and mitigate risks throughout the product lifecycle. This includes assessing risks associated with raw materials, manufacturing processes, packaging, and distribution, among others.
4. Training and Competence
Training and competence are critical aspects of a pharmaceutical quality system. Employees should receive adequate training to perform their assigned tasks competently and in compliance with quality standards. Training programs should be well-documented, regularly reviewed, and tailored to the specific needs of different roles within the organization. By investing in employee development, companies can ensure a skilled workforce capable of upholding product quality.
5. Change Control 
Change control is a formal process that manages changes to processes, equipment, systems, and documents within a pharmaceutical company. It ensures that changes are properly evaluated, approved, and implemented while considering their potential impact on product quality, safety, and efficacy. Change control helps maintain consistency and prevent unauthorized modifications that could compromise the integrity of the pharmaceutical quality system.
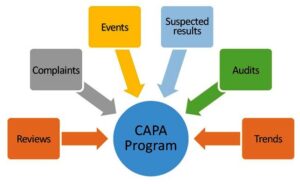
6. Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
The CAPA system is a fundamental component of a pharmaceutical quality system. It involves investigating and addressing any deviations, non-conformances, or complaints related to product quality. By identifying the root causes of issues and implementing corrective and preventive actions, companies can continuously improve their processes and prevent recurrence of problems.
7. Supplier Management
Pharmaceutical companies rely on suppliers for raw materials, components, and services. Supplier management ensures that suppliers meet specified quality standards and regulatory
Key steps of the pharmaceutical quality system.
| Key Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Development | The process of developing and designing a pharmaceutical product, including formulation, process development, and stability testing. This step ensures that the product is safe, effective, and meets the required quality standards. |
| Quality Risk Management | The process of identifying, assessing, and controlling risks associated with pharmaceutical products. This step helps to minimize the potential for product defects and failures and ensures patient safety. |
| Quality Control | The process of testing and analyzing raw materials, in-process samples, and finished products to ensure that they meet the required quality standards. This step includes both physical and chemical testing. |
| Quality Assurance | The process of ensuring that all pharmaceutical manufacturing processes are conducted according to the required quality standards and regulatory requirements. This step includes documentation review, process validation, and audits. |
| Continuous Improvement | The process of monitoring, analyzing, and improving the pharmaceutical quality system to ensure that it remains effective and efficient. This step includes corrective and preventive actions and ongoing training and education. |
ich q10 pharmaceutical quality system
ICH Q10 is a guideline developed by the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) that provides guidance on pharmaceutical quality systems. It emphasizes the importance of a comprehensive and integrated approach to pharmaceutical quality that covers all aspects of the product lifecycle.
The guideline outlines the following principles for a pharmaceutical quality system:
- A quality system should be designed to meet the specific needs of the company and its products.
- A quality system should be based on sound scientific principles and risk management.
- Quality should be built into the product and process design, and not just tested in.
- The quality system should cover all aspects of the product lifecycle, from development through commercialization and discontinuation.
- The quality system should be continuously improved through the use of quality risk management and performance metrics.
ICH Q10 also emphasizes the importance of a quality culture within the company, where quality is everyone’s responsibility and is integrated into all aspects of the organization. The guideline highlights the need for effective communication, training, and education to ensure that all employees understand their role in maintaining product quality and patient safety.
In summary, ICH Q10 provides guidance on the critical elements of a pharmaceutical quality system, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive and integrated approach that covers all aspects of the product lifecycle.
Worldwide Guidance about the PQS
- International Council for Harmonization (ICH) Q10 – Pharmaceutical Quality System
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) Regulations for Finished Pharmaceuticals (21 CFR Part 211)
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) – Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) Guidelines for Medicinal Products for Human and Veterinary Use
- World Health Organization (WHO) – WHO Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceutical Products
- Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention and Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) – Guide to Good Manufacturing Practice for Medicinal Products
These guidelines and regulations provide guidance on the critical elements of a pharmaceutical quality system, including product development, quality control, quality assurance, and continuous improvement. They emphasize the importance of meeting regulatory requirements, maintaining product quality and integrity, and ensuring patient safety. By following these guidelines, pharmaceutical companies can ensure that their products meet the required quality standards and are safe and effective for patients
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a pharmaceutical quality system?
Answer: A pharmaceutical quality system is a system that ensures that pharmaceutical products are consistently manufactured to meet the required quality standards and are safe and effective for patients.
What are the critical elements of a pharmaceutical quality system?
Answer: The critical elements of a pharmaceutical quality system include quality control, quality assurance, product development, risk management, documentation, and continuous improvement.
Why is a pharmaceutical quality system important?
Answer: A pharmaceutical quality system is important because it ensures that pharmaceutical products are safe and effective for patients, and that they meet regulatory requirements and industry standards.
What is quality control?
Answer: Quality control is the process of monitoring and testing products to ensure that they meet the required quality standards.
What is quality assurance?
Answer: Quality assurance is the process of ensuring that the systems and processes used to manufacture pharmaceutical products are capable of consistently producing products that meet the required quality standards.
What is risk management?
Answer: Risk management is the process of identifying and assessing potential risks to product quality and patient safety, and developing strategies to mitigate those risks.
What is documentation?
Answer: Documentation is the process of recording and maintaining information related to product development, manufacturing, and quality control to ensure traceability and accountability.
What is continuous improvement?
Answer: Continuous improvement is the process of continually evaluating and improving processes and systems to enhance product quality and efficiency.
What is validation?
Answer: Validation is the process of establishing documented evidence that a process, system, or equipment consistently produces products that meet the required quality standards.
What is qualification?
Answer: Qualification is the process of demonstrating that equipment, facilities, and utilities are suitable for their intended use.
What is a deviation?
Answer: A deviation is a departure from established procedures or specifications, which may affect product quality.
What is a corrective action?
Answer: A corrective action is a response to a deviation or non-conformance, intended to address the root cause and prevent recurrence.
What is a preventive action?
Answer: A preventive action is a proactive measure taken to prevent potential problems from occurring.
What is change control?
Answer: Change control is the process of evaluating, approving, and implementing changes to processes, systems, or equipment, while ensuring that product quality and patient safety are not compromised.
What is a quality culture?
Answer: A quality culture is an organizational culture that prioritizes and values quality, with a focus on continuous improvement, communication, and accountability at all levels of the organization.
You may also read about Microbiology Guidelines