Track and Trace System, nowadays, plays a vital role in preventing counterfeiting during trading, assisting in optimizing monitoring at each level of the supply chain, and maintaining the integrity of the customer. however, the entire process is full of challenges, although continuous measures are being taken by both manufacturers and services providers to minimize the errors while transit at various levels of the supply chain as well as packing operations and to ensure minimum impact on productivity.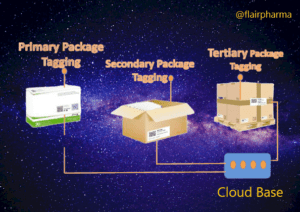
Introduction:
In the world of pharmaceuticals, ensuring the safety and authenticity of medications is of paramount importance. Counterfeit drugs and unauthorized distribution pose significant risks to public health, highlighting the need for robust systems that track and trace pharmaceutical packaging throughout the supply chain. This article explores the significance of track and trace systems in pharmaceutical packing, examining their role in enhancing safety, quality control, and regulatory compliance.
Ensuring Product Authenticity:
Counterfeit drugs have emerged as a global concern, jeopardizing patient health and undermining trust in the pharmaceutical industry. Track and trace systems play a vital role in combating this menace by allowing comprehensive monitoring of pharmaceutical packaging from production to distribution. By employing unique identification codes, such as serial numbers or barcodes, these systems enable the verification of product authenticity, facilitating the swift identification of counterfeit or substandard medications.
Enhanced Safety and Quality Control:
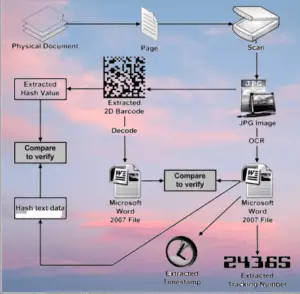
Track and trace systems empower pharmaceutical manufacturers and regulatory authorities to implement robust safety and quality control measures. Through real-time monitoring and traceability, these systems enable the identification of potential issues or deviations within the supply chain. Timely detection of problems, such as tampering, contamination, or temperature excursions, ensures that appropriate measures can be taken to safeguard the integrity of the products and protect patient health.
Efficient Recalls and Investigations:
In cases where product defects or safety concerns arise, track and trace systems provide invaluable support for efficient recalls and investigations. By tracking the entire journey of pharmaceutical packaging, authorities can swiftly identify the affected products, their distribution channels, and the specific batches involved. This information enables targeted recalls, minimizing the impact on patients and streamlining the retrieval process. Furthermore, track and trace systems facilitate thorough investigations into the root causes of issues, helping prevent future occurrences and ensuring continuous improvement in safety and quality.
Regulatory Compliance and Supply Chain Transparency:
The pharmaceutical industry is subject to stringent regulations aimed at safeguarding public health. Track and trace systems assist manufacturers and distributors in complying with these regulations by providing comprehensive documentation and accountability throughout the supply chain. By capturing data on production, distribution, and sales, these systems offer transparency, enabling regulatory authorities to monitor compliance and enforce necessary actions, if required.
Challenges and Future Advancements:
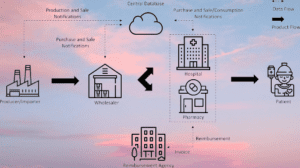
While track and trace systems have proven to be invaluable, their implementation is not without challenges. Integrating these systems across a vast network of manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacies requires collaboration and standardization. Additionally, addressing concerns related to data privacy and cybersecurity is crucial to maintaining the integrity of the system. Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence hold promise for further enhancing the capabilities of track and trace systems, allowing for even greater efficiency, security, and transparency.
Conclusion: Track and trace systems in pharmaceutical packaging offer a powerful solution to ensure product authenticity, enhance safety and quality control, enable efficient recalls, and ensure regulatory compliance. By embracing these systems, the pharmaceutical industry can bolster public confidence, protect patient health, and mitigate the risks posed by counterfeit medications. As technology continues to advance, the future of track and trace systems holds tremendous potential in transforming the pharmaceutical supply chain into a safer and more transparent ecosystem.
