A Rotameter is a simple and reliable device used for measuring the flow rate of liquids or gases in a closed system. Operating on the principle of variable area, the fluid flow causes a float to move in a tapered tube, providing an accurate and precise measurement of the flow rate. Widely used in industrial applications, rotameters offer advantages such as easy installation and maintenance, accurate measurement, and low cost. Discover more about the working principle and benefits of rotametrs in our comprehensive guide.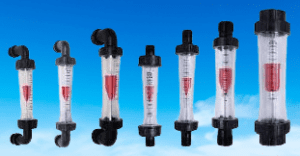
The name “rotameter” is derived from the Latin word “rota” which means wheel or rotating object, and the term “meter” which refers to an instrument used for measuring.
Although rotametrs do not actually have any rotating parts, the float inside the tapered tube does move up and down as the fluid flows through the tube. This movement is similar to that of a rotating object, hence the term “rota” in the name.
The “meter” part of the name refers to the fact that the device is used for measuring the flow rate of liquids or gases.
So, the name “rotameter” reflects the principle of variable area, where the movement of a float inside a tapered tube is used to measure fluid flow rate, and it has become a widely accepted term for this type of flow meter.
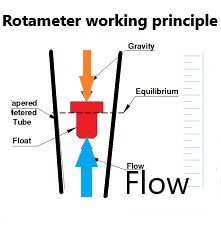
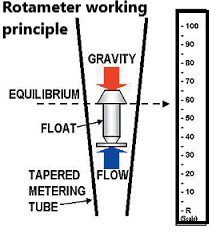
A rotametr is a device that measures the flow rate of liquids or gases in a closed system. It operates on the principle of variable area, where the flow of fluid causes a float to move in a tapered tube, thereby indicating the flow rate.
The working principle of a Rotameter:
- Fluid flows through a tapered tube with a float inside it.
- The float is designed to be larger at the bottom and smaller at the top, which allows it to move freely up and down the tube.
- As the fluid flows through the tube, it exerts a force on the float, pushing it upward.
- The tapered tube is calibrated, so that the height of the float corresponds to the flow rate of the fluid.
- The float reaches a stable position when the upward force of the fluid is equal to the downward force of gravity acting on the float.
- The position of the float is then read off a scale, which is calibrated in units of flow rate (such as liters per minute or cubic feet per hour).
- The float’s position can be affected by changes in fluid density, viscosity, and temperature, so these factors must be considered when interpreting the readings.
Rotametrs are widely used in industrial applications, such as in chemical processing, water treatment, and oil and gas production, where accurate and reliable flow measurement is critical for process control and optimization.
The Calculation Factor:
The calculation factor in a rotametr is used to convert the position of the float inside the rotametr to the flow rate of the fluid passing through it. The calculation factor depends on the size of the rotametr, the fluid properties (such as density and viscosity), and the specific gravity of the float.
The calculation factor is typically provided by the manufacturer and is expressed as a calibration constant or as a conversion factor. It is based on the rotametr’s dimensions, the fluid density and viscosity, and the specific gravity of the float.
To calculate the flow rate using a rotametr, the operator must first read the position of the float on the graduated scale. The operator then uses the calculation factor and the float position to determine the flow rate of the fluid. The formula for calculating the flow rate is:
Flow rate = (calculation factor x float position) / time
Where time is the period of time over which the float position was observed (usually in seconds).
It is important to note that the accuracy of the flow rate measurement using a rotametr depends on the calibration of the device and the accuracy of the calculation factor. For best results, the rotametr should be calibrated periodically and the calculation factor should be verified or adjusted as needed.
Advantages:
Rotameters are used for flow rate measurement of liquids and gases in various water systems of industries. The main advantages of using rotametrs are:
- Simple design: Rotametrs are easy to install, operate and maintain. They have no moving parts or electrical connections, which makes them very reliable and less prone to failure.
