Fogging and Fumigation play vital roles In the pharmaceutical industry in maintaining a sterile and contamination-free environment. To achieve this, fumigation and fogging techniques play a critical role. In this article, we explore the significance of fumigation and fogging in pharmaceutical settings, highlighting their crucial contributions to ensuring product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Sterilization and Disinfection:
- Fumigation and fogging serve as indispensable tools for sterilization and disinfection in pharmaceutical facilities. These techniques effectively eliminate microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that may contaminate the manufacturing areas, equipment, or storage spaces. By eradicating these pathogens, fumigation and fogging help prevent product contamination and ensure the production of safe and effective medications.
- Controlling Cross-Contamination:
- Pharmaceutical facilities often have multiple production areas or cleanrooms dedicated to different processes or products. Fumigation and fogging help control cross-contamination between these areas by neutralizing any lingering microorganisms in the air or on surfaces. By implementing regular fumigation and fogging protocols, pharmaceutical companies can maintain the integrity and purity of their products, safeguarding both patient safety and brand reputation.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
- The pharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulatory guidelines, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and various health authorities’ requirements. Fumigation and fogging are crucial components of compliance, as they contribute to maintaining the required level of cleanliness and sterility. By adhering to these standards, pharmaceutical companies demonstrate their commitment to quality, regulatory compliance, and patient well-being.
- Preventing Contamination of Raw Materials and Packaging:
- Raw materials and packaging components used in pharmaceutical production are susceptible to contamination. Fumigation and fogging help create an environment free from pests, insects, or airborne microorganisms that could compromise the integrity of these critical materials. By implementing robust fumigation and fogging protocols, pharmaceutical manufacturers can ensure the purity and safety of their raw materials, protecting the overall quality of the finished products.
- Enhanced Product Stability:
- Some pharmaceutical products are sensitive to environmental conditions, including microbial contamination. Fumigation and fogging contribute to maintaining the stability and shelf life of such products by minimizing the risk of microbial growth or degradation. By implementing these techniques in appropriate areas, pharmaceutical companies can enhance the longevity and effectiveness of their products, ensuring consistent quality for patients.
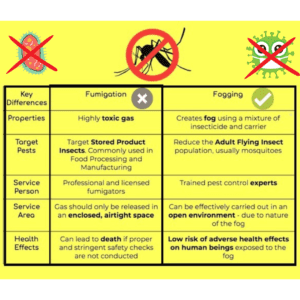
fogging vs fumigation
| Aspect | Fumigation | Fogging |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Release of gaseous agents (e.g., formaldehyde) | Dispersion of fine mist or fog of disinfectant |
| Coverage | Comprehensive coverage of entire space | Targeted application in specific areas |
| Reach | Reaches inaccessible areas and hidden spaces | Reaches surfaces, including intricate crevices |
| Application | Typically used for whole-room disinfection | Suitable for localized sanitization and disinfection |
| Efficiency | Effective against a wide range of microorganisms | Effective in reducing pathogens on surfaces |
| Equipment | Requires specialized fumigation equipment | Comprehensive coverage of the entire space |
| Ventilation | Requires adequate ventilation after fumigation | Requires minimal ventilation after fogging |
| Downtime | Longer downtime due to ventilation requirements | Shorter downtime as ventilation is not required |
| Residue | Leaves no residue on surfaces | Leaves minimal residue, if any |
| Accessibility | Requires sealing of the area for treatment | Can be applied in open or accessible areas |
| Regulatory | Compliance with regulatory guidelines | Compliance with regulatory guidelines |
| Examples | Sterilizing production rooms, equipment, or packaging areas | Disinfecting cleanrooms, laminar flow hoods, or specific equipment |
Importance of Fogging and Fumigation in pharmaceutical
In the pharmaceutical industry, maintaining a sterile and contamination-free environment is of utmost importance. To achieve this, fumigation and fogging techniques play a critical role. In this article, we explore the significance of fumigation and fogging in pharmaceutical settings, highlighting their crucial contributions to ensuring product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Sterilization and Disinfection:
- Fumigation and fogging serve as indispensable tools for sterilization and disinfection in pharmaceutical facilities. These techniques effectively eliminate microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that may contaminate the manufacturing areas, equipment, or storage spaces. By eradicating these pathogens, fumigation and fogging help prevent product contamination and ensure the production of safe and effective medications.
