Pharmaceutical plants rely on advanced equipment and technologies to ensure efficient and high-quality production processes. Among these tools, the Multimill stands out as a valuable asset in pharmaceutical manufacturing. With its versatile capabilities and reliable performance, the Multimill plays a crucial role in various stages of pharmaceutical production. In this article, we will explore the significance of Multimill in pharmaceutical plants and its contributions to enhancing efficiency and product quality.
The Multimill finds application in a range of processes within pharmaceutical plants, primarily focusing on size reduction. This equipment efficiently reduces the size of raw materials, such as powders, granules, or semi-solids, to achieve the desired particle size range. By precisely controlling the size reduction process, the Multimill enables uniformity and consistency in the final pharmaceutical formulations.
One of the primary benefits of incorporating the Multimill into pharmaceutical plants is its ability to improve downstream processes. By reducing the particle size of raw materials, the Multimill enhances the efficiency of subsequent operations such as blending, granulation, and compression. The uniformly sized particles obtained through Multimill processing contribute to homogenous mixing and granule formation, ensuring consistent drug content and dosage.
In addition to improving efficiency, the Multimill also plays a crucial role in maintaining product quality. The equipment’s precise size reduction mechanism helps achieve the desired particle size distribution, leading to better dissolution properties and enhanced bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients. This, in turn, ensures that the formulated medications exhibit optimal therapeutic effects and efficacy.
Multimill diagram
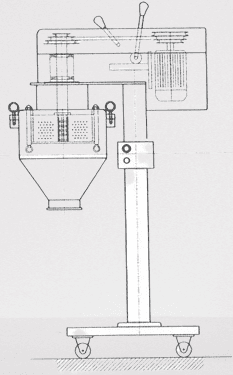
Multimill working principle
The Multimill, a powerful apparatus utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing, operates on a well-defined principle that governs its impressive functionality. Understanding the working principle behind the Multimill is essential in comprehending its role and significance in the size reduction process. In this article, we will delve into the intricate workings of the Multimill, shedding light on its operational principle and its impact in the pharmaceutical industry.
The core working principle of the Multimill revolves around the concept of size reduction. By employing a combination of mechanical forces, the Multimill effectively reduces the size of raw materials, thereby enabling downstream processes and ensuring the attainment of the desired particle size range. This fundamental principle lies at the heart of the Multimill’s exceptional performance and efficiency.

At the center of the Multimill’s working principle lies a high-speed rotor, which is driven by an electric motor. This rotor rotates at a rapid pace, generating intense shearing and cutting actions on the raw materials. The raw materials are subjected to a relentless barrage of forces, resulting in their transformation into smaller particles within the specified size range. This process of size reduction is critical in achieving uniformity and consistency in the final pharmaceutical product.
An integral component that contributes to the Multimill’s working principle is the sieve assembly. This assembly plays a crucial role in the segregation of particles based on their size. It ensures that only particles within the desired size range are allowed to pass through the sieve, while larger particles are retained for further processing. This sieving mechanism guarantees the production of particles with precise dimensions, enhancing the quality and uniformity of the pharmaceutical formulation.
The working principle of the Multimill is a delicate balance between mechanical forces, sieving, and precision. By harnessing the power of these mechanisms, the Multimill efficiently transforms raw materials into finely sized particles, meeting the strict requirements of pharmaceutical manufacturing. The working principle enables manufacturers to achieve optimal results in terms of particle size distribution, ensuring uniformity and enhancing the effectiveness of the final product.
Principles Explored:
- Size Reduction: The fundamental principle guiding the Multimill’s operation revolves around size reduction. By subjecting the raw material to intense mechanical forces, the Multimill effectively reduces particle size, thus facilitating downstream processes and enhancing product uniformity.
- Sieving: The inclusion of a well-designed sieve assembly within the Multimill ensures the segregation of particles based on their size. This enables the production of particles within a specific range, meeting the precise requirements of pharmaceutical formulations.
- Versatility: Bursting with versatility, the Multimill accommodates a wide range of applications. It caters to various materials, including powders, granules, and even semi-solids, making it an indispensable asset in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities.
