In pharmaceutical plants, the Bursting Strength Tester plays a pivotal role in quality assurance and compliance with stringent packaging standards. This specialized instrument is instrumental in evaluating the integrity and resilience of packaging materials, such as blister packs, pouches, and other containment systems crucial for preserving the efficacy and stability of pharmaceutical products.
The operational significance of the Bursting Strength Tester in pharmaceutical applications lies in its ability to simulate and quantify the internal stresses that packaging materials may encounter during handling, transportation, and storage. By subjecting these materials to controlled hydraulic pressure, the tester assesses their resistance to rupture, providing critical data for optimizing packaging designs and ensuring the protection of pharmaceutical products from external influences.
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, where product safety and regulatory adherence are paramount, the Bursting Strength Tester serves as an indispensable tool for quality control. It aids in the selection of materials that meet or exceed industry-specific bursting strength requirements, ensuring the reliability of packaging in safeguarding the pharmaceutical products from contamination, moisture, and other environmental factors.
Calculation and formulas used in bursting strength tester:
The bursting strength of a material is calculated by dividing the maximum force applied during the test by the area of the material being tested. The formula for bursting strength is as follows:
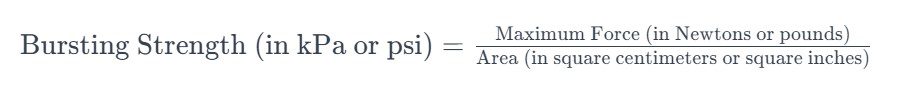
Bursting Strength (in kPa or psi)=Maximum Force (in Newtons or pounds)Area (in square centimeters or square inches)Bursting Strength (in kPa or psi)=Area (in square centimeters or square inches)Maximum Force (in Newtons or pounds)
This formula provides a quantitative measure of the material’s resistance to bursting under internal pressure.
Additionally, Bursting Factor (BF) is another parameter calculated in the paper and packaging industry. The Bursting Factor is the ratio of bursting strength to grammage (weight per unit area) of the material. The formula for Bursting Factor is:
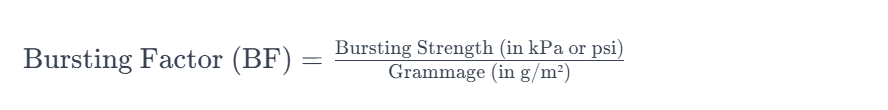
Bursting Factor (BF)=Bursting Strength (in kPa or psi)Grammage (in g/m²)Bursting Factor (BF)=Grammage (in g/m²)Bursting Strength (in kPa or psi)
It is important to note that specific units may vary depending on the measurement system used (e.g., kPa or psi for bursting strength, g/m² or oz/ft² for grammage). It is crucial to use consistent units throughout the calculations to ensure accurate and meaningful results.

Working Principle of Bursting Strength Tester.
The Bursting Strength Tester operates on the fundamental principle of subjecting a material specimen to controlled internal hydraulic pressure to assess its resistance to rupture. This methodological approach provides a quantitative measure of the material’s strength under pressure, a critical parameter in various industries, particularly in packaging and textiles.
The core components and working principle of the Bursting Strength Tester can be outlined as follows:
- Specimen Clamping:
- The material specimen under evaluation is meticulously secured between two concentric clamping rings. This ensures a defined and consistent area of the material is subjected to pressure during the test.
- Sealed Chamber Creation:
- The clamped specimen creates a sealed chamber, isolating it from the external environment. This chamber is designed to withstand the internal hydraulic pressure without leakage.
- Hydraulic Pressure Application:
- A hydraulic system is employed to introduce controlled pressure into the sealed chamber. This pressure is gradually increased, simulating the internal stresses that the material may experience during various stages of its application.
- Diaphragm Mechanism:
- A precision-engineered diaphragm, often made of materials with high elastic modulus, is employed as a transfer mechanism for the hydraulic force. This diaphragm ensures a uniform and gradual application of pressure onto the specimen.
- Pressure Detection and Measurement:
- Sensors or transducers are integrated into the system to meticulously measure the internal pressure within the sealed chamber. These sensors are capable of capturing subtle variations in pressure, providing accurate data during the test.
- Rupture Detection:
- The test concludes when the material specimen ruptures under the applied pressure. This rupture event is detected by monitoring changes in pressure and is a crucial point for determining the bursting strength of the material.
