HEPA filter is a crucial component in the pharmaceutical industry to maintain a sterile and clean environment. These filters are designed to trap small particles and microorganisms that could contaminate pharmaceutical products, compromising their safety and efficacy. HEPA filters are typically used in cleanrooms, which are highly controlled environments, to reduce the risk of contamination. They are also used in other stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, such as filling and packaging, to ensure that the final products are free of harmful particles. In summary, HEPA filters are essential for the production of safe and effective drugs and other medical products.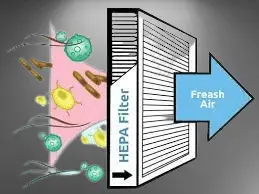
hepa full form
High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filter
Differences between True HEPA filters and HEPA-Type filters
| Filter Type | Particle Size Efficiency | Filtration Rate | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| True HEPA | 0.3 microns and larger | 99.97% | Higher |
| HEPA-Type | 2-3 microns and larger | 50% – 99% | Lower |

hepa filter types
HEPA filters are classified based on their efficiency in capturing particles of different sizes. The European standard for classifying HEPA filters is EN 1822, which defines several filter classes based on their efficiency in capturing particles of various sizes.
The HEPA filter classes defined by EN 1822 are:
- Class E10: Efficiency of 85% at 0.3 microns
- Class E11: Efficiency of 95% at 0.3 microns
- Class E12: Efficiency of 99.5% at 0.3 microns
- Class H13: Efficiency of 99.95% at 0.3 microns
- Class H14: Efficiency of 99.995% at 0.3 microns
The classes H13 and H14 are commonly used in cleanrooms and other critical environments, where a higher level of air filtration is required. They are able to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns with a filtration efficiency of 99.95% and 99.995%, respectively.
In summary, EU 13 and EU 14 are not the names of specific HEPA filter types, but rather the filter classes defined by the European standard EN 1822, which are used to indicate the efficiency of a HEPA filter in capturing particles of different sizes.
HEPA Filter in the HVAC
Choosing the right HEPA filter depends on the specific application and the requirements for air quality. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a HEPA filter:
- Filtration Efficiency: Consider the level of filtration efficiency needed for the application. True HEPA filters are more efficient than HEPA-Type filters and are able to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns with a filtration rate of 99.97%, while HEPA-Type filters are less efficient and capture particles larger than 2 or 3 microns with a filtration rate ranging from 50% to 99%.
- Filter Class: Consider the filter class needed for the application. Filter classes are defined by standards such as EN 1822, and indicate the filter’s efficiency in capturing particles of different sizes. For example, H13 and H14 filters are commonly used in critical environments, where a higher level of air filtration is required.
- Airflow Rate: Consider the airflow rate required for the application. HEPA filters with a high filtration efficiency can restrict airflow, which may be a concern in some applications. Choose a filter with an appropriate airflow rate to ensure that the system can operate efficiently.
- Size: Choose a filter that fits the dimensions of the air handling system. Oversized or undersized filters can lead to decreased performance and reduced filtration efficiency.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the filter, as well as the cost of replacement filters. True HEPA filters are generally more expensive than HEPA-Type filters but may be necessary for critical applications.
By considering these factors, you can choose the right HEPA filter to ensure that the air quality in your environment meets the necessary standards.
Critical details of HEPA Filters
- Efficiency: HEPA filters must meet the efficiency standards of capturing at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 microns or larger.
- MERV rating: The Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) rating of a HEPA filter indicates its ability to capture particles of different sizes. HEPA filters typically have a MERV rating of 17-20.
- Construction: HEPA filters are constructed using a dense mat of randomly arranged fibers, such as fiberglass, which is then pleated to increase the filter’s surface area. The fibers are typically held together with a binder or adhesive to form a rigid structure.
- Frame: The frame of a HEPA filter is usually made of aluminum or galvanized steel to provide structural support and prevent air leakage around the filter.
- Seals: HEPA filters must be installed with appropriate gaskets or seals to prevent air from bypassing the filter and to ensure that all air passes through the filter.
- Testing: HEPA filters must be tested and certified by a third-party testing agency to ensure that they meet efficiency and performance standards.
- Replacement: HEPA filters should be replaced regularly to maintain their effectiveness. The replacement frequency depends on the specific application and environmental conditions.
- Size and shape: HEPA filters come in different sizes and shapes to fit various applications, from small portable air purifiers to large industrial cleanroom systems.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure that HEPA filters continue to operate effectively. This includes periodic inspections, filter replacements, and cleaning or replacement of pre-filters or other components that protect the HEPA filter.
