Incidents in the pharmaceutical industry refer to unexpected events or occurrences that disrupt normal operations and have implications for patient safety, regulatory compliance, or ethical standards. These incidents can encompass a wide range of situations, such as product recalls, adverse drug reactions, manufacturing issues, regulatory violations, data breaches, ethical misconduct, and supply chain disruptions.
When an incident occurs in the pharmaceutical sector, it triggers investigations and analyses to identify the root causes, evaluate the impact, and implement appropriate corrective actions. The goal is to prevent recurrence, protect patient safety, ensure regulatory compliance, and maintain the integrity of the industry.
Incidents in pharmaceuticals are of significant importance due to their potential impact on public health, patient well-being, and the overall reputation of pharmaceutical companies. They expose vulnerabilities in processes and systems, highlighting the need for improved safety measures, stricter regulations, and enhanced quality control practices. Incidents also serve as learning opportunities, driving continuous improvement, fostering scientific advancements, and promoting industry-wide knowledge sharing.
Effective management of incidents involves collaboration among pharmaceutical companies, regulatory authorities, healthcare professionals, and other stakeholders. Transparent communication, timely reporting, and proactive risk management are crucial in mitigating the consequences of incidents and restoring trust in the industry.
By learning from incidents and implementing preventive measures, the pharmaceutical industry aims to continuously improve patient safety, enhance product quality, and uphold ethical standards. The ability to effectively respond to incidents and embrace a culture of continuous learning and improvement is paramount in ensuring the integrity and sustainability of the pharmaceutical sector.
Important critical key parameters of incident
| Critical Key Parameters of Incidents in Pharma |
|---|
| 1. Impact on Patient Safety: Assessing the potential impact of an incident on patient safety is a crucial parameter, considering the severity of adverse effects and the number of individuals affected. |
| 2. Regulatory Compliance: Evaluating the incident’s alignment with regulatory requirements and guidelines helps determine the level of compliance and potential consequences for non-compliance. |
| 3. Root Cause Analysis: Conducting a comprehensive root cause analysis helps identify the underlying factors that contributed to the incident, enabling targeted corrective actions to address the core issues. |
| 4. Severity of Consequences: Determining the severity of the consequences resulting from the incident, such as patient harm, financial losses, reputational damage, or legal implications, aids in assessing the gravity of the incident. |
| 5. Preventability: Assessing the degree to which the incident could have been prevented by implementing appropriate measures, such as quality control protocols, risk management strategies, or adherence to best practices. |
| 6. Organizational Response: Evaluating the effectiveness and timeliness of the organization’s response to the incident, including communication with stakeholders, implementation of corrective actions, and preventive measures. |
| 7. Recurrence Potential: Analyzing the likelihood of similar incidents occurring in the future based on the identified root causes, vulnerabilities, and systemic issues uncovered during the incident investigation. |
| 8. Lessons Learned: Identifying and documenting the lessons learned from the incident to facilitate continuous improvement, knowledge sharing, and the implementation of preventive measures. |
Types of Incidents in pharma
Within the pharmaceutical industry, various types of incidents can occur, each with its own unique implications and consequences. Here are some common types of incidents that can occur in the realm of pharmaceuticals:
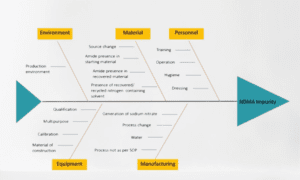
- Product Recalls: Product recalls involve the removal or withdrawal of a pharmaceutical product from the market due to safety concerns, manufacturing defects, contamination, or labeling issues. These incidents aim to protect public health and ensure the integrity of the medication.
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Adverse drug reactions refer to unexpected or harmful reactions experienced by patients after taking a medication. These incidents can range from mild side effects to severe allergic reactions or even life-threatening complications. Monitoring and reporting adverse drug reactions are essential to assess the safety and effectiveness of pharmaceutical products.