Working principle of Track and Trace System
The working principle of a Track and Trace system in pharmaceutical packaging involves a combination of technologies and processes to monitor and trace the movement of pharmaceutical products throughout the supply chain. Let’s delve into the key components and steps involved:
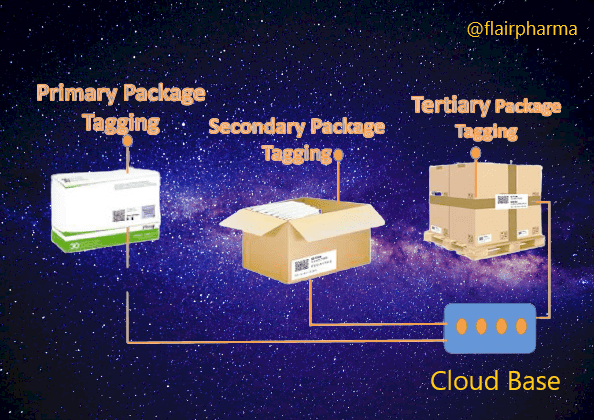
- Unique Identification: Each pharmaceutical product or packaging unit is assigned a unique identifier, such as a serial number, barcode, or QR code. This identifier serves as a digital fingerprint for the product, enabling its traceability.

- Data Capture: Throughout the manufacturing and packaging process, relevant information about the product is captured and associated with its unique identifier. This data includes details such as batch number, manufacturing date, expiration date, and destination.
- Packaging Integration: The unique identifier is then applied to the pharmaceutical packaging using labeling, printing, or marking technologies. This ensures that each individual package is uniquely identifiable.
- Data Management: The captured information, along with the unique identifiers, is stored in a centralized database or cloud-based system. This database acts as a repository for tracking and tracing the product’s journey.
- Serialization: Serialization refers to the process of assigning unique serial numbers or codes to individual packages or units within a batch. It enables precise tracking of each unit throughout the supply chain.
- Aggregation: Aggregation involves linking the unique identifiers of individual packages to higher-level packaging, such as cases, pallets, or shipments. This hierarchical relationship enables the tracking of product movement at different levels of packaging.

- Data Exchange: The Track & Trace system facilitates the exchange of data between various stakeholders in the supply chain, including manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, and pharmacies. This real-time data sharing ensures transparency and visibility across the entire distribution network.
- Scanning and Verification: At different stages of the supply chain, stakeholders utilize scanning devices, such as barcode readers or handheld scanners, to capture the unique identifiers of the packages. This allows for verification of product authenticity, tracking its location, and recording movement data.
- Traceability and Monitoring: The Track & Trace system enables real-time monitoring and traceability of pharmaceutical products from manufacturing to distribution. This includes tracking the movement of products between different facilities, warehouses, and transportation routes.
- Compliance and Reporting: The system generates reports and documentation to comply with regulatory requirements, providing a comprehensive audit trail of the product’s journey. This information aids in regulatory inspections and investigations if needed.
- Recall Management: In the event of a product recall, the Track & Trace system plays a crucial role in swiftly identifying the affected products, their distribution channels, and the specific batches involved. This enables targeted recalls, minimizing the impact on patient safety.

By implementing a robust Track and Trace system, pharmaceutical companies can enhance supply chain security, improve product authenticity, ensure regulatory compliance, and effectively respond to safety concerns. This technology-driven approach helps safeguard patient health and maintains the integrity of pharmaceutical packaging throughout its lifecycle.