Components of Multimill
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| High-speed rotor | Rotates at a rapid speed and generates intense shearing and cutting actions on the raw materials |
| Electric motor | Powers the high-speed rotor, enabling its rotation |
| Sieve assembly | Ensures segregation of particles based on size, allowing only particles within the desired range to pass through |
| Hopper | Container for holding the raw materials to be processed |
| Discharge chute | Directs the processed materials to the desired location or downstream processes |
| Control panel | Allows for control and adjustment of various operating parameters of the Multimill |
| Safety features | Incorporates safety mechanisms to prevent accidents and ensure operator protection |
| Frame and housing | Provides structural support and protection for the internal components of the Multimill |
| Inlet and outlet | Facilitates the entry of raw materials into the Multimill and the discharge of processed materials |
| Knives and blades | Responsible for the cutting and shearing actions on the raw materials during size reduction |
| Motor drive system | Transmits power from the electric motor to the high-speed rotor |
SOP for Multimill
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Multimill
Objective: To outline the standard operating procedure for the safe and efficient operation of the Multimill in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Scope: This SOP applies to all personnel involved in the operation of the Multimill equipment in the pharmaceutical manufacturing facility.
Responsibilities:
- The operator is responsible for following this SOP and ensuring the proper operation of the Multi-mill.
- The supervisor or designated personnel are responsible for providing training on the operation and safety protocols of the Multi-mill.

Procedure:
- Pre-Operational Checks: a. Inspect the Multi-mill equipment for any visible damage or abnormalities. b. Ensure that the Multi-mill is clean and free from any residue from previous operations. c. Verify that all safety features and interlocks are in proper working condition. d. Check that the power supply is connected and stable.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): a. Put on the required PPE, including safety goggles, gloves, and a lab coat or protective clothing. b. Ensure that loose clothing, jewelry, and long hair are secured or covered.
- Material Preparation: a. Verify that the raw materials to be processed are suitable for the Multi-mill and comply with the approved specifications. b. Weigh and measure the required quantity of raw materials accurately. c. Ensure that the raw materials are properly labeled and identified.
- Machine Setup: a. Set the appropriate rotor speed and ensure it is within the recommended range for the material being processed. b. Install the correct size of sieve based on the desired particle size range. c. Position the discharge chute to direct the processed material to the designated collection container.
- Operation: a. Start the Multi-mill and allow it to reach the desired operating speed. b. Gradually feed the pre-weighed raw materials into the hopper, taking care not to overload the equipment. c. Monitor the operation to ensure smooth material flow and proper size reduction. d. Regularly inspect the processed material to ensure it meets the desired particle size specifications. e. If necessary, adjust the operating parameters (e.g., rotor speed) to achieve the desired particle size range. f. Continuously monitor the Multi-mill for any signs of abnormalities, unusual noises, or excessive vibrations.
- Post-Operational Checks: a. Stop the Multi-mill and ensure that it comes to a complete halt before proceeding. b. Thoroughly clean the Multi-mill, including the hopper, sieves, and other components, using approved cleaning procedures. c. Remove any residual material or dust from the equipment. d. Document any deviations, issues, or maintenance requirements encountered during the operation.
- Equipment Maintenance: a. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for routine maintenance and calibration of the Multi-mill. b. Report any malfunction, damage, or maintenance requirements to the supervisor or maintenance personnel.
Applications of Multimill
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Size reduction | Used to reduce the size of raw materials to achieve the desired particle size range for downstream processes such as blending, granulation, and compression. |
| Granulation | Enables the granulation of materials by breaking down larger particles into smaller, uniform granules, which are easier to handle and compress into tablets or capsules. |
| Mixing | Facilitates the uniform mixing of powders or granules, ensuring homogeneity of the pharmaceutical formulation. |
| Pulverization | Converts materials into fine powders, enhancing their solubility and bioavailability for improved absorption and therapeutic effects. |
| Homogenization | Ensures consistent distribution and dispersion of active ingredients within a formulation, resulting in uniform drug content and dosage. |
| Wet granulation | Assists in the wet granulation process by breaking down wet mass into granules, aiding in the formation of granules with desirable properties. |
| Particle sizing | Used to control and refine particle size distribution, ensuring consistent and accurate dosing in formulations. |
| Comminution | Facilitates the comminution of materials, including solid dosage forms, to reduce their particle size for easier processing or dissolution. |
| Fine milling | Enables the milling of materials to produce fine particles, suitable for applications such as inhalation products or high-potency drug formulations. |
| Micronization | Supports the micronization of materials, reducing particle size to the micron level for enhanced dissolution and bioavailability. |
You may also read about the Principles and Workings of Vibratory Sifter
What is cone mill vs multi Mill?
| Cone Mill | Multimill |
|---|---|
| Operates on the principle of size reduction through impaction | Operates on the principle of size reduction through shearing and cutting |
| Utilizes a conical-shaped rotor and a conical screen | Utilizes a high-speed rotor and a sieve assembly |
| Ideal for achieving uniform particle size distribution | Ideal for achieving uniform particle size distribution |
| Multi mill | Provides a wider range of particle sizes |
| Suitable for processing heat-sensitive materials | Suitable for processing a wide range of materials, including heat-sensitive ones |
| May have limitations in handling sticky or cohesive materials | Can handle sticky or cohesive materials with proper design and adjustments |
| Requires less energy compared to Multi-mill for size reduction | Generally used for low to moderate-capacity applications |
| Generally used for moderate to high-capacity applications | Provides a narrow particle size range |
| Requires less floor space | Requires more floor space due to larger size and additional components |
| May have lower throughput compared to Multi-mill | Can achieve higher throughput due to higher rotor speed and design features |
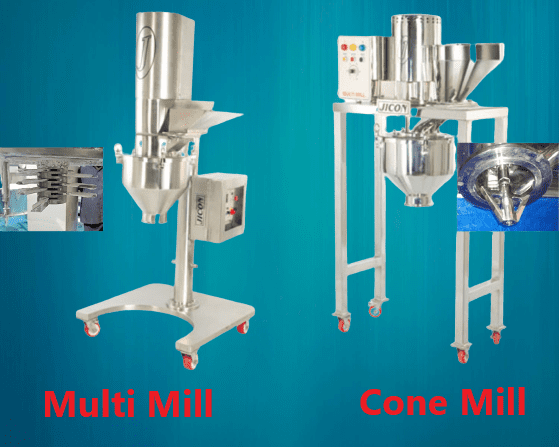

Advantages and Disadvantages of Multimill
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Efficient size reduction of raw materials | Noise generation during operation |
| Enables uniform particle size distribution | Requires regular cleaning and maintenance |
| Improves downstream processes such as blending | Initial investment cost can be high |
| Enhances granulation and compression processes | May require skilled personnel for operation |
| Versatile and adaptable to various formulations | May produce fine dust particles during operation |
| Improves dissolution properties and bioavailability | Risk of contamination if not properly cleaned |
| Enhances homogeneity of formulations | Requires proper calibration and adjustment |
| Contributes to consistent drug content and dosage | Power consumption may be relatively high |
| Facilitates micronization for improved solubility | May have limitations in handling certain materials |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the working principle of a Multimill?
Answer: The Multi-mill operates on the principle of size reduction, using mechanical forces and sieving mechanisms to break down raw materials into smaller particles.
What are the main components of a Multimill?
Answer: The main components of a Multi-mill include a high-speed rotor, electric motor, sieve assembly, hopper, discharge chute, control panel, safety features, frame and housing, inlet and outlet, knives and blades, and motor drive system.

How does the Multimill achieve uniform particle size distribution?
Answer: The Multi-mill achieves uniform particle size distribution by utilizing precise rotor speed control, sieving mechanisms, and a properly selected sieve size.
What types of materials can be processed using a Multimill?
Answer: Multi-mills are versatile and can process a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, and semi-solids used in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
How does the Multimill contribute to downstream processes?
Answer: The Multi-mill improves downstream processes by reducing particle size, which enhances blending, granulation, compression, and ensures uniform drug content and dosage.
What safety features are typically incorporated in a Multimill?
Answer: Safety features in a Multi-mill may include interlocks, emergency stop buttons, protective covers, and sensors to ensure operator protection and prevent accidents.
How is maintenance and cleaning of a Multimill performed?
Answer: Regular maintenance and cleaning of a Multi-mill involve following manufacturer guidelines, performing routine inspections, and using approved cleaning procedures to ensure equipment hygiene.
What are some considerations for choosing the appropriate sieve size in a Multimill?
Answer: Factors such as the desired particle size range, material characteristics, and process requirements influence the selection of the appropriate sieve size for a Multi-mill.
Can a Multimill handle heat-sensitive materials?
Answer: Yes, Multi-mills can handle heat-sensitive materials by employing techniques such as cryogenic milling or using cooling systems to prevent excessive temperature rise during operation.
How can the performance of a Multimill be optimized?
Answer: The performance of a Multi-mill can be optimized by ensuring proper calibration and adjustment, regular maintenance, operator training, and adherence to recommended operating parameters.