- Manufacturing Issues: Manufacturing incidents encompass problems arising during the production process, such as quality control failures, contamination, deviations from standard operating procedures, or equipment malfunctions. These incidents can impact the quality, purity, and consistency of pharmaceutical products.
- Regulatory Violations: Regulatory violations occur when pharmaceutical companies fail to comply with applicable laws, regulations, or guidelines. This can involve issues related to product registration, clinical trial misconduct, improper marketing practices, or failure to meet quality and safety standards. Regulatory authorities closely monitor and enforce compliance to ensure the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products.
- Data Breaches: With the increasing reliance on digital systems and data management, incidnts involving data breaches have become a concern in the pharmaceutical industry. These incidnts can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of sensitive patient information, intellectual property, or research data.
- Ethical Misconduct: Ethical incidnts involve breaches of ethical standards or misconduct within the pharmaceutical sector. This can include conflicts of interest, inappropriate relationships with healthcare professionals, biased research practices, or failures to disclose relevant information. Maintaining high ethical standards is crucial to preserve the trust and credibility of the industry.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Supply chain incidnts encompass disruptions in the distribution and availability of pharmaceutical products. These can be caused by factors such as natural disasters, transportation issues, regulatory barriers, or manufacturing challenges. Such incidnts can lead to shortages or delays in the availability of essential medications.
It is important to note that these incidnts are not exhaustive, and the pharmaceutical industry faces ongoing challenges in ensuring product safety, regulatory compliance, and ethical conduct. Prompt identification, effective management, and preventive measures are essential to mitigate the impact of incidnts and uphold public health and trust in the industry.
Importance of Incidents in Pharma
| Importance of Incidents in Pharma |
|---|
| 1. Patient Safety: Incidents play a crucial role in identifying and addressing risks to patient safety, ensuring the well-being of individuals who rely on pharmaceutical products. |
| 2. Regulatory Compliance: Incidents serve as indicators of potential regulatory violations, prompting authorities to enforce compliance and maintain high standards within the industry. |
| 3. Quality Improvement: Incidents drive continuous improvement in manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and product safety, leading to enhanced quality assurance in pharmaceutical production. |
| 4. Risk Management: Incidents highlight potential risks and vulnerabilities within the pharmaceutical sector, enabling proactive risk management strategies and the development of preventive measures. |
| 5. Industry Reputation: Effectively managing and learning from incidents is essential for preserving the reputation and credibility of pharmaceutical companies, fostering trust among healthcare professionals, regulators, and the public. |
| 6. Scientific Advancement: Incidents can lead to scientific discoveries and advancements as investigations into the root causes provide valuable insights and drive innovation in drug development, manufacturing, and safety practices. |
| 7. Regulatory Framework Enhancement: Incidents prompt regulatory authorities to reassess and strengthen regulations, guidelines, and oversight mechanisms, ensuring greater accountability and protection for patients and the public. |
| 8. Continuous Learning: Incidents serve as learning opportunities for the pharmaceutical industry, enabling stakeholders to identify areas for improvement, share best practices, and enhance knowledge and expertise. |
Lab incident in pharma
A lab incident in the pharmaceutical industry refers to an unexpected event or mishap that occurs within a laboratory setting. These incidnts can range from minor accidents or errors to more serious events that may impact the safety of personnel, compromise experimental integrity, or pose risks to the environment or public health.
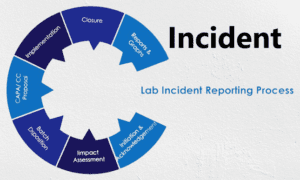
Lab incidnts in the pharmaceutical industry can take various forms, including chemical spills, fires, equipment malfunctions, contamination issues, procedural errors, or personal injuries. Such incidnts can disrupt research and development activities, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and regulatory compliance.
When a lab incidnt occurs, it is essential to follow established safety protocols and procedures to mitigate immediate risks and ensure the well-being of personnel. This may involve evacuation procedures, containment of hazardous materials, provision of medical attention if needed, and prompt reporting of the incidnt to relevant authorities.