Critical Parameters of Track and Trace System
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Unique Identification | Each pharmaceutical product or packaging unit is assigned a unique identifier, such as a serial number, barcode, or QR code. |
| Data Capture | Relevant information about the product, including batch number, manufacturing date, expiration date, and destination, is captured and associated with its unique identifier. |
| Packaging Integration | The unique identifier is applied to pharmaceutical packaging using labeling, printing, or marking technologies. |
| Data Management | The captured information and unique identifiers are stored in a centralized database or cloud-based system for tracking and tracing purposes. |
| Serialization | Individual packages or units within a batch are assigned unique serial numbers or codes to enable precise tracking. |
| Aggregation | The unique identifiers of individual packages are linked to higher-level packaging (cases, pallets, etc.) to track product movement at different levels. |
| Data Exchange | Real-time data sharing between stakeholders in the supply chain (manufacturers, distributors, etc.) to ensure transparency and visibility. |
| Scanning and Verification | Scanning devices such as barcode readers or handheld scanners are used to capture unique identifiers for verification and tracking purposes. |
| Traceability and Monitoring | Real-time monitoring and traceability of pharmaceutical products from manufacturing to distribution, tracking movement between facilities and transportation routes. |
| Compliance and Reporting | Generation of reports and documentation to comply with regulatory requirements and provide an audit trail of the product’s journey. |
| Recall Management | Swift identification of affected products, distribution channels, and specific batches in the event of a recall for targeted and efficient recalls. |
Major Components of Track and Trace System in Pharmaceutical
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Unique Identification | Assigns unique identifiers (serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes) to pharmaceutical products or packaging units. |
| Data Capture | Captures and associates relevant data (batch number, manufacturing date, expiration date, etc.) with unique identifiers. |
| Packaging Integration | Applies unique identifiers to pharmaceutical packaging using labeling, printing, or marking technologies. |
| Data Management | Stores captured data and unique identifiers in a centralized database or cloud-based system for tracking and tracing. |
| Serialization | Assigns unique serial numbers or codes to individual packages or units within a batch for precise tracking. |
| Aggregation | Links unique identifiers of individual packages to higher-level packaging (cases, pallets, etc.) for tracking at different levels. |
| Data Exchange | Facilitates real-time data sharing between supply chain stakeholders (manufacturers, distributors, etc.) for transparency and visibility. |
| Scanning Devices | Utilizes barcode readers or handheld scanners to capture unique identifiers for verification and tracking. |
| Traceability and Monitoring | Enables real-time monitoring and traceability of pharmaceutical products throughout the supply chain. |
| Compliance and Reporting | Generates reports and documentation to comply with regulations and provide an audit trail of product movements. |
| Recall Management | Supports swift identification of affected products, distribution channels, and specific batches during recall processes. |
Validation steps in Track and Trace System
The validation steps of a Track and Trace system in pharmaceutical packing involve a series of activities to ensure that the system is functioning accurately and in compliance with regulatory requirements. Here are the key validation steps:
User Requirements Specification (URS): This step involves defining and documenting the specific requirements of the Track and Trace system based on user needs, regulatory guidelines, and industry standards. It outlines the functionalities, performance criteria, and system capabilities.
Design Specification: The design specification phase focuses on translating the user requirements into a detailed technical design. It includes the hardware, software, and network infrastructure components, as well as the integration with existing systems and data management processes.
Installation Qualification (IQ): IQ validates the proper installation of the Track and Trace system components, such as servers, scanners, databases, and software. It verifies that all hardware and software components are correctly installed, configured, and integrated.
Operational Qualification (OQ): OQ tests the functionality of the Track and Trace system in line with the predefined requirements. It verifies that the system operates as intended and performs the expected functions accurately. This includes testing barcode scanning, data capture, serialization, aggregation, and data exchange processes.
Performance Qualification (PQ): PQ evaluates the performance of the Track and Trace system under normal operating conditions. It assesses the system’s ability to handle a realistic volume of data, process transactions within acceptable timeframes, and maintain data integrity and security.
System Integration Testing: This step ensures that the Track and Trace system seamlessly integrates with other relevant systems, such as manufacturing execution systems (MES), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and supply chain management systems. It verifies data exchange, synchronization, and interoperability.
