The GMP Audit Checklist is a comprehensive tool designed to facilitate meticulous self-assessment within the scope of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP). As a cornerstone of excellence in the manufacturing industry, GMP sets forth stringent guidelines to ensure the production of safe and high-quality products while complying with regulatory standards.
This GMP Audit Checklist serves as a guiding compass for organizations, empowering them to conduct internal audits with precision and efficacy. By systematically examining various facets of their operations, companies can identify potential areas of improvement, mitigate risks, and enhance overall compliance.
The GMP Audit Checklist encompasses a wide range of criteria, covering critical aspects of GMP compliance. It begins by delving into the fundamental elements, such as facility design and maintenance. Adequate infrastructure, including suitable layout, sanitation practices, and control of environmental factors, lays the foundation for maintaining product integrity and safety.
The self-inspection process then extends to personnel practices, ensuring that personnel are appropriately trained, qualified, and adhere to hygienic practices. Effective training programs, coupled with robust competency assessments, foster a culture of excellence and contribute to the overall success of GMP compliance.
Further examination is dedicated to the control of raw materials and components, emphasizing the importance of proper identification, verification, storage, and handling. This section ensures that organizations have robust systems in place to prevent cross-contamination and maintain the integrity of their supply chain.
The GMP Audit Checklist also scrutinizes the manufacturing process itself, focusing on equipment validation, calibration, and maintenance. By evaluating adherence to standard operating procedures, organizations can safeguard product quality and consistency throughout the production lifecycle.
Documentation plays a vital role in GMP compliance, and the GMP Audit Checklist reflects this significance. It assesses the adequacy and accuracy of documentation practices, encompassing procedures, records, and batch documentation. Accurate and up-to-date documentation serves as a crucial tool for traceability, accountability, and regulatory compliance.
Quality control and quality assurance systems are pivotal elements in GMP, warranting dedicated scrutiny within the GMP Audit Checklist. Organizations are required to demonstrate effective monitoring, testing, and release of products, ensuring they meet predetermined specifications and comply with regulatory requirements.
Lastly, the GMP Audit Checklist addresses complaint handling, deviation management, and the robustness of the internal audit system. These components reinforce the importance of timely identification and resolution of non-conformances, continual improvement, and the establishment of a culture of quality throughout the organization.
By diligently utilizing the GMP Audit Checklist, organizations embark on a journey of self-assessment and continuous improvement. This comprehensive tool empowers them to identify areas of strength, address vulnerabilities, and fortify their commitment to GMP compliance. Through meticulous examination of each criterion, organizations can proactively enhance their operations, thereby ensuring the production of safe and high-quality products while upholding regulatory standards.
Importance of the WHO GMP Audit Checklist:
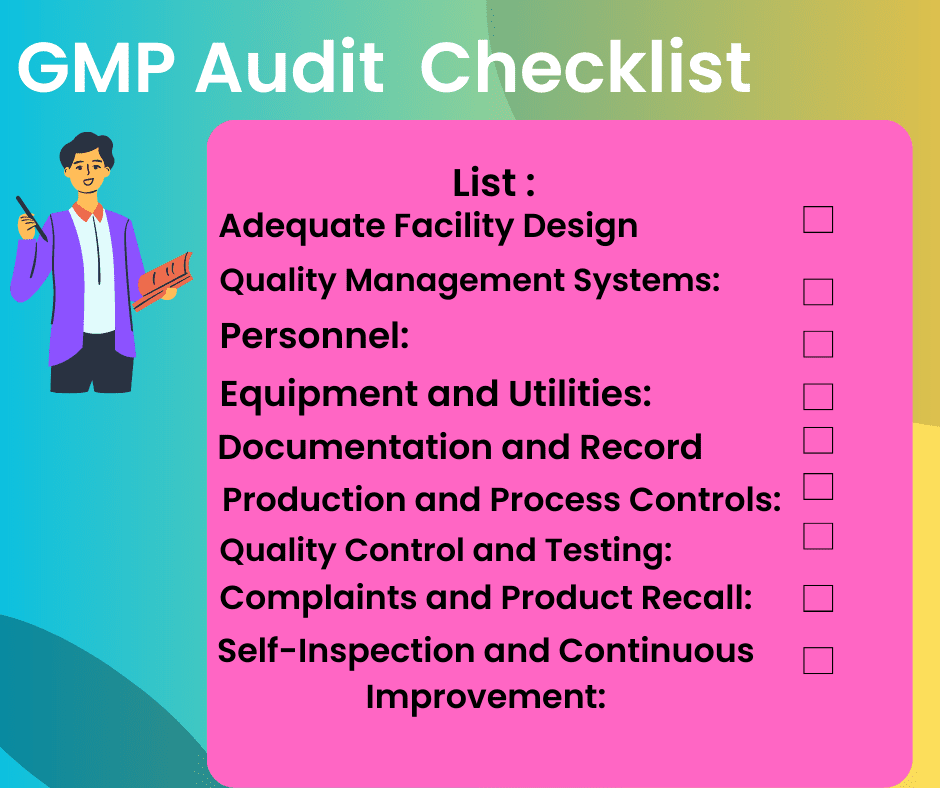
- Adequate Facility Design:
- Proper layout and segregation of production, storage, and quality control areas
- Appropriate ventilation, lighting, and environmental control measures
- Adequate sanitation practices and waste management systems
- Quality Management Systems:
- Implementation of a comprehensive quality management system
- Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for quality-related activities
- Documented procedures and records for all GMP-related processes
- Personnel:
- Proper training, qualification, and ongoing competency assessment of personnel
- Adequate hygiene practices and compliance with GMP requirements
- Documentation of training records and qualifications
- Equipment and Utilities:
- Adequate qualification, calibration, and maintenance of equipment
- Validation of critical processes and utilities
- Adequate documentation of equipment use, cleaning, and maintenance
- Documentation and Recordkeeping:
- Robust document control systems to ensure accurate and up-to-date procedures
- Proper recording of production, testing, and distribution activities
- Adequate retention of records to enable traceability and accountability
- Production and Process Controls:
- Adherence to defined manufacturing procedures and batch records
- Validation of critical processes, including cleaning and sterilization
- Effective monitoring and control of critical process parameters
- Quality Control and Testing:
- Proper testing and release of raw materials, intermediates, and finished products
- Validation and qualification of analytical methods
- Adequate storage and handling of reference standards and samples
- Complaints and Product Recall:
- Effective management of product complaints and timely investigation
- Implementation of a robust system for product recall, if necessary
- Documentation of complaint investigations and appropriate corrective actions
- Self-Inspection and Continuous Improvement:
- Regular self-inspections to identify areas for improvement
- Timely implementation of corrective and preventive actions (CAPA)
- Continuous training and development programs to enhance GMP compliance
It’s important to note that these bullet points provide a general overview, and the specific requirements may vary depending on the regulatory authority and the specific industry. It’s crucial to consult the WHO guidelines and relevant GMP regulations for a comprehensive understanding of the requirements.