Investigating lab incidnts is crucial to identify the root causes and implement corrective actions to prevent future occurrences. Root cause analysis involves examining factors such as human error, equipment failure, inadequate training, or deficiencies in standard operating procedures. Lessons learned from these incidnts help improve lab safety measures, refine protocols, enhance training programs, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Proactive risk management is essential in preventing lab incidnts in the pharmaceutical industry. This includes implementing robust safety protocols, providing adequate training and supervision for lab personnel, maintaining well-maintained equipment, enforcing proper storage and handling of chemicals, and regularly assessing and addressing potential hazards.
Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and other relevant agencies, play a role in overseeing lab safety and may require reporting of significant incidnts. Compliance with regulatory requirements is crucial to ensure the integrity of research, development, and manufacturing processes within the pharmaceutical industry.
Ultimately, effective management of lab incidents in the pharmaceutical industry relies on a proactive approach to safety, continuous training and education, adherence to protocols, and fostering a culture that prioritizes the well-being of personnel and the integrity of scientific endeavors.
Applications of Incident in pharma
| Applications of Incidents in Pharma |
|---|
| 1. Root Cause Analysis: Incidnts provide valuable opportunities for conducting thorough root cause analyses, allowing pharmaceutical companies to identify underlying factors that contributed to the incidnt and implement targeted corrective actions. |
| 2. Process Improvement: By analyzing incidnts, pharmaceutical companies can identify areas for process improvement, optimizing manufacturing practices, quality control measures, and supply chain management to prevent similar incidnts in the future. |
| 3. Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Incidnts help in assessing and mitigating risks associated with pharmaceutical products, enabling companies to implement appropriate risk management strategies and preventive measures to enhance product safety and efficacy. |
| 4. Regulatory Compliance: Incidnts assist pharmaceutical companies in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, as they provide insights into areas where non-compliance occurred, prompting corrective actions and measures to align with regulations. |
| 5. Training and Education: Incidnts serve as valuable educational opportunities for training employees and enhancing their awareness of potential risks and best practices. They enable the development of targeted training programs to improve quality, safety, and compliance within the organization. |
| 6. Stakeholder Communication: Incidnts necessitate effective communication with various stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, patients, regulatory authorities, and the public. Transparent and timely communication helps in maintaining trust and ensuring stakeholders are informed about the incidnt and its resolution. |
| 7. Continuous Improvement: Incidnts drive a culture of continuous improvement within the pharmaceutical industry. By learning from past incidnts, companies can implement systemic changes, adopt new technologies, and enhance processes to continuously raise the bar for product quality and patient safety. |
| 8. Prevention of Recurrence: The analysis and lessons learned from incidnts enable pharmaceutical companies to develop preventive measures, protocols, and risk mitigation strategies to minimize the likelihood of similar incidnts occurring in the future. |
Example of the Incident in QC Quality Control Laboratory
Incident: Chemical Spillage
In a pharmaceutical quality control laboratory, an incidnt occurred involving a chemical spillage. During a routine analysis of a raw material sample, a technician accidentally knocked over a container containing a volatile solvent, resulting in the spillage of the chemical on the laboratory bench.
Immediate actions were taken to address the incidnt and mitigate any potential risks. The technician quickly alerted the laboratory supervisor and colleagues in the vicinity. Following established safety protocols, the affected area was cordoned off, and nearby personnel were evacuated to ensure their safety.
The spillage was contained using appropriate absorbent materials and spill response kits available in the laboratory. Personal protective equipment, including gloves and safety goggles, were worn by trained personnel to minimize exposure to the spilled chemical.
The incidnt was promptly reported to the laboratory manager and documented in the laboratory incidnt logbook. The spillage was assessed for its potential impact on the environment, laboratory operations, and personnel safety. The spilled chemical was identified, and its Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) was consulted to understand the hazards associated with it.
Root cause analysis was conducted to determine the factors that contributed to the incidnt. It was found that the technician’s momentary lapse of attention and insufficient adherence to safety procedures played a role in the spillage.