- Standards: HEPA filters must meet certain standards set by organizations such as the Institute of Environmental Sciences and Technology (IEST) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Benefits of HEPA Filters
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| High Filtration Efficiency | HEPA filters are able to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns in size with a filtration efficiency of 99.97% to 99.995%, depending on the filter class. |
| Improved Air Quality | HEPA filters remove a wide range of harmful airborne particles such as dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and viruses, which can improve indoor air quality and reduce the risk of respiratory problems and allergies. |
| Reduces Spread of Contaminants | HEPA filters can help reduce the spread of infectious diseases by capturing and containing airborne pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. |
| Improves HVAC System Performance | HEPA filters can help improve the performance of HVAC systems by reducing the build-up of dirt and debris in air ducts and on system components. |
| Suitable for Critical Environments | HEPA filters are commonly used in cleanrooms, hospitals, laboratories, and other critical environments where a high level of air filtration is required to maintain a sterile and safe environment. |
| Energy Efficient | HEPA filters are energy efficient and can help reduce energy costs associated with air conditioning and heating systems. |
Role of HEPA Filters in Pharma Cleanrooms.
HEPA filters play a critical role in maintaining the cleanliness and sterility of pharmaceutical cleanrooms. Cleanrooms are environments that are designed to maintain a controlled level of airborne particles and microorganisms to ensure product quality and safety.
HEPA filters are used in cleanrooms to remove airborne particles and microorganisms from the air. They are typically installed in the air handling units of the cleanroom and can be located in the ceiling, walls, or floor, depending on the design of the cleanroom.
The role of HEPA filters in pharmaceutical cleanrooms is to maintain a high level of air filtration, which helps to prevent the contamination of products and surfaces in the cleanroom. HEPA filters remove particles as small as 0.3 microns in size, which include many common airborne contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, mold, and dust.
HEPA filters also play a crucial role in maintaining the sterility of aseptic processing areas, which are critical in pharmaceutical manufacturing. These areas must be kept free of contamination to ensure the safety and efficacy of sterile products. HEPA filters are used to provide the high level of air filtration required to maintain the sterility of these areas.
In summary, the implementation of HEPA filters in pharmaceutical cleanrooms is essential for maintaining a controlled environment and preventing contamination of products and surfaces. By removing harmful airborne particles and microorganisms, HEPA filters help ensure the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products and maintain the highest level of product quality.
Maintenance of HEPA Filters in Pharma Cleanrooms
- Regular Filter Inspections: Schedule routine inspections to visually check for any physical damage or signs of deterioration in the HEPA filters.
- Filter Replacement: Follow manufacturer recommendations for filter replacement schedules based on usage and contamination levels. Replace filters promptly when they reach their end of life.
- Preventing Contamination: Implement procedures to minimize potential contamination during filter replacements, ensuring proper sealing and cleanliness.
- Cleaning the Surrounding Areas: Maintain cleanliness in the vicinity of the HEPA filters to prevent the accumulation of dust and particles that could impact their efficiency.
- Documentation and Compliance: Keep detailed records of filter maintenance activities, including replacement dates, inspection results, and any deviations from standard procedures, to comply with regulatory requirements.
Difference between EU13 Filter & EU14 HEPA Filter
| Feature | EU13 Filter | EU14 Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration Efficiency | Minimum efficiency of 99.95% for particles of 0.3 microns and above | Minimum efficiency of 99.995% for particles of 0.3 microns and above |
| Maximum Particle Size | Can capture particles as small as 0.1 microns | Can capture particles as small as 0.1 microns |
| Airflow Capacity | Lower airflow capacity than EU14 filters | Higher airflow capacity than EU13 filters |
| Applications | Suitable for use in cleanrooms, hospitals, and laboratories where a high level of air filtration is required. | Suitable for use in critical environments such as semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and nuclear facilities where a high level of air filtration is essential. |
EPA filters are typically made from a dense mat of randomly arranged glass fibers that are tightly woven together to form a filter media. The fibers are usually made from borosilicate glass, which is known for its high strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals.
The filter media is often pleated or folded to increase the surface area and maximize the filtration capacity of the filter. The pleats are typically separated by thin aluminum foil separators that help to maintain the distance between the pleats and provide support to the filter media.
The frame of the HEPA filter is typically made from aluminum, stainless steel, or other materials that are durable and resistant to corrosion. The frame is designed to hold the filter media in place and provide a secure seal between the filter and the air handling system.
In some cases, HEPA filters may be coated with a layer of activated carbon to provide additional air purification capabilities. Activated carbon is a porous material that can trap volatile organic compounds (VOCs), gases, and odors, making it a useful addition to HEPA filters in specific applications.
In summary, the main material of construction for HEPA filters is borosilicate glass fibers, which are tightly woven together to form a dense filter media. The frame of the filter is typically made from aluminum or stainless steel, and in some cases, HEPA filters may be coated with activated carbon to provide additional air purification capabilities.
HEPA filters in Microbiology.
HEPA filters are essential components in microbiology laboratories, cleanrooms, and other controlled environments where sterile conditions are critical. Here are some ways HEPA filters are used in microbiology:
Biosafety cabinets: HEPA filters are used in Class II and III biosafety cabinets to prevent contamination of biological samples and protect laboratory personnel or LAF
Cleanrooms: HEPA filters are used in cleanrooms for microbial testing, cell culture, and other microbiology applications to maintain sterile conditions and prevent cross-contamination.
