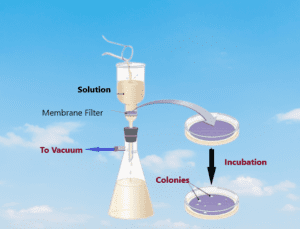
The membrane filter method stands as a formidable technique, offering a window into the intricate world of microorganisms. With its unique approach and diverse applications, this method has revolutionized the field, enabling researchers to isolate, enumerate, and study microbial communities with precision. In this article, we delve into the essence of the membrane filter method, unraveling its fundamental principles, exploring its methodology, and highlighting its significance in microbial analysis.
At the heart of the membrane filter method lies a set of core principles that underpin its efficacy. The method harnesses the power of specialized membranes, designed with precise pore sizes, to act as sieves, selectively trapping microorganisms while allowing the passage of fluids. This principle of size-based separation forms the foundation of the technique, facilitating the isolation and concentration of microorganisms from complex samples.
Types of membrane filters
Cellulose Acetate Filters:
- Cellulose acetate filters are commonly used in pharmaceutical manufacturing due to their excellent flow characteristics and low protein binding properties. These filters offer high filtration efficiency and are often employed for sterile filtration, removal of particulate matter, and clarification of pharmaceutical solutions.
Polyethersulfone Filters:
- Polyethersulfone (PES) filters are widely utilized in pharmaceutical applications due to their high thermal and chemical resistance. These filters provide reliable retention of microorganisms, viruses, and particulate matter. PES filters are commonly employed for sterile filtration, virus removal, and final filtration steps in pharmaceutical production.
Polyvinylidene Difluoride Filters:
- Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filters are known for their exceptional chemical compatibility and hydrophobic nature. These filters are resistant to a wide range of solvents and aggressive chemicals, making them suitable for filtration processes that involve harsh conditions. PVDF filters are commonly used for sterile filtration, solvent filtration, and clarification of pharmaceutical solutions.
Nylon Filters:
- Nylon filters possess excellent strength and durability, making them suitable for various pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. These filters offer high flow rates and are commonly used for the filtration of solutions with large particulate matter, pre-filtration, and clarification steps in pharmaceutical production.
Polytetrafluoroethylene Filters:
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) filters are characterized by their exceptional chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance. These filters are utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes that involve aggressive chemicals and elevated temperatures. PTFE filters are commonly employed for sterile filtration, solvent filtration, and gas filtration applications.
Mixed Cellulose Esters Filters:
- Mixed cellulose esters (MCE) filters combine the advantages of cellulose acetate and nitrocellulose filters. They offer good chemical compatibility and low protein binding properties. MCE filters are commonly used for general filtration applications in pharmaceutical manufacturing, including sterile filtration, particulate removal, and clarification of solutions.
Membrane Filter Cartridges:
- Membrane filter cartridges consist of membranes integrated into cartridge housings, allowing for easy and efficient filtration in pharmaceutical processes. These cartridges are available in various membrane materials such as PES, PVDF, and nylon. They are commonly utilized for large-scale sterile filtration, final filtration, and process filtration in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Each type of membrane filter offers specific characteristics and advantages, making them suitable for different applications within pharmaceutical manufacturing. The selection of the appropriate membrane filter depends on factors such as the nature of the pharmaceutical solution, required filtration efficiency, chemical compatibility, and regulatory compliance.