- Data Analysis and Presentation:
- The recorded pressure data is then analyzed to calculate the bursting strength of the material. This quantitative measurement serves as a critical parameter for evaluating the material’s suitability for specific applications, particularly in industries where structural integrity is paramount.
Technical details and specifications of the Bursting Strength Tester
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Test Method | ASTM D3786, ISO 2758, TAPPI T403, etc. |
| Pressure Range | 0 to 1000 kPa (customizable based on model) |
| Test Chamber Material | Stainless Steel or Hardened Alloy |
| Clamping Mechanism | Pneumatically Operated |
| Diaphragm Material | High Elastic Modulus Alloy |
| Specimen Diameter Range | 20 mm to 100 mm (customizable based on model) |
| Pressure Application Rate | Adjustable, 95 ± 5 ml/min |
| Pressure Measurement Accuracy | ± 0.1% of Full Scale |
| Display and Controls | Touchscreen Interface with User-Friendly Software |
| Data Output | USB, RS232, Ethernet |
| Safety Features | Overpressure Protection, Emergency Stop |
| Power Requirements | 110-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz |
| Dimensions (H x W x D) | 1200 mm x 800 mm x 600 mm (may vary by model) |
| Weight | 150 kg (may vary by model) |
| Compliance | CE Mark, ISO 9001:2015 |
| Calibration | Traceable Calibration Certificate Included |
| Warranty | 12 months (extended warranty options available) |
Note: These specifications are illustrative and may vary depending on the manufacturer and model of the Bursting Strength Tester.
Features of the Advanced Bursting Strength Tester:
- Automatic Burst Factor Calculation:
- The instrument facilitates seamless and automatic calculation of burst factors in paper materials, streamlining the testing process for paper and packaging manufacturers.
- Single Push Button Operation:
- User-friendly operation with a single push-button interface ensures simplicity and efficiency in conducting bursting strength tests.
- Microprocessor-Based Display:
- Equipped with a sophisticated microprocessor-based display, the instrument ensures precision and accuracy in test results, providing reliable data for material evaluation.
- Peak Hold Facility:
- Incorporates a peak hold feature that retains the maximum value of test results in memory, allowing users to easily track and analyze critical data points.
- Memory Capacity:
- Offers memory storage for up to 9 test readings, enabling convenient record-keeping and comparative analysis of multiple test sessions.
- Multidirectional Force Accuracy:
- Delivers highly accurate test results under multidirectional force applications, ensuring comprehensive assessment of material strength from different perspectives.
- Strong Gripping Clamps:
- Robust and reliable gripping clamps provide a secure hold on various materials, including corrugated boxes, cardboard, and paper boards.
- Grooved Structure of Test Specimen Holder:
- The grooved structure of the test specimen holder prevents slippage, ensuring the secure and intact positioning of the specimen during testing.
- Uniform Specimen Tightening:
- The operating wheel allows for uniform and controlled tightening of the specimen, minimizing the risk of slippage during testing.
- Bright LED Display:
- Features a vivid LED display for clear visibility of test results, enhancing the user experience and facilitating quick data interpretation.
- Feather Touch Controls:
- Incorporates feather-touch controls for responsive and intuitive operation, enhancing user convenience during testing procedures.
- Calibration Lock & Key Feature:
- Ensures calibration integrity with a lock and key feature, preventing unauthorized adjustments and maintaining the accuracy of the testing apparatus.
Optional Features:
- Pneumatic and Computerized Models:
- Optional models with pneumatic and computerized functionalities are available, offering enhanced automation and data processing capabilities.
- Printer Facility:
- Select models come equipped with a printer facility, allowing users to generate hard copies of test results for documentation and quality assurance purposes.
Display of Bursting Strength:
- The bursting strength in Kg/cm² is prominently displayed on the digital interface, providing immediate and easily interpretable results for further analysis.
Calculation Features:
- Users have the capability to calculate bursting factors and burst indices based on the obtained bursting strength data, facilitating comprehensive material characterization.