- Controlling Cross-Contamination:
- Pharmaceutical facilities often have multiple production areas or cleanrooms dedicated to different processes or products. Fumigation and fogging help control cross-contamination between these areas by neutralizing any lingering microorganisms in the air or on surfaces. By implementing regular fumigation and fogging protocols, pharmaceutical companies can maintain the integrity and purity of their products, safeguarding both patient safety and brand reputation.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards:
- The pharmaceutical industry operates under strict regulatory guidelines, including Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and various health authorities’ requirements. Fumigation and fogging are crucial components of compliance, as they contribute to maintaining the required level of cleanliness and sterility. By adhering to these standards, pharmaceutical companies demonstrate their commitment to quality, regulatory compliance, and patient well-being.
- Preventing Contamination of Raw Materials and Packaging:
- Raw materials and packaging components used in pharmaceutical production are susceptible to contamination. Fumigation and fogging help create an environment free from pests, insects, or airborne microorganisms that could compromise the integrity of these critical materials. By implementing robust fumigation and fogging protocols, pharmaceutical manufacturers can ensure the purity and safety of their raw materials, protecting the overall quality of the finished products.
- Enhanced Product Stability:
- Some pharmaceutical products are sensitive to environmental conditions, including microbial contamination. Fumigation and fogging contribute to maintaining the stability and shelf life of such products by minimizing the risk of microbial growth or degradation. By implementing these techniques in appropriate areas, pharmaceutical companies can enhance the longevity and effectiveness of their products, ensuring consistent quality for patients.
Conclusion:
Fumigation and fogging techniques play an indispensable role in the pharmaceutical industry, where maintaining a sterile and contamination-free environment is crucial. These techniques effectively eliminate microorganisms, prevent cross-contamination, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. By embracing fumigation and fogging as integral components of their sanitation protocols, pharmaceutical companies can safeguard product quality, protect patient safety, and uphold their commitment to excellence in healthcare
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better, a fogger or a fumigator?
Answer: The choice between a fogger and a fumigator depends on the specific application and requirements. Fogging is effective for targeted applications in localized areas, while fumigation provides comprehensive coverage in larger spaces. It is best to consider the intended use and consult with experts to determine the most suitable option for a particular situation.
What is the difference between fumigation and spraying?
Answer: Fumigation involves the release of gaseous agents, such as formaldehyde, to eliminate pests or microorganisms in a sealed space. It reaches inaccessible areas and provides a thorough treatment. On the other hand, spraying involves the application of liquid solutions using sprayers or spray guns. Spraying is generally used for surface disinfection or pest control in open or accessible areas.
What is the difference between fumigation and disinfection?
Answer: Fumigation primarily targets pests, insects, or microorganisms in enclosed spaces using gaseous agents. It is often used for pest control in storage facilities, grains, or buildings. Disinfection, on the other hand, focuses on eliminating or reducing the presence of pathogens on surfaces or in the air. It is commonly employed in healthcare settings, food processing areas, or public spaces to minimize the risk of infections.
What is fogging used for?

Answer: Fogging is used for sanitization and disinfection purposes. It is effective for treating large areas, hard-to-reach spaces, and surfaces. Fogging is commonly employed in healthcare facilities, hotels, schools, public transportation, and other settings where comprehensive sanitization is required.
What chemical is used for fogging?
Answer: Various disinfectants or sanitizing solutions can be used for fogging, depending on the specific requirements and targeted pathogens. Common chemicals used include quaternary ammonium compounds, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine dioxide, or alcohol-based solutions. It is important to use approved and registered chemicals suitable for fogging applications.
What is the principle of fogging?
Answer: The principle of fogging involves transforming liquid disinfectants or sanitizing solutions into tiny droplets, creating a fog or mist. These microdroplets disperse in the air and settle on surfaces, effectively covering a large area and reaching hidden or difficult-to-access spaces. The fog or mist allows for thorough coverage and contact time with pathogens, ensuring effective disinfection.
What are the two types of fumigation process?
Answer: The two types of fumigation processes are:
a) Chamber Fumigation: This process involves sealing an enclosed space, such as a room or a container, and introducing the fumigant to eliminate pests, insects, or microorganisms. It is commonly used in storage facilities or buildings.
b) Soil Fumigation: This process targets pests, pathogens, or weed seeds in the soil. It is typically conducted in agricultural settings or prior to planting crops to control pests and diseases.
What are the two types of fumigation?
Answer: The two types of fumigation are:
a) Gas Fumigation: This type involves using gaseous agents, such as methyl bromide or sulfuryl fluoride, to exterminate pests or microorganisms. It is commonly employed in storage facilities, ships, or buildings.
b) Liquid Fumigation: This type utilizes liquid fumigants, like formaldehyde or potassium permanganate, which are released in a vapor form to eliminate pests or microorganisms. Liquid fumigation is often used in closed or confined spaces.