Data Integrity Testing: Data integrity testing validates the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data captured, stored, and exchanged by the Track and Trace system. It includes checks for data validation, error handling, data synchronization, and backup and recovery processes.
Compliance Validation: Compliance validation ensures that the Track and Trace system meets regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as those set by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) guidelines. It verifies adherence to serialization regulations and data privacy and security standards.
Documentation and Training: Thorough documentation of the validation activities, test results, and system configurations is crucial. Additionally, training programs should be conducted to ensure that system users and operators are well-trained on the functionality, operation, and maintenance of the Track & Trace system.
Periodic Revalidation: Regular revalidation should be performed to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness of the Track & Trace system. This includes retesting the system after any significant changes, upgrades, or modifications.
Validation of the Track & Trace system is essential to demonstrate its reliability, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It helps pharmaceutical companies ensure the integrity of their packaging processes, maintain product safety, and meet regulatory obligations throughout the supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Track & Trace system in pharmaceutical packing?
Answer: A Track & Trace system is a technology-driven solution that enables the monitoring and tracing of pharmaceutical products throughout the supply chain, ensuring product authenticity, safety, and regulatory compliance.
What are the unique identifiers used in a Track & Trace system?
Answer: Unique identifiers in a Track & Trace system can include serial numbers, barcodes, QR codes, or other unique codes assigned to each pharmaceutical product or packaging unit.
How does a Track & Trace system capture and associate data with unique identifiers?
Answer: Relevant data, such as batch numbers, manufacturing dates, expiration dates, and destination information, is captured and associated with unique identifiers through data capture processes integrated into the packaging workflow.
What is serialization in a Track & Trace system?
Answer: Serialization is the process of assigning unique serial numbers or codes to individual packages or units within a batch. It allows for precise tracking and traceability of each unit throughout the supply chain.
How does aggregation work in a Track & Trace system?
Answer: Aggregation involves linking the unique identifiers of individual packages to higher-level packaging, such as cases, pallets, or shipments. This hierarchical relationship enables tracking at different levels of packaging.
What scanning devices are used in a Track & Trace system?
Answer: Scanning devices such as barcode readers, handheld scanners, or mobile devices with scanning capabilities are commonly used to capture the unique identifiers for verification and tracking purposes.
How does a Track & Trace system ensure data exchange between supply chain stakeholders?
Answer: A Track & Trace system facilitates real-time data sharing through secure data exchange protocols or platforms, enabling stakeholders such as manufacturers, distributors, and pharmacies to access and exchange information.
What is the role of a centralized database in a Track and Trace system?
Answer: A centralized database or cloud-based system stores the captured data and unique identifiers, acting as a repository for tracking and tracing pharmaceutical products. It allows for efficient data management and retrieval.
How does a Track & Trace system enhance supply chain visibility and transparency?
Answer: By capturing and sharing real-time data, a Track & Trace system provides visibility into the movement of pharmaceutical products across the supply chain, promoting transparency and accountability.
What are the benefits of a Track & Trace system for recall management?
Answer: A Track & Trace system enables swift identification of affected products, their distribution channels, and specific batches, facilitating targeted recalls and minimizing the impact on patient safety.
How does a Track & Trace system support regulatory compliance?
Answer: A Track & Trace system generates reports and documentation that comply with regulatory requirements, providing an audit trail of product movements and facilitating regulatory inspections.
What role does a Track & Trace system play in combating counterfeit drugs?
Answer: A Track & Trace system helps verify the authenticity of pharmaceutical products, aiding in the detection and prevention of counterfeit drugs in the market.
How does a Track & Trace system assist in quality control processes?
Answer: By monitoring and tracking the movement of pharmaceutical products, a Track & Trace system enables the identification of quality issues, such as tampering or contamination, facilitating timely corrective actions.
Can a Track & Trace system help in investigating counterfeit drug cases?
Answer: Yes, a Track & Trace system provides detailed traceability data, assisting in forensic analysis and investigations to identify the source and distribution of counterfeit drugs.