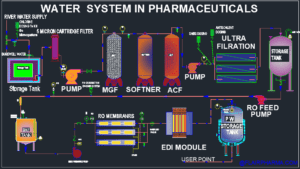
- OBJECTIVE:
- To lay down the procedure for the Regeneration of a Mixed Bed in a DM plant.
- SCOPE:
- This SOP is applicable for the regeneration of a mixed bed in a DM plant.
- RESPONSIBILITY:
- Officer / Executive Engineering: To follow SOP.

- ACCOUNTABILITY:
- Head Engineering: Implementation of SOP.
- ABBREVIATIONS:
SOP Standard Operating Procedure
RO Reverse Osmosis
HDPE High Density Poly Ethylene
QC Quality Control
UV Ultra Violet
- PROCEDURE:
- Ensure that the mixed bed and pipelines are clean.
- Open the RO water storage tank outlet valve.
- Open the required valve and start the pump.
- Do the backwash for 15 minutes.
- Regeneration of mixed bed with sodium hydroxide. (NAOH)
- Take 40 ltrs. RO water from the RO tank in an HDPE container and add 4 kg of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and Mix with the help of a rod.
- Insert the ejector tube in HDPE container containing sodium hydroxide solution.
- Open the required valve & start the Feed water pump at the pressure of 1 to 2 kg/cm2.
- After starting the pump, pass out all NAOH solution through a mixed bed. Its take approx 15 to 20 minutes. After completion of the process, allow slow rinsing with RO water for about 05 to 10 minutes.
- After completion of slow rinsing, switch off the motor and close the valve no. and open the required valve.
- Now start the pump and allow the fast rinsing with RO water for 05 to 10 minutes.
- Regeneration of mixed bed with Hydrochloric acid.
- Take 36 ltrs. RO water from RO tank in HDPE container & add 12 ltrs. hydrochloric acid with stirring.
- Insert the Ejector tube in HDPE container containing hydrochloric acid.
- Open the required valves & close other valves.
- Open the RO water valve & switch on the pump.
- After start the pump allow to pass out all hydrochloric acid solution through mixed bed. Its take approx 15 to 20 minutes. After completion of process, & allow rinsing with RO water about 05 to 10 minutes.
- After completion of slow rinsing, switch off the motor and close the valve no. 3, 5 and open the valve no. 4.
- Now start the pump and allow the fast rinsing with RO water for 05 to 10 minutes.
- Stop the in feed motor and closed all valve.
- Mixing of Resin with air.
- Open the 07 and 12 No.valve.
- Pass the compressed air at low pressure (0.7 kg/cm2) through mixed bed for 10 to 15 minutes.
- Open the required valve and Switch ON the feed water pump and run the water through the mixed bed and check the conductivity.
- The conductivity shall be less than 1.3 µS/cm.
- Now open the valve no. 06 and close the valve no. 13 & 14
- Start UV light hour meter counter and conductivity meter.
- Check the conductivity of water it should be NMT 1.3 µS/cm. if the conductivity of water is more than the specified limit then repeat the points 6.4, 6.5 & 6.6.
- Inform to QC department to collect the sample.
- Collect the purified water in SS tank after approval from QC.
- Maintain the regeneration record in Annexure – I “Mixed Bed Regeneration Record”.
- Maintain the Mixed Bed Regeneration Output Record in Annexure – II “Mixed Bed Output Record”.

- ANNEXURES:
| ANNEXURES NO. | TITLE OF ANNEXURE | FORMAT NO. |
| Annexure-I | Mixed Bed Regeneration Record | EN-0XX/FYY-00 |
| Annexure-II | Mixed Bed Output Record | EN-0XX/FYY-00 |
- DISTRIBUTION:
- Controlled Copy No. 1 Head Engineering
- Master Copy Quality Assurance Department
- REFERENCES:
Not applicable
- REVISION HISTORY:
| Revision No. | Change Control No. | Details of Changes | Reason for Change | Effective Date | Updated By |
| 00 | CC/XX/XXX | Preparation of New SOP |
MIXED BED REGENERATION RECORD
| MIXED BED REGENERATION RECORD | |||||||||||
| Date | Qty. of NaOH for Regeneration | Qty. of water added | Regeneration detail | Qty. of HCL for Regeneration | Qty. of water added | Regeneration detail | Done by | Checked by Sign & Date | |||
| From | To | From | To | ||||||||
MIXED BED OUTPUT RECORD
| Date | Start time | Stop time | Duration | Qty. generate (Ltrs.) | Conductivity (NMT 1.3 µS/cm | pH (5.5 to 7.0) | U.V. Light Reading | Operated By | Checked by Sign & Date | |
| At start time | At stop time | |||||||||
You may also read about:
Water Systems in the Pharmaceuticals