The Antibiotic Zone Reader is an essential tool in the Microbiology Laboratory. Its precise and reliable tools are used to understand the interactions between microorganisms and antibiotics. Among the arsenal of instruments used in modern laboratories, the Antibiotic Zone Reader holds a prominent position. This unassuming yet indispensable device has become a cornerstone in antimicrobial research, aiding scientists and healthcare professionals in their quest to combat antibiotic resistance and improve patient care.
Working Principle of Antibiotic Zone Reader:
At its core, the Antibiotic Zone Reader operates on the principle of measuring zones of inhibition. This method, known as the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion test, is widely used to determine the susceptibility of bacteria to various antibiotics. The process involves placing antibiotic discs onto an agar plate previously inoculated with bacteria. Over time, the antibiotics diffuse into the agar, creating zones of inhibition where bacterial growth is inhibited. By measuring the diameters of these zones, researchers can ascertain the effectiveness of the antibiotics against the specific bacterial strain.

- Precise Data Acquisition
- One of the key advantages of the Antibiotic Zone Reader lies in its ability to provide accurate and reproducible data. Manual measurements of zone diameters can be subject to human error, leading to inconsistent results. The reader’s integrated software automates the process, eliminating the potential for human bias and ensuring precision in data acquisition. This not only saves time but also enhances the reliability of antimicrobial susceptibility testing, facilitating informed treatment decisions and fostering effective antibiotic stewardship.
- Advancing Antimicrobial Research
- In the study of antimicrobial research, the Antibiotic Zone Reader plays an essential role in investigating new antibiotics and studying resistance patterns. Researchers can use the reader to assess the efficacy of novel antimicrobial compounds, allowing for the identification of potential candidates for further development. Moreover, the device aids in monitoring the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains, enabling swift responses to prevent the spread of resistant bacteria.
- Clinical Application and Patient Care
- In the clinical setting, the Antibiotic Zone Reader is an indispensable tool for guiding treatment decisions. Physicians and healthcare professionals rely on antimicrobial susceptibility testing to select the most appropriate antibiotics for patients with bacterial infections. Timely and accurate information from the reader empowers medical teams to tailor treatments, ensuring patients receive the most effective therapies while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance.

- Educational Utility
- Beyond research and clinical applications, the Antibiotic Zone Reader holds educational value in training the next generation of microbiologists and healthcare professionals. Its user-friendly interface and straightforward operation make it an ideal tool for teaching students about antimicrobial susceptibility testing and the principles of antibiotic action.
Conclusion:
In microbiology laboratories, the Antibiotic Zone Reader stands tall as an indispensable instrument. Its ability to provide precise data, support cutting-edge research, aid in clinical decision-making, and facilitate educational endeavors makes it an essential asset in the battle against antibiotic resistance. As the field of antimicrobial research continues to advance, the Antibiotic Zone Reader will remain a steadfast ally in the pursuit of effective antibiotics and improved patient care.
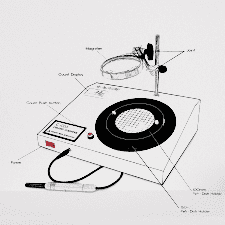
Standard Operating Procedure for the Operation and Calibration of Zone Reader
- Equipment details:
- Name : Antibiotic Zone Reader
- Make :
- Model :
- ID :
- Precautions:
- Ensure the power supply is switched OFF before starting the cleaning of the instrument.
- Do not keep the light source ON for a long period of time.
- The lens from which light passes should be clean and free from dust.
- Operation:
- Ensure that the instrument is clean and free from dust before starting the operation.
- Connect the main cord to the supply socket and switch it ‘ON’.
- Set the digital scale to zero-zero coincidence.
- After fixing the prism at the rough side in the mirror reflects the light side position.
- Turn the left side drum to its maximum clockwise position, so that zero marking on the scale of the right side drum coincides with the zero marking on the Vernier scale.
- Keep the petri-dish on the Top belt and rotate it manually, so that one end of the zone image just touches the mark line on the prism.
- Now turn the left-side drum slowly, in anti-clockwise position, till the other end of the zone image touches the marked line on the prism.
- The digital scale reading gives the exact value in mm having least count 0.1 mm.
- Record the activity of usage of zone reader as per Annexure – I.
- Switch OFF the instrument when not in use.
- Frequency of calibration: Quarterly ± 5 days. (By external Agency)
- Cleaning:
- Clean the outer surface of the instrument daily or as and when required.
- Clean outer surface of zone reader before and after use with a lint free mop in 0.2 µ filtered IPA 70 %.
- Maintenance:
- In case of any discrepancy, inform the Engineering department for rectification, and the Engineering department will affix the “Under Maintenance” tag with the sign & date.
- Cleaning:

