21 CFR Part 11, also known as Title 21 Code of Federal Regulations Part 11, is a regulation issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that sets forth the requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries. It applies to pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), clinical research organizations (CROs), and other entities that are subject to FDA regulations and use electronic systems to create, modify, maintain, archive, retrieve, or transmit electronic records that are required to be maintained by the FDA.
The main purpose of 21 CFR Part 11 is to ensure the integrity, authenticity, and reliability of electronic records and electronic signatures, which are used as substitutes for paper records and handwritten signatures. It establishes requirements for the security, integrity, and availability of electronic records and the validation of electronic systems used for GxP (Good Laboratory Practices, Good Clinical Practices, Good Manufacturing Practices) activities. It also outlines the procedures for creating, reviewing, and approving electronic signatures and requires that electronic signatures be legally binding and equivalent to handwritten signatures.

Key requirements of 21 CFR Part 11 include
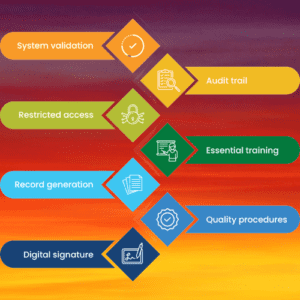
- System validation: Electronic systems used for GxP activities must be validated to ensure that they are operating reliably, securely, and accurately, and that they are capable of generating accurate and reliable electronic records.
- Access controls: Access to electronic records must be restricted to authorized personnel, and there must be controls in place to prevent unauthorized access, modification, or deletion of electronic records.
- Audit trails: Electronic systems must have audit trail functionality that captures and retains a record of all changes made to electronic records, including the identity of the person making the change, the date and time of the change, and a description of the change.
- Electronic signatures: Electronic signatures used to sign electronic records must be unique to the individual, verifiable, and protected from unauthorized use. There must be controls in place to ensure that electronic signatures are applied only by authorized signatories and that they cannot be tampered with.
- Record retention: Electronic records must be retained in a manner that ensures their integrity, authenticity, and reliability throughout their retention period, and they must be readily retrievable for inspection, review, and copying by authorized personnel.
Compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 is important for pharmaceutical companies and other regulated entities to ensure that their electronic records and electronic signatures are accepted by the FDA as legally equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures. Failure to comply with 21 CFR Part 11 can result in regulatory enforcement actions, including warning letters, fines, and product recalls.
History of 21 CFR Part 11
The history of 21 CFR Part 11 dates back to the 1990s when the use of electronic records and signatures in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries was becoming more prevalent. The FDA recognized the need to establish regulatory requirements to ensure the integrity, authenticity, and reliability of electronic records and signatures, as well as to provide guidance on their use in regulated industries.
In August 1997, the FDA issued a proposed rule for electronic records and electronic signatures, which was published in the Federal Register as “Part 11 – Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures“ (62 FR 13429). The proposed rule aimed to establish requirements for the use of electronic records and signatures that would be equivalent to the requirements for paper records and handwritten signatures, as set forth in other FDA regulations.
After receiving public comments on the proposed rule, the FDA issued the final rule for 21 CFR Part 11 on March 20, 1997, and it became effective on August 20, 1997. The final rule was published in the Federal Register as “Part 11 – Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures” (62 FR 24230). The final rule included requirements for the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in FDA-regulated industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical devices, and outlined the expectations for compliance.
Over the years, there have been various interpretations, clarifications, and guidance documents issued by the FDA to provide further guidance on the implementation and compliance of 21 CFR Part 11. In particular, the FDA issued a guidance document titled “Part 11, Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures – Scope and Application” in 2003, which provided additional clarity on the scope of Part 11 and the FDA’s enforcement approach.
In recent years, the FDA has been actively engaging with stakeholders and considering modernization efforts for Part 11 to keep pace with technological advancements and industry practices, including the use of cloud computing, mobile devices, and advanced data analytics. As of the knowledge cutoff date of this model (September 2021), the FDA has not issued any significant updates or revisions to 21 CFR Part 11, but it’s always important to stay up-to-date with the latest regulatory guidance and requirements from the FDA or other relevant regulatory authorities. 21 CFR Part 11 also helps in cyber securities.
Step for implementation of 21 CFR part 11
Implementing 21 CFR Part 11 in pharmaceutical plants involves several steps, which may include:
- Gap Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of existing systems and processes to identify gaps between current practices and the requirements outlined in 21 CFR Part 11. This may involve reviewing electronic systems, data management processes, and standard operating procedures (SOPs) to identify areas that need to be addressed for compliance.