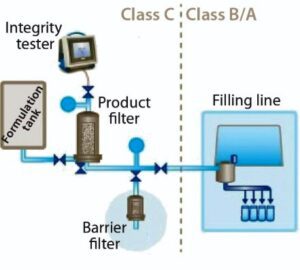
Applications of Membrane filtration
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Sterilization of Liquids | Membrane filtration is commonly used for the sterile filtration of liquids, ensuring the removal of microorganisms and particles to maintain product integrity and safety. |
| Removal of Particulate Matter | Membrane filters are employed to remove particulate matter, such as contaminants, debris, and aggregates, from pharmaceutical solutions, ensuring product clarity and quality. |
| Virus Removal | Membrane filtration plays a vital role in removing viruses from biopharmaceutical products, ensuring the safety and purity of therapeutic agents. |
| Protein Concentration | Membrane filters are utilized for protein concentration through ultrafiltration, enabling the removal of excess solvent and low-molecular-weight impurities. |
| Formulation and Buffer Preparation | Membrane filtration is employed in the preparation of formulation components and buffers, ensuring their sterility and removing any potential contaminants. |
| Aseptic Sampling | Membrane filters are used for aseptic sampling during pharmaceutical manufacturing processes, allowing for microbiological testing and quality control. |
| Endotoxin Testing | Membrane filters are utilized in endotoxin testing to remove endotoxins from pharmaceutical samples, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. |
| Parenteral Drug Manufacturing | Membrane filtration is a critical step in the manufacturing of parenteral drugs, ensuring the removal of microbial contaminants and particles from the final product. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Membrane Filters
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Precise and Selective Filtration | Potential Membrane Fouling |
| High Filtration Efficiency | Limited Scalability |
| Versatility in Pore Size Selection | Cost of Filter Replacement and Maintenance |
| Compatibility with a Wide Range of Solutions | Potential Loss of Biological Activity |
| Removal of Microorganisms and Particulate Matter | Variability in Membrane Performance |
| Minimal Sample Loss | Susceptibility to Chemical and Physical Damage |
| Sterile Filtration | Potential Adsorption or Binding of Components |
| Facilitates Concentration and Purification Processes | Requirement for Optimal Operating Conditions |
Frequently Asked Questions:
what is a membrane filter?
Answer: A membrane filter, also known as a microporous filter, is a thin, porous material that selectively separates particles and substances based on their size and molecular weight. It is commonly used in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, environmental monitoring, and research laboratories.
The membrane filter consists of a matrix of tiny pores that allow the passage of specific particles or molecules while retaining others. The size of the pores can vary depending on the application and the desired filtration requirements. Membrane filters can have pore sizes ranging from nanometers to micrometers.
The material used to construct membrane filters can vary, including polymers such as cellulose acetate, polyethersulfone, polyvinylidene difluoride, nylon, and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Each material offers different characteristics such as chemical compatibility, thermal stability, and hydrophobic or hydrophilic properties.
Membrane filters can be used for a wide range of filtration processes, including sterilization, particulate removal, clarification, concentration, and separation. They can be employed in liquid filtration to remove microorganisms, particulate matter, or impurities, ensuring the purity and quality of the filtrate. In gas or air filtration, membrane filters can trap contaminants and airborne particles, providing clean and pure air.
The selection of a membrane filter depends on the specific application, including the type of fluid or gas being filtered, the desired filtration efficiency, the chemical compatibility, and the regulatory requirements. Different pore sizes and materials may be chosen to achieve the desired level of filtration and retain specific particles or microorganisms.
In summary, a membrane filter is a porous material that acts as a selective barrier, allowing the passage of certain particles or molecules while retaining others. It is an essential tool for various filtration processes, ensuring the purification, sterilization, and separation of substances in industries where precise filtration is crucial.
What are membrane filters in the context of pharmaceuticals?
Answer: Membrane filters are porous materials that selectively separate particles and microorganisms from pharmaceutical solutions through filtration.
What are the key applications of membrane filters in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: Membrane filters are used for sterile filtration, removal of particulate matter, virus removal, protein concentration, formulation and buffer preparation, aseptic sampling, endotoxin testing, and parenteral drug manufacturing.
What factors should be considered when selecting a membrane filter for pharmaceutical applications?
Answer: Factors to consider include filtration efficiency, pore size, chemical compatibility, flow rate, scalability, membrane integrity, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
How do membrane filters ensure sterility in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes?
Answer: Membrane filters act as barriers, preventing the passage of microorganisms and particles, thereby maintaining the sterility of pharmaceutical solutions and protecting the final product.
How do membrane filters contribute to the removal of particulate matter in pharmaceutical solutions?
Answer: Membrane filters with appropriate pore sizes selectively trap and retain particles, contaminants, and aggregates, ensuring product clarity and quality.
What challenges can be encountered with membrane filters in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: Membrane fouling, filter clogging, potential loss of biological activity, and variability in membrane performance are some challenges that may arise.
What steps can be taken to optimize the performance of membrane filters in pharmaceutical applications?