Advantages & disadvantages of the Bursting Strength Tester:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| 1. Provides Accurate Results: | 1. Initial Cost: The acquisition cost of a Bursting Strength Tester can be relatively high, impacting the budget for smaller enterprises. |
| 2. Quality Assurance: Ensures that packaging materials meet or exceed industry standards, contributing to quality assurance in various sectors. | 2. Maintenance: Requires periodic maintenance to ensure precision and reliability. Neglecting maintenance may lead to inaccurate results. |
| 3. Versatile Applications: Suitable for testing a wide range of materials such as paper, cardboard, corrugated boxes, and textiles. | 3. Operator Skill: Proper operation and interpretation of results may require trained personnel, posing a challenge for inexperienced users. |
| 4. Quantitative Data: Provides quantitative data on bursting strength, aiding in material selection and process optimization. | 4. Limited Sample Size: Some models may have restrictions on the size and shape of specimens, limiting flexibility in testing various materials. |
| 5. Objective Testing: Reduces subjective variability in testing by automating the process, ensuring consistent and reliable results. | 5. Size and Space: The physical size of the equipment may require dedicated space, which could be a constraint in smaller laboratories or production facilities. |
| 6. Compliance with Standards: Conforms to international standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for testing, ensuring compliance with industry norms. | 6. Energy Consumption: Some models may consume a significant amount of energy during operation, leading to higher operational costs over time. |
| 7. Data Logging Capabilities: Allows for the storage of test results, enabling trend analysis and documentation for quality control purposes. | 7. Complexity: Advanced features may introduce complexity, necessitating thorough training for operators to utilize the equipment effectively. |
| 8. Optional Features: Many models offer additional features such as peak hold, memory storage, and computerized data analysis, enhancing functionality. | 8. Technology Obsolescence: Rapid advancements in testing technology may render older models obsolete, potentially requiring upgrades for staying current. |
List of the accessories of the bursting strength tester:
Accessories for a Bursting Strength Tester may vary based on the model and manufacturer, but here’s a generic list of common accessories that might be associated with such testing equipment:
- Bursting Strength Test Grips:
- These are specialized grips or clamps designed to securely hold the specimen during the test. They ensure uniform force distribution.
- Diaphragms:
- Replacement or additional diaphragms may be included for the Bursting Strength Tester, allowing for maintenance and adapting to various testing requirements.
- Specimen Cutter:
- A cutting tool designed for preparing standardized specimen sizes for testing, ensuring consistency in sample dimensions.
- Pressure Plates:
- Interchangeable pressure plates or anvil plates that come in various sizes to accommodate different specimen diameters.
- Seals and Gaskets:
- Replacement seals and gaskets for maintaining the integrity of the hydraulic system and preventing leaks during testing.
- Calibration Weights:
- Precision weights used for calibrating and verifying the accuracy of the force or pressure applied by the Bursting Strength Tester.
- Digital Micrometer or Thickness Gauge:
- A tool for measuring the thickness of specimens accurately, ensuring uniformity in test samples.
- Printer:
- In the case of models with data output capabilities, a printer may be an accessory for generating hard copies of test results.
- Software and Data Management Tools:
- Additional software for data analysis, storage, and management, enhancing the capabilities of the Bursting Strength Tester.
- Pressure Regulator:
- A regulator for controlling and adjusting the hydraulic pressure applied during the test.
- Tool Kit:
- A set of tools required for routine maintenance, adjustments, and minor repairs of the Bursting Strength Tester.
- Instruction Manual:
- A comprehensive guide providing detailed instructions for operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
- Carrying Case:
- For portable or field-testing models, a carrying case facilitates easy transport and protection of the Bursting Strength Tester.
- USB/RS232 Cables:
- Cables for connecting the Bursting Strength Tester to external devices for data transfer and analysis.
- Spare Parts Kit:
- A collection of commonly replaced or worn-out parts, ensuring minimal downtime during maintenance.
It’s essential to refer to the specific product documentation provided by the manufacturer for the Bursting Strength Tester in use to identify the exact accessories and their compatibility.
Points to be considered while purchasing new Bursting Strength Tester:
When purchasing a new Bursting Strength Tester, it’s crucial to consider various factors to ensure that the chosen equipment meets your specific testing requirements and provides reliable and accurate results. Here are key points to consider:
- Testing Standards:
- Ensure that the Bursting Strength Tester complies with relevant international testing standards such as ASTM, ISO, TAPPI, or other industry-specific standards applicable to your materials.
- Testing Range:
- Evaluate the pressure range the tester can handle. Choose a model that covers the bursting strength range of the materials you will be testing.
- Specimen Size Compatibility:
- Consider the range of specimen sizes the equipment can accommodate. Ensure it can handle the size and shape of specimens relevant to your testing needs.
- Clamping Mechanism:
- Evaluate the clamping mechanism for securing specimens. Ensure it provides a reliable and consistent grip to prevent slippage during testing.