- ABBREVIATIONS
- IPA : Isopropyl Alcohol
- mm : Millimetre
- % : Percentage
- MB : Microbiology
- SOP : Standard Operating Procedure
- µ : Micron
- REFERENCES
- Operation Manual
- ANNEXURES
- Annexure-I : Usage Log For Zone Reader
- Annexure-II : Zone Reader Calibration Record
| USAGE LOG FOR ZONE READER |
| S. No. | Date | Product/ material name/ activity | Batch No. | Microbiology Ref. No. | Usage Time | Operated by (Sign/Date) | Reviewed by (Sign/Date) | Remarks | |
| Start | End | ||||||||
ZONE READER CALIBRATION RECORD
| Calibration Done On | Calibration Due On | |||
| Object | Diameter with Zone Reader | Diameter with Vernier Scale | Difference | Remarks |
| 25 Paisa Coin | ||||
| 50 Paisa Coin | ||||
| 01 Rupee Coin | ||||
| Acceptance criteria: Difference between reading of zone reader and vernier scale is : NMT 0.2 mm. |
Frequently Asked Questions:
What is the Antibiotic Zone Reader?
Answer: The Antibiotic Zone Reader is a device used in microbiology laboratories to measure zones of inhibition around antibiotic discs on agar plates. It helps determine the susceptibility of bacteria to different antibiotics, aiding in antimicrobial research and clinical decision-making.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader work?
Answer: The reader operates on the principle of the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion test. Antibiotic discs are placed on an agar plate previously inoculated with bacteria. As the antibiotics diffuse into the agar, they create zones of inhibition where bacterial growth is prevented. The reader measures the diameters of these zones to assess the effectiveness of the antibiotics.
What are the advantages of using the Antibiotic Zone Reader?
Answer: The Antibiotic Zone Reader offers several advantages, including automated data acquisition, which ensures precision and eliminates human error in measurements. It saves time, enhances the reliability of antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and aids in monitoring antibiotic resistance patterns.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader contribute to antimicrobial research?
Answer: In antimicrobial research, the reader is instrumental in evaluating the efficacy of novel antimicrobial compounds. It helps identify potential candidates for further development and assists in monitoring the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.
What is the clinical application of the Antibiotic Zone Reader?
Answer: In clinical settings, the Antibiotic Zone Reader plays a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions. Healthcare professionals use antimicrobial susceptibility testing to select the most appropriate antibiotics for patients with bacterial infections, ensuring tailored and effective therapies.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader benefit educational purposes?
Answer: The reader has educational utility in training students and aspiring healthcare professionals. Its user-friendly interface and straightforward operation make it an ideal tool for teaching about antimicrobial susceptibility testing and antibiotic action principles.
Why is the Antibiotic Zone Reader considered essential in the battle against antibiotic resistance?
Answer: Antibiotic resistance is a significant global health concern. The reader’s ability to provide accurate and timely information on antibiotic effectiveness and resistance patterns empowers healthcare professionals to make informed treatment decisions and implement antibiotic stewardship programs effectively.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader contribute to improved patient care?
Answer: By guiding clinicians in selecting the most effective antibiotics for bacterial infections, the Antibiotic Zone Reader ensures that patients receive appropriate treatments promptly. This approach minimizes the risk of antibiotic resistance and leads to better patient outcomes.
What are some key features of the Antibiotic Zone Reader?
Answer: The Antibiotic Zone Reader often comes equipped with an integrated software system for automated data analysis, ensuring precise measurements. It may have a user-friendly interface, customizable settings, and the capability to handle multiple agar plates simultaneously, enhancing efficiency in the laboratory.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader help in identifying new antibiotics?
Answer: Researchers can use the reader to test the effectiveness of various antimicrobial compounds against bacterial strains. By measuring the zones of inhibition, they can identify promising candidates with potent antibacterial properties, which may lead to the development of new antibiotics.
Can the Antibiotic Zone Reader be used for susceptibility testing of different types of microorganisms?
Answer: Yes, the reader is versatile and can be employed to test the susceptibility of various microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi. It aids in determining the sensitivity of different strains to specific antibiotics.
How does the Antibiotic Zone Reader aid in monitoring the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains?
Answer: By regularly testing bacterial isolates from clinical samples or environmental sources, the reader helps track changes in susceptibility patterns over time. It enables researchers to identify the development of resistant strains, which is crucial in tackling antibiotic resistance.
Is the Antibiotic Zone Reader a cost-effective tool for laboratories?
Answer: Yes, the reader is generally considered cost-effective due to its ability to automate data acquisition and streamline the testing process. It can reduce labor-intensive manual measurements and increase the efficiency of antimicrobial testing.
What are some potential limitations of the Antibiotic Zone Reader?
Answer: While highly useful, the reader may have certain limitations. It requires proper calibration and maintenance to ensure accurate results. Additionally, it may not be suitable for testing some types of antimicrobial agents or for certain bacterial species with specific growth requirements.
Can the Antibiotic Zone Reader be integrated with other laboratory instruments?
Answer: Yes, the reader can be integrated with various laboratory systems and software, enabling seamless data sharing and analysis. Integration with other technologies, such as automated incubators or data management systems, further enhances laboratory workflows.

1 thought on “Operation and Calibration of Zone Reader in Microbiology”