Answer: Proper filter selection, optimization of filtration parameters, adherence to handling and storage protocols, and regular maintenance are key steps to ensure optimal filter performance.
What are the consequences of membrane fouling in pharmaceutical filtration processes?
Answer: Membrane fouling can lead to reduced filtration efficiency, increased pressure drop, and decreased throughput, necessitating filter replacement or cleaning.
How can the integrity of membrane filters be assessed during pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: Integrity testing methods such as bubble point, diffusion, or pressure hold tests can be employed to ensure the integrity of membrane filters and validate their performance.
What advancements are being made in membrane filtration technology for pharmaceutical applications?
Answer: Ongoing research aims to develop improved membrane materials, enhanced filtration techniques, and innovative solutions to address challenges such as fouling, scalability, and compatibility with complex pharmaceutical formulations.
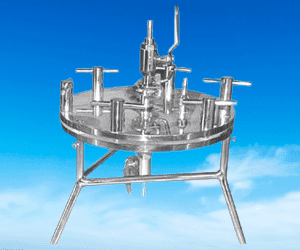
What is a membrane filter holder used for?
Answer: A membrane filter holder, also known as a filter funnel, is a device specifically designed for the efficient use of membrane sterile filters in various filtration processes. It serves as a support structure for the membrane sterile filter, facilitating its proper positioning and secure attachment during filtration operations. The primary purpose of a membrane filter holder is to hold the filter in place while allowing the flow of the filtrate through the filter membrane.
The membrane filter holder typically consists of a funnel-shaped component with a connection point for the vacuum source or pressure system. The membrane sterile filter is placed on the holder, ensuring that it is evenly supported and properly aligned. The holder may have a seal or O-ring to create a tight seal between the filter and the holder, preventing any bypass or leakage during filtration.
By using a membrane filter holder, the filtration process becomes more efficient and convenient. It enables the controlled passage of the liquid or gas through the membrane filter, ensuring that only the desired particles or microorganisms are retained while allowing the filtrate to pass through. The holder also facilitates the easy removal and replacement of the membrane sterile filter after filtration is complete.
Membrane sterile filter holders find extensive applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, environmental monitoring, and research laboratories. They are essential tools for processes such as sterilization, clarification, particulate removal, and microorganism enumeration, where precise filtration is required to achieve reliable and consistent results.
What is sterile membrane filter?
Answer: A membrane sterile filter, also known as a sterile filter or sterilizing-grade filter, is a specialized type of membrane sterile filter that is designed to achieve microbial sterility by effectively removing microorganisms from fluids or gases during filtration. It is commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food and beverage, and healthcare settings to ensure the sterility of products, processes, and environments.
A sterile membrane sterile filter possesses a pore size small enough to retain microorganisms while allowing the passage of the desired filtrate. The typical pore sizes used for sterile filtration range from 0.1 to 0.45 micrometers, effectively capturing bacteria, fungi, and larger viruses. The membrane material is selected for its compatibility with the intended application and the ability to provide reliable microbial retention.
To maintain sterility, the sterile membrane sterile filter is manufactured and packaged under controlled and validated conditions to prevent any contamination. It is commonly pre-sterilized using methods such as gamma irradiation or ethylene oxide gas. The filter is then provided in a sealed and sterile packaging to preserve its sterility until ready for use.
During filtration, the sterile membrane sterile filter is connected to a filter holder or filtration system, and the fluid or gas to be filtered is passed through the filter. The filter retains any microorganisms present in the fluid or gas, ensuring that the filtrate is free from viable contaminants. This process is crucial in applications where microbial contamination can compromise product quality, safety, or efficacy.
Sterile membrane sterile filters are widely utilized in various processes, including sterile filtration of liquids, aseptic processing, air and gas sterilization, and biological fluid filtration. They play a critical role in maintaining the sterility of pharmaceutical formulations, parenteral drug manufacturing, vaccine production, laboratory research, and cleanroom environments.
Overall, membrane sterile filters provide a reliable and efficient means of achieving microbial sterility in fluid and gas streams, ensuring the safety and integrity of products and processes in industries that require stringent control of microbial contamination.

1 thought on “Membrane Filter Technique in Pharma 2023”