GMP Audit Checklist :
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Facility Design and Maintenance | 1. Adequate facility Layout to support GMP requirements. 2. Proper sanitation practices. 3.- Control of environmental factors. |
| Personnel Practices | 1. Personnel training and qualification. 2. Adherence to hygienic practices. 3. Competency assessments. |
| Control of Raw Materials and Components | 1. Proper identification and verification of raw materials. 2. Appropriate storage and handling. 3. Prevention of cross-contamination. |
| Manufacturing Process | 1. Equipment validation, calibration, and maintenance. 2. Adherence to standard operating procedures. |
| Documentation | 1. Adequacy and accuracy of procedures, records, and batch documentation. 2. Traceability and regulatory compliance. |
| Quality Control and Quality Assurance Systems | 1. Monitoring, testing, and release of products. 2. Compliance with predetermined specifications. 3. Regulatory compliance. |
| Complaint Handling | 1. Timely identification and resolution of complaints. 2. Effective complaint management system. |
| Deviation Management | 1. Identification and handling of deviations from established procedures. 2. Root cause analysis and corrective actions. |
| Internal Audit System | 1. Robust internal audit program. 2. Timely identification and resolution of non-conformances. 3. Continual improvement. |
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is a GMP Audit Checklist?
Answer: A GMP Audit Checklist is a comprehensive tool that outlines the criteria and requirements for assessing Good Manufacturing Practice compliance during an audit.
Why is a GMP Audit Checklist important?
Answer: A GMP Audit Checklist serves as a guide to ensure that all relevant aspects of GMP compliance are assessed during an audit. It helps auditors systematically review processes, identify gaps, and implement corrective actions.
What does a GMP Audit Checklist typically include?
Answer: A GMP Audit Checklist typically includes criteria related to facility design, personnel practices, raw material control, manufacturing processes, documentation, quality control, complaint handling, and more.
How is a GMP Audit Checklist used?
Answer: Auditors use the GMP Audit Checklist as a reference during audits to evaluate compliance against GMP requirements. They assess each criterion, document findings, and identify areas that require corrective actions.
Can a GMP Audit Checklist be customized for specific industries?
Answer: Yes, a GMP Audit Checklist can be tailored to specific industries by incorporating industry-specific regulations, standards, and guidelines to ensure compliance with relevant requirements.
Who typically conducts GMP audits?
Answer: GMP audits are usually conducted by internal or external auditors who have expertise in GMP regulations and auditing processes. They can be employees of the company or independent third-party auditors.
What are the objectives of a GMP audit?
Answer: The primary objectives of a GMP audit are to assess compliance with GMP regulations, identify areas of non-compliance, evaluate the effectiveness of quality systems, and ensure the production of safe and high-quality products.
How often should GMP audits be conducted?
Answer: GMP audits should be conducted regularly based on a predetermined schedule or as required by regulatory authorities. The frequency may vary depending on the nature of the business, the level of risk, and regulatory requirements.
What happens if non-compliance is identified during a GMP audit?
Answer: If non-compliance is identified during a GMP audit, the auditor documents the findings, assigns a severity level, and recommends corrective actions. The company is then responsible for implementing the necessary measures to address the non-compliance.
Can GMP audits lead to certification?
Answer: GMP audits themselves do not lead to certification. However, successful completion of a GMP audit can demonstrate compliance with GMP regulations and serve as supporting evidence for certification processes conducted by regulatory bodies or certification agencies.
Are GMP audits mandatory?
Answer: GMP audits are not mandatory in all cases, but they are highly recommended for companies in regulated industries to ensure compliance, maintain product quality, and meet regulatory requirements.
What are the benefits of conducting GMP audits?
Answer: Some benefits of conducting GMP audits include identifying areas for improvement, enhancing product quality and safety, ensuring regulatory compliance, minimizing risks, and maintaining customer confidence.
Can GMP audits be performed by internal teams?
Answer: Yes, GMP audits can be conducted by internal teams, especially in large organizations that have dedicated audit departments or qualified personnel with expertise in GMP regulations and auditing processes.
How can companies prepare for a GMP audit?
Answer: Companies can prepare for a GMP audit by conducting self-inspections using a GMP Audit Checklist, addressing any non-compliance issues, maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation, and ensuring proper training and qualification of personnel.
How can companies benefit from GMP audits in the long term?
Answer: GMP audits help companies establish robust quality systems, maintain regulatory compliance, enhance product quality and safety, improve process efficiency, minimize risks, and build a reputation for excellence in the industry.