Corrective actions were implemented to prevent similar incidnts in the future. These included reinforcing safety training programs for laboratory personnel, emphasizing the importance of attention to detail and following established protocols. Additionally, the layout of the laboratory workspace was reassessed to minimize the risk of accidental spills, ensuring proper storage and labeling of chemicals.
The incidnt served as a valuable learning opportunity for the laboratory staff. Lessons were shared during safety meetings and incorporated into training programs to enhance awareness of the potential hazards associated with chemical handling and the importance of maintaining a vigilant and safety-conscious work environment.
Regular inspections, audits, and evaluations of safety procedures were subsequently conducted to ensure ongoing compliance with safety regulations and best practices within the quality control laboratory.
Through effective incidnt response, investigation, and implementation of corrective actions, the quality control laboratory demonstrated its commitment to maintaining a safe working environment, protecting personnel, and upholding quality standards in pharmaceutical analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an incident in the context of the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: An incidnt in the pharmaceutical industry refers to an unexpected event or occurrence that disrupts normal operations and has implications for patient safety, regulatory compliance, or ethical standards.
Why are incidents in the pharmaceutical industry important?
Answer: Incidnts are important as they help identify risks, drive improvements, ensure regulatory compliance, enhance patient safety, and foster a culture of continuous learning within the industry.
What are some common types of incidents in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Common types of incidnts include product recalls, adverse drug reactions, manufacturing issues, regulatory violations, data breaches, ethical misconduct, and supply chain disruptions.
How are incidents in the pharmaceutical industry investigated?
Answer: Incidnts are typically investigated through comprehensive root cause analyses, involving the examination of factors such as processes, systems, human error, and external influences.
What role do regulatory authorities play in incidents?
Answer: Regulatory authorities play a crucial role in incidnts by overseeing compliance, conducting investigations, enforcing regulations, and imposing penalties or corrective actions when necessary.
How can incidents in the pharmaceutical industry impact patient safety?
Answer: Incidnts can impact patient safety by causing adverse drug reactions, product defects, contamination, or breaches in quality control measures, leading to harm or compromised effectiveness of medications.
What is the significance of conducting a root cause analysis in incidents?
Answer: Conducting a root cause analysis helps identify the underlying factors that contributed to the incidnt, allowing for targeted corrective actions to address the core issues and prevent recurrence.
How do incidents contribute to continuous improvement in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Incidnts drive continuous improvement by highlighting areas for process enhancement, risk management strategies, training programs, and the implementation of preventive measures.
What are the potential consequences of non-compliance in incidents?
Answer: Non-compliance with regulations in incidnts can lead to legal repercussions, reputational damage, financial losses, product recalls, or regulatory sanctions.
How does communication play a role in managing incidents?
Answer: Effective communication is essential in managing incidnts, as it facilitates transparency, stakeholder engagement, and the dissemination of crucial information regarding the incidnt, its impact, and resolution.
What measures can be taken to prevent recurrence of incidents in the future?
Answer: Preventive measures include implementing robust quality control systems, risk management protocols, adherence to regulatory requirements, training programs, and continuous monitoring and improvement.
How do incidents drive scientific advancements in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Incidnts provide opportunities for scientific discoveries and advancements by uncovering vulnerabilities, prompting research and innovation to improve drug development, manufacturing, and safety practices.
How do incidents contribute to industry-wide learning and knowledge sharing?
Answer: Incidnts serve as learning opportunities, enabling the identification of best practices, sharing of lessons learned, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders to enhance overall industry knowledge and expertise.
How can incidents impact the reputation of pharmaceutical companies?
Answer: Incidnts can significantly impact the reputation of pharmaceutical companies due to their potential effects on patient safety, regulatory compliance, and public perception of the organization’s commitment to quality and ethics.
What role does risk assessment play in managing incidents in the pharmaceutical industry?
Answer: Risk assessment helps identify potential risks associated with incidnts, enabling the implementation of appropriate risk mitigation strategies, preventive measures, and continuous monitoring to safeguard patient safety and organizational performance.