Air purification systems: HEPA filters are used in air purification systems to remove airborne contaminants, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, from the air.
Sterilization equipment: HEPA filters are used in autoclaves and other sterilization equipment to filter the exhaust air and prevent the release of infectious agents.
Environmental monitoring: HEPA filters are used in microbial air samplers to collect airborne particles and microorganisms for environmental monitoring and testing.
Animal facilities: HEPA filters are used in animal facilities to maintain sterile conditions and prevent the spread of infectious diseases among laboratory animals.
Overall, HEPA filters are critical components in microbiology labs and facilities that require high levels of cleanliness and sterility. They play an important role in preventing contamination, protecting laboratory personnel, and ensuring the accuracy and reliability of test results.
Applications of HEPA filters
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical manufacturing | HEPA filters are used in cleanrooms and other controlled environments to maintain sterile conditions during drug manufacturing and packaging. |
| Healthcare facilities | HEPA filters are used in hospital operating rooms, isolation rooms, and other areas where clean air is essential to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. |
| Laboratories | HEPA filters are used in biological safety cabinets and other types of lab equipment to protect researchers and prevent cross-contamination between experiments. |
| Aerospace industry | HEPA filters are used in the cabins of commercial airplanes to improve air quality and remove airborne particles and pollutants. |
| Nuclear industry | HEPA filters are used in nuclear power plants and other facilities to capture and remove radioactive particles from the air. |
| Electronics manufacturing | HEPA filters are used in cleanrooms and other controlled environments to prevent contamination of sensitive electronic components during manufacturing and assembly. |
| Food processing | HEPA filters are used in food processing facilities to maintain clean and sterile conditions and prevent contamination of food products. |
| Cleanrooms for scientific research | HEPA filters are used in cleanrooms for scientific research in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. |
Frequently Asked Questions:
What does HEPA stand for and what is its purpose in pharmaceuticals?
Answer: HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air, and its purpose in pharmaceuticals is to remove contaminants from the air to maintain clean and sterile conditions.
What is the minimum efficiency of HEPA filters in capturing particles?
Answer: The minimum efficiency of HEPA filters in capturing particles is 99.97% for particles as small as 0.3 microns.
What is the difference between HEPA filters and ULPA filters?
Answer: HEPA filters are designed to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns, while ULPA filters are designed to capture particles as small as 0.12 microns.
What is the MERV rating of HEPA filters?
Answer: HEPA filters do not have a MERV rating because they are designed to meet a different set of standards.
What is the typical air flow rate through HEPA filters in pharmaceutical cleanrooms?
Answer: The typical air flow rate through HEPA filters in pharmaceutical cleanrooms is between 0.45 and 0.75 meters per second.
What is the recommended air change rate for a pharmaceutical cleanroom?
Answer: The recommended air change rate for a pharmaceutical cleanroom is between 20 and 30 air changes per hour.
How often should HEPA filters be replaced in a pharmaceutical cleanroom?
Answer: HEPA filters should be replaced at least once a year, but may need to be replaced more frequently depending on the level of contamination in the air.
Can HEPA filters be cleaned and reused?
Answer: HEPA filters can be cleaned in some cases, but it is typically more cost-effective to replace them.
What is the pressure drop across a HEPA filter?
Answer: The pressure drop across a HEPA filter is typically between 200 and 300 pascals.
What is the role of HEPA filters in preventing cross-contamination in pharmaceutical manufacturing?
Answer: HEPA filters prevent cross-contamination by capturing and removing airborne particles that could potentially contaminate products or equipment.
How are HEPA filters validated for use in pharmaceutical cleanrooms?
Answer: HEPA filters are validated by testing their efficiency in capturing particles of various sizes and validating their performance under typical operating conditions.
Can HEPA filters be used in explosive environments?
Answer: Yes, HEPA filters can be designed for use in explosive environments by incorporating features such as grounding wires and explosion-proof construction.
What is the difference between a HEPA filter and a pre-filter?
Answer: A pre-filter is designed to capture larger particles before they reach the HEPA filter, helping to extend its lifespan and reduce maintenance costs.
How do HEPA filters contribute to energy efficiency in pharmaceutical cleanrooms?
Answer: HEPA filters contribute to energy efficiency by reducing the load on HVAC systems and improving indoor air quality, which can lead to lower energy consumption and operating costs.
How are HEPA filters integrated into the HVAC system of a pharmaceutical cleanroom?
Answer: HEPA filters are typically installed as the final stage of the air handling system in pharmaceutical cleanrooms, with pre-filters and other types of filters installed upstream to remove larger particles before the air passes through the HEPA filter.


2 thoughts on “What is HEPA filter Basic and how does it work 2023”