- System Validation: Ensure that electronic systems used for GxP activities, such as manufacturing, laboratory testing, and documentation, are validated according to the FDA’s guidelines for computerized systems validation. This includes documenting and verifying that the systems are operating as intended, and that they meet the requirements for accuracy, reliability, and security.
- Access Controls: Establish and implement appropriate access controls to restrict access to electronic records and systems to authorized personnel only. This may involve implementing unique user IDs, strong passwords, and role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that users have appropriate permissions and privileges based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Audit Trails: Implement audit trail functionality in electronic systems to capture and retain a record of all changes made to electronic records. This includes capturing the identity of the person making the change, the date and time of the change, and a description of the change, to ensure the integrity and traceability of electronic records.
- Electronic Signatures: Implement electronic signature functionality in accordance with the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11. This may involve establishing procedures for creating, managing, and verifying electronic signatures, and ensuring that electronic signatures are unique to the individual, verifiable, and protected from unauthorized use.
- Record Retention: Establish procedures for the retention and archiving of electronic records in a manner that ensures their integrity, authenticity, and reliability throughout their retention period. This may involve implementing appropriate backup and storage mechanisms, and ensuring that records are readily retrievable for inspection, review, and copying by authorized personnel.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Review and update SOPs to reflect the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, including procedures for the use of electronic records and electronic signatures, system validation, access controls, audit trails, and record retention.
- Training and Documentation: Provide training to personnel involved in the use of electronic records and electronic signatures, as well as documentation of the procedures and processes implemented to comply with 21 CFR Part 11. This includes maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation of all relevant processes, procedures, and training records.
- Ongoing Compliance Monitoring: Establish processes for ongoing monitoring and review of electronic systems and processes to ensure continued compliance with 21 CFR Part 11. This may involve conducting periodic audits, reviews, and assessments to identify and address any gaps or non-compliance issues that may arise.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintain accurate and complete documentation of all activities related to the implementation and ongoing compliance with 21 CFR Part 11. This includes documenting any changes or updates made to systems, processes, or procedures, as well as preparing and submitting reports to regulatory authorities as required.
It’s important to note that implementing 21 CFR Part 11 in pharmaceutical plants is a complex and ongoing process that requires a thorough understanding of the regulation, as well as diligent planning, implementation, and monitoring to ensure continued compliance. Seeking guidance from regulatory experts and legal counsel is recommended to ensure proper implementation and adherence to the regulation.
Different parts of 21 CFR Part 11
21 CFR Part 11 consists of several sections, or subparts, that outline the requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures in the pharmaceutical industry. The different parts of 21 CFR Part 11 are as follows:
- Subpart A: General Provisions: This section provides general definitions, scope, and applicability of 21 CFR Part 11, and sets forth the purpose and objectives of the regulation.
- Subpart B: Electronic Records: This section outlines the requirements for electronic records, including validating electronic systems, access controls, audit trails, electronic signatures, record retention, and documentation.
- Subpart C: Electronic Signatures: This section details the requirements for electronic signatures, including their use, creation, and management, as well as their security and integrity.
- Subpart D: Controls for Closed Systems: This section focuses on the controls required for closed systems, which are electronic systems where only authorized personnel can access the operating system.
- Subpart E: Controls for Open Systems: This section covers the controls required for open systems, which are electronic systems that are accessible to both authorized and unauthorized personnel.
- Subpart F: Signature Manifestations: This section outlines the requirements for signature manifestations, which are the methods used to display or indicate electronic signatures in electronic records.
- Subpart G: General Requirements: This section provides general requirements for electronic records and electronic signatures, including their accuracy, integrity, availability, and legibility.
- Subpart H: Preservation of Records: This section focuses on the requirements for the preservation of electronic records, including their retention, protection from loss, and access during inspections.
- Subpart I: Electronic Copies of Records: This section details the requirements for electronic copies of records, including their creation, maintenance, and retrieval.
- Subpart J: Audit Trail: This section outlines the requirements for audit trails, which are electronic records that capture and retain information about changes made to electronic records.
It’s important to note that compliance with all applicable sections of 21 CFR Part 11 is necessary to ensure compliance with the regulation as a whole. The specific requirements may vary depending on the type and complexity of the electronic systems and processes used in the pharmaceutical industry. It’s recommended to consult with regulatory experts and legal counsel to ensure proper implementation and adherence to the regulation.


21 cfr part 11 compliance checklist
A compliance checklist can be a helpful tool to ensure that pharmaceutical plants are meeting the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11. Here is a general checklist that may be used as a reference for implementing and maintaining compliance with 21 CFR Part 11:
- System Validation:
- Are all electronic systems used for GxP activities validated according to FDA guidelines for computerized systems validation?
- Is there documentation that verifies that electronic systems are operating as intended and meeting the requirements for accuracy, reliability, and security?