- Pressure Application Control:
- Check if the equipment allows for adjustable pressure application rates. This feature is essential for controlling the speed at which pressure is applied to the specimen.
- Data Output and Display:
- Consider whether the tester provides digital data output options such as USB, RS232, or Ethernet. A clear and user-friendly display interface is also important for real-time monitoring.
- Memory and Data Storage:
- If data storage is a concern, check the tester’s capacity for storing test readings. Some models may offer memory for multiple test sessions.
- Optional Features:
- Evaluate optional features such as computerized models, data logging, and printer facilities. Determine if these features align with your testing requirements and workflow.
- Calibration and Accuracy:
- Ensure that the Bursting Strength Tester comes with a calibration certificate and offers a high level of accuracy in pressure measurement.
- Ease of Operation:
- Consider the user interface and controls. An intuitive and user-friendly design can contribute to efficient operation and reduce the learning curve for users.
- Maintenance and Support:
- Check for the availability of spare parts, maintenance kits, and customer support services. Consider the ease of maintenance and the availability of technical assistance when needed.
- Compliance and Certification:
- Ensure that the Bursting Strength Tester meets safety and quality standards, and look for certifications such as CE marking.
- Price and Budget:
- Establish a budget and compare the features offered by different models within that budget. Consider the long-term value and return on investment.
- Manufacturer Reputation:
- Research the reputation of the manufacturer. Consider factors such as reliability, durability, and customer reviews to gauge the overall quality of the equipment.
- Training and Documentation:
- Check if the manufacturer provides comprehensive training materials and documentation. This is crucial for proper usage, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
FAQ:
What is a bursting strength tester?
Answer: A bursting strength tester is a laboratory instrument designed to measure the ability of materials, such as paper, cardboard, textiles, and packaging, to withstand pressure or force applied internally until the material ruptures or bursts. It is commonly used in quality control to assess the structural integrity of materials.
How do you calculate bursting strength?
Answer: Bursting strength is calculated by dividing the maximum force applied to a material during a bursting strength test by the area of the material being tested. The formula is: Bursting Strength (in kPa or psi) = Maximum Force (in Newtons or pounds) / Area (in square centimeters or square inches).
How do you test fabric bursting strength?
Answer: Fabric bursting strength is typically tested using a bursting strength tester. The fabric specimen is clamped securely in the instrument, and hydraulic pressure is applied until the fabric ruptures. The maximum pressure recorded during this process represents the fabric’s bursting strength by Bursting Strength Tester.
What is the principle of bursting strength?
The principle of bursting strength is based on subjecting a material to increasing internal hydraulic pressure until it ruptures. The force required to burst the material is measured and used to calculate the bursting strength, providing insights into the material’s ability to withstand pressure.
What is the ISO for bursting strength test?
ISO 2758 is the international standard that outlines the method for determining the bursting strength of paper by Bursting Strength Tester.
Why is bursting test important?
The bursting test is important as it assesses the strength and durability of materials, especially in packaging and textile industries. It helps ensure that materials can withstand the internal pressures they might encounter during transportation, handling, or storage.
What is the relationship between GSM and bursting strength?
GSM (Grams per Square Meter) is a measure of the weight of paper or fabric per unit area. There is a correlation between GSM and bursting strength; generally, higher GSM values indicate greater material density and may correlate with higher bursting strength of Bursting Strength Tester.
What is GSM and BF?
GSM stands for Grams per Square Meter, representing the weight of a material per unit area. BF stands for Bursting Factor, which is a ratio calculated by dividing the Bursting Strength Tester of a material by its grammage (weight per unit area).
What is the unit of BF in paper?
Answer: The unit of Bursting Factor (BF) in paper is expressed as kPa·m²/g or psi·in²/oz.
What does 32 ECT stand for?
Answer: 32 ECT stands for Edge Crush Test, a measure of the stacking strength of corrugated cardboard. It represents the amount of force required to crush a short column of corrugated material in a controlled manner.
What is bursting in textile?
Answer: In textiles, bursting refers to the ability of a fabric to resist bursting or tearing forces. Bursting Strength Tester tests are conducted to evaluate a textile material’s resistance to bursting under pressure.
How do you test material strength?
Answer: Material strength can be tested using various methods, including tensile testing, compression testing, flexural testing, and bursting strength tester testing. Each method is designed to assess specific aspects of a material’s mechanical properties under different types of stress.