- Accurate measurement: Rotametrs provide accurate and precise measurement of fluid flow rate. They have a linear response over a wide range of flow rates, and their calibration can be easily adjusted to match the specific application.
- Wide range of applications: Rotametrs can be used to measure the flow rates of liquids and gases in various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and HVAC systems.
- Low cost: Rotametrs are relatively inexpensive compared to other types of flow meters. They are also very cost-effective in terms of maintenance and repair.
- Easy to read: Rotametrs have a simple design with a clear, easy-to-read scale. This makes it easy for operators to quickly determine the flow rate of the fluid, without the need for complex calculations or additional equipment.
Overall, the simplicity, accuracy, versatility, and low cost of rotametrs make them a popular choice for flow rate measurement and Water Quality Monitoring in many industries.
Disadvantages:
Although rotametrs have many advantages, they also have some disadvantages that should be considered:
- Limited range: Rotametrs have a limited range of flow rates that they can accurately measure. They are best suited for low to moderate flow rates, and may not be suitable for high flow rates or for applications where the flow rate varies widely.
- Limited precision: While rotametrs are generally accurate, they may not be precise enough for some applications that require very precise flow rate measurements. The measurement error may be significant for low flow rates, and accuracy may decrease as the viscosity of the fluid increases.
- Sensitivity to changes in fluid properties: Rotametrs are sensitive to changes in fluid properties such as temperature, viscosity, and density. This can affect the accuracy of the measurement, especially if the fluid properties vary significantly.
- Limited compatibility with certain fluids: Some fluids may not be compatible with the materials used to construct the rotametr. For example, some plastic rotametrs may not be compatible with certain chemicals, or may not be able to withstand high temperatures or pressures.
- Fragility: Rotametrs made of glass or plastic are relatively fragile and can break if mishandled. They should be handled with care during installation, maintenance, and transport.
Overall, rotametrs are reliable and cost-effective flow meters for many applications, but they may not be suitable for all applications. It is important to carefully consider the specific requirements of the application before selecting rotametrs or any other flow meter.
Frequently Asked Question
What is a rotameter?
Answer: rotameters is a device used to measure the flow rate of liquids or gases in a closed system. It operates on the principle of variable area, where the flow of fluid causes a float to move in a tapered tube, indicating the flow rate.
How does rotameters work?
Answer: rotameters work by the movement of a float inside a tapered tube, where the fluid flow causes the float to move up and down the tube, thereby indicating the flow rate. The height of the float corresponds to the flow rate, which can be read off a calibrated scale.
What are the advantages of using rotameters?
Answer: The advantages of using rotameters include simple design, accurate measurement, a wide range of applications, low cost, and an easy-to-read scale.
What industries use rotameters?
Answer: Rotameters are used in various industries, including chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, water treatment, and HVAC systems.
Can rotameters measure both liquids and gases?
Answer: Yes, rotameters can measure both liquids and gases.
What is the maximum flow rate that can be measured with rotameters?
Answer: The maximum flow rate that can be measured with rotameters depends on the size of the tapered tube and the float design. Larger tubes and floats can measure higher flow rates.
How do you calibrate a rotameter?
Answer: Rotameters are calibrated by adjusting the position of the float to correspond to a known flow rate. This is typically done by adjusting a set screw or other mechanisms to move the float up or down the tapered tube.
Can rotameters be used for high-pressure applications?
Answer: Yes, rotameters can be used for high-pressure applications. However, it is important to ensure that the tube material and float design can withstand the pressure.
How do you select the right size rotameters for your application?
Answer: The size of the rotameters depends on the maximum flow rate of the fluid and the required measurement accuracy. The manufacturer’s specifications can be used to select the appropriate size for a given application.
What are some common types of rotameters?
Answer: Common types of rotameters include glass tube rotameters, metal tube rotameters, and plastic tube rotameters. The choice of material depends on the specific application and the fluid being measured.