- Access Controls:
- Are appropriate access controls in place to restrict access to electronic records and systems to authorized personnel only?
- Do users have unique user IDs, strong passwords, and role-based access controls (RBAC) based on their roles and responsibilities?
- Audit Trails:
- Do electronic systems capture and retain an audit trail of all changes made to electronic records, including the identity of the person making the change, the date and time of the change, and the description of the change?
- Is there a process in place to review and analyze audit trails for any unauthorized or inappropriate activities?
- Electronic Signatures:
- Are electronic signatures implemented in accordance with the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, including procedures for creating, managing, and verifying electronic signatures?
- Are electronic signatures unique to the individual, verifiable, and protected from unauthorized use?
- Record Retention:
- Are there procedures in place for the retention and archiving of electronic records that ensure their integrity, authenticity, and reliability throughout their retention period?
- Are electronic records backed up and stored in a secure manner, and readily retrievable for inspection, review, and copying by authorized personnel?
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
- Have SOPs been reviewed and updated to reflect the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, including procedures for the use of electronic records and electronic signatures, system validation, access controls, audit trails, and record retention?
- Are SOPs accurate, up-to-date, and followed consistently by personnel?
- Training and Documentation:
- Have personnel involved in the use of electronic records and electronic signatures received appropriate training?
- Is there documentation of the training provided, as well as the procedures and processes implemented to comply with 21 CFR Part 11?
- Ongoing Compliance Monitoring:
- Are there processes in place for ongoing monitoring and review of electronic systems and processes to ensure continued compliance with 21 CFR Part 11?
- Are periodic audits, reviews, and assessments conducted to identify and address any gaps or non-compliance issues that may arise?
- Documentation and Reporting:
- Is there accurate and complete documentation of all activities related to the implementation and ongoing compliance with 21 CFR Part 11?
- Are reports prepared and submitted to regulatory authorities as required?
It’s important to note that this checklist serves as a general reference and that the specific requirements for compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 may vary depending on the individual pharmaceutical plant and the electronic systems and processes in use. It’s recommended to consult with regulatory experts and legal counsel to ensure proper implementation and adherence to the regulation.


Frequently Asked Questions for 21 CFR Part 11
What is 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: 21 CFR Part 11 is a regulation established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that outlines the requirements for the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in FDA-regulated industries, including pharmaceuticals.
Why was 21 CFR Part 11 introduced?
Answer: 21 CFR Part 11 was introduced to keep pace with the increasing use of electronic systems and technology in FDA-regulated industries while maintaining the same level of data integrity, authenticity, and reliability as paper-based systems.
Who is required to comply with 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Companies that use electronic records and electronic signatures in FDA-regulated activities, including pharmaceutical manufacturers, contract research organizations, and other stakeholders in the pharmaceutical industry, are required to comply with 21 CFR Part 11.
What are the key requirements of 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: The key requirements of 21 CFR Part 11 include system validation, access controls, audit trails, electronic signatures, and record retention. These requirements ensure the integrity, authenticity, and reliability of electronic records and electronic signatures used in FDA-regulated activities.
What is system validation as per 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: System validation refers to the process of demonstrating that electronic systems used for GxP activities (e.g., Good Manufacturing Practice, Good Laboratory Practice, Good Clinical Practice) are reliable, accurate, and secure and that they are suitable for their intended use in accordance with regulatory requirements.
What are access controls under 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Access controls refer to the measures put in place to restrict access to electronic records to authorized personnel only. This includes using unique user IDs, passwords, and role-based access controls (RBAC) to manage user permissions and privileges and prevent unauthorized access, modification, or deletion of electronic records.
What are audit trails according to 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Audit trails are a requirement of 21 CFR Part 11 that involves the capture and retention of a record of all changes made to electronic records. This includes capturing the identity of the person making the change, the date and time of the change, and a description of the change, to ensure the integrity and traceability of electronic records.
What are electronic signatures under 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Electronic signatures are used as a means of signing electronic records in lieu of traditional paper-based signatures. According to 21 CFR Part 11, electronic signatures must be unique to the individual, verifiable, and protected from unauthorized use, and must be linked to the corresponding electronic record.
What are record retention requirements under 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Record retention requirements under 21 CFR Part 11 specify that electronic records must be retained in a manner that ensures their integrity, authenticity, and reliability throughout their retention period. They must also be readily retrievable for inspection, review, and copying by authorized personnel in accordance with record retention policies.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with 21 CFR Part 11?
Answer: Non-compliance with 21 CFR Part 11 can result in regulatory action by the FDA, including warning letters, fines, or product recalls, which can have significant legal and financial consequences for pharmaceutical companies and other stakeholders in the regulated